1、使用多线程模拟多个ATM机同时存取款的并发问题
class Account { //持有人 private string _holderName; public string HolderName { get { return _holderName; } set { _holderName = value; } } //密码 private string _password; public string Password { get { return _password; } set { _password = value; } } //账号余额 private float _amount; public float Amount { get { return _amount; } set { _amount = value; } } /// <summary> /// 构造函数 /// </summary> /// <param name="holdderName"></param> /// <param name="password"></param> /// <param name="amount"></param> public Account(string holdderName, string password, float amount) { this._holderName = holdderName; this._password = password; this._amount = amount; } //存款 public void Deposit(float amount) { if (amount > 0) { this._amount = this._amount + amount; } } //取款 public void Withdraw(float amount) { if (this._amount >= amount && amount > 0) { this._amount = this._amount - amount; } } //获取余额 public float CheckBalance() { return this._amount; } } class ATM { //账号 public Account account; //存款 public void Deposit(float amount) { account.Deposit(amount); } //取款 public void WithDraw(float amount) { account.Withdraw(amount); } //获取余额 public float GetBalance() { return account.CheckBalance(); } }
class Program { Account acc = new Account("张兰", "0000", 5000); static void Main(string[] args) { Thread[] threads = new Thread[10]; Program p = new Program(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { threads[i] = new Thread(new ThreadStart(p.Run)); threads[i].Name = "线程" + (i + 1); } foreach (Thread t in threads) { t.Start(); } Console.ReadKey(); } public void Run() { ATM atm = new ATM(); atm.account = acc; Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":查询当前" + atm.GetBalance()); Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":取款2000"); //取款 atm.WithDraw(2000); Thread.Sleep(100); Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":查询当前" + atm.GetBalance()); Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":存款2000"); //存款 atm.Deposit(2000); Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":查询当前" + atm.GetBalance()); } }

我们可以发现,10个人同时进行存款 2000,取款2000,最后的余额应该是不变的,但是结果却出现了混乱,说明多个线程是交替进行的,就出现了并发问题。
2、解决方案
(1)使用lock解决并发问题
lock 关键字将语句块标记为临界区,方法是获取给定对象的互斥锁,执行语句,然后释放该锁。 此语句的形式如下:
Object thisLock = new Object();
lock (thisLock)
{
// Critical code section.
}
lock 关键字可确保当一个线程位于代码的临界区时,另一个线程不会进入该临界区。 如果其他线程尝试进入锁定的代码,则它将一直等待(即被阻止),直到该对象被释放。
Lock关键字的含义是:允许定义一段线程同步的代码,他的语法是:

把一些代码放到lock块中,那么这些代码就是安全的
这里要加到的代码块是取款和存款的操作代码放到lock块里
首先定义一个object类型的对象
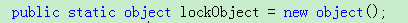
接下来我们对操作账户的代码放到lock块里:
class Program { public static readonly object _lockObject = new object(); Account acc = new Account("张兰", "0000", 5000); static void Main(string[] args) { Thread[] threads = new Thread[10]; Program p = new Program(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { threads[i] = new Thread(new ThreadStart(p.Run)); threads[i].Name = "线程" + (i + 1); } foreach (Thread t in threads) { t.Start(); } Console.ReadKey(); } public void Run() { ATM atm = new ATM(); atm.account = acc; //对额度相关的操作代码加锁 lock (_lockObject) { Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":查询当前" + atm.GetBalance()); Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":取款2000"); //取款 atm.WithDraw(2000); Thread.Sleep(100); Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":查询当前" + atm.GetBalance()); Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":存款2000"); //存款 atm.Deposit(2000); Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":查询当前" + atm.GetBalance()); } } }
运行结果没有并发问题!
线程1对账户进行操作,当他操作完毕之后,其他的线程才能对账户进行操作。即每一个线程对账户进行查询、取款和存款等一系列的操作之后,那么其他的线程才能对这个账户进行操作,就保证了账户余额不再出现问题
(2)使用Monitor解决并发问题
Monitor类提供同步访问对象的机制
Monitor 类通过向单个线程授予对象锁来控制对对象的访问。
对象锁提供限制访问代码块(通常称为临界区)的能力。当一个线程拥有对象的锁时,其他任何线程都不能获取该锁。还可以使用 Monitor 来确保不会允许其他任何线程访问正在由锁的所有者执行的应用程序代码节,除非另一个线程正在使用其他的锁定对象执行该代码。
使用 Monitor 锁定对象(即引用类型)而不是值类型。
使用Monitor解决并发问题会用到Monitor的两个方法:TryEnter和Exit方法

TryEnter方法获取指定对象的排它锁,他有几个重载版本,这是带两个参数的情况,方法返回值是bool值,如果当前线程在不阻止的情况下获取该锁,那么就返回true,否则返回false 。
Exit方法释放指定对象的排它锁,有一个object类型的参数。

class Program { public static readonly object _lockObject = new object(); Account acc = new Account("张兰", "0000", 5000); static void Main(string[] args) { Thread[] threads = new Thread[10]; Program p = new Program(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { threads[i] = new Thread(new ThreadStart(p.Run)); threads[i].Name = "线程" + (i + 1); } foreach (Thread t in threads) { t.Start(); } } public void Run() { ATM atm = new ATM(); atm.account = acc; //对额度相关的操作代码加锁 try { if (Monitor.TryEnter(_lockObject, -1)) { Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":查询当前" + atm.GetBalance()); Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":取款2000"); //取款 atm.WithDraw(2000); Thread.Sleep(100); Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":查询当前" + atm.GetBalance()); Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":存款2000"); //存款 atm.Deposit(2000); Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":查询当前" + atm.GetBalance()); } } finally { Monitor.Exit(_lockObject); } } }