第一次在博客园写东西,最近在重温算法,在这里记录一下,以便以后查阅及修改。
首先是优化冒泡排序

#region 优化冒泡排序 public static List<int> bubble_sort(List<int> result) { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); //result_orginal = new List<int>(result); int index = result.Count - 1; bool flag = false;//定义标志位标记已经有序或无序 int max_index = 0;//每一次找到无序区的上界 for (int i = 0; i < result.Count; i++) { flag = true;//开始置为1 for (int j = 0; j < index; j++) { if (result[j] > result[j + 1]) { int temp = result[j + 1]; result[j + 1] = result[j]; result[j] = temp; flag = false;//交换后对flag置0,表示已经有序(已交换,如全列有序,则为1) max_index = j;//注意不要在这里直接将index置为j } } if (flag) break;//如果flag为1则说明排序前已经有序 index = max_index;//若排序过则将index置为最后一次交换的坐标,若没有则表示已经有序 } watch.Stop(); //获取当前实例测量得出的总运行时间(以毫秒为单位) time = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds.ToString(); Console.WriteLine("优化冒泡排序排{0}个0~{1}的数字需要{2}豪秒", result.Count, result.Count - 1, time); return result; } #endregion
其次是计数排序

#region 计数排序 public static List<int> Counting_sort(List<int> result) { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); int[] b = new int[result.Count]; List<int> s = new List<int>(); for (int i = 0; i < b.Length; i++) { b[i] = 0; } for (int ii = 0; ii < result.Count; ii++) { b[result[ii]] = b[result[ii]] + 1; s.Add(0); } for (int i2 = 1; i2 < b.Length; i2++) { b[i2] = b[i2 - 1] + b[i2]; } for (int i3 = result.Count - 1; i3 >= 0; i3--) { s[b[result[i3]] - 1] = result[i3]; b[result[i3]] = b[result[i3]] - 1; } for (int j = 0; j < result.Count;j++ ) { result[j] = s[j]; } watch.Stop(); //获取当前实例测量得出的总运行时间(以毫秒为单位) time = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds.ToString(); Console.WriteLine("计数排序排{0}个0~{1}的数字需要{2}豪秒", result.Count, result.Count - 1, time); return result; } #endregion
快速排序,这里用到了递归

#region 快速排序 public static List<int> Quick_sort(List<int> result) { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); int low = 0; int high = result.Count - 1; // int i = 0; Quicksort_recursion(result, low, high); watch.Stop(); //获取当前实例测量得出的总运行时间(以毫秒为单位) time = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds.ToString(); Console.WriteLine("快速排序排{0}个0~{1}的数字需要{2}豪秒", result.Count, result.Count - 1, time); return result; } public static void Quicksort_recursion(List<int> result, int _low, int _high) { int a; if (_low < _high) { a = partition(result, _low, _high); Quicksort_recursion(result, _low, a - 1); Quicksort_recursion(result, a + 1, _high); } } public static int partition(List<int> result, int _low, int _high) { int low = _low; int high =_high; int k = result[_low]; while (low < high) { while (result[high] >= k && high > low) { --high; } /*比key小的放左边*/ result[low] = result[high]; while (result[low] <= k && high > low) { ++low; } result[high] = result[low]; } result[low] = k; int p = low; return p; } #endregion
插入排序,实现比较简单

#region 插入排序 public static List<int> insert_sort(List<int> result) { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); for (int i = 1; i < result.Count; i++) { if (result[i-1]> result[i]) { int temp = result[i]; for(int j = i-1;j>=0;j--) { if (result[j] > temp) { result[j+1]= result[j]; result[j] = temp; } } } } watch.Stop(); //获取当前实例测量得出的总运行时间(以毫秒为单位) time = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds.ToString(); Console.WriteLine("插入排序排{0}个0~{1}的数字需要{2}豪秒", result.Count, result.Count - 1, time); return result; } #endregion
希尔排序,我选择的通项是3K+1

#region 希尔排序 public static List<int> shell_sort(List<int> result) { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); //int gap = 1; for (int k =1; k < result.Count/3; k++) { k = 3 * k + 1; } for (int i = 1; i < result.Count; i++) { if (result[i - 1] > result[i]) { int temp = result[i]; for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) { if (result[j] > temp) { result[j + 1] = result[j]; result[j] = temp; } } } } watch.Stop(); //获取当前实例测量得出的总运行时间(以毫秒为单位) time = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds.ToString(); Console.WriteLine("希尔排序排{0}个0~{1}的数字需要{2}豪秒", result.Count, result.Count - 1, time); return result; } #endregion
选择排序

#region 选择排序 public static List<int> selection_sort(List<int> result) { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); int k = 0; int min = 0; for (int i = 0; i < result.Count; i++) { k = i; min = k; for (int j = i; j < result.Count; j++) { if (result[min] > result[j]) { min = j; } } if (k!=min) { int temp = result[min]; result[min] = result[k]; result[k] = temp; } } watch.Stop(); //获取当前实例测量得出的总运行时间(以毫秒为单位) time = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds.ToString(); Console.WriteLine("选择排序排{0}个0~{1}的数字需要{2}豪秒", result.Count, result.Count - 1, time); return result; } #endregion
以上就是最近复习的排序算法。同时运行这几个排序,时间长短不一。问题来了,当数据量很大的时候,不同算法运行的时间差异很大。冒泡甚至是计数排序算法运行时间的100多倍。所以,用多线程来同时运行几个算法。并通过反射来获得方法。
class Program { static internal Thread[] threads = new Thread[6]; static int i = 0; static void Main(string[] args) { Console.Clear(); Console.WriteLine("请输入需要排序的数据个数"); int in_put = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); int[] x = new int[in_put]; System.Random rnd = new Random(); //rnd.Next(0, 100); for (int i = 0; i < x.Length;i++ ) { int num = rnd.Next(0, x.Length); x[i] = num; } Dictionary<string, List<int>> sort_fuction = new Dictionary<string, List<int>>(); //添加元素 Type trypInfo = typeof(sort);// sort为类名 //获得方法名 string str = "包括的方法名列表:\r\n"; MethodInfo[] methodInfo = trypInfo.GetMethods(BindingFlags.Static | BindingFlags.InvokeMethod | BindingFlags.Public); foreach (MethodInfo mInfo in methodInfo) { //str = mInfo.ToString() ; str = mInfo.Name.ToString(); ParameterInfo[] paramsInfo = mInfo.GetParameters();//得到指定方法的参数列表 if (paramsInfo.Length == 1 && paramsInfo[0].ParameterType.IsGenericType) { Type[] genericArgTypes = paramsInfo[0].ParameterType.GetGenericArguments(); if (genericArgTypes[0] == typeof(int)) { //for (int i = 0; i < paramsInfo.Length; i++)//循环参数列表 //{ // Console.Write(paramsInfo[i].ParameterType.Name + " " + paramsInfo[i].Name);//在方法打的括号里面添加每个参数类型和名称 // if (i + 1 < paramsInfo.Length)//最后一个参数就不用加逗号了 // { // Console.Write(",");//用逗号隔开 // } //} //Console.WriteLine("{0}", str); sort_fuction.Add(str, new List<int>(x)); } } } //int thread_count = sort_fuction.Count; Type t1 = Assembly.Load("sort1(n)").GetType(string.Format("sort1_n_.sort")); foreach (KeyValuePair<string, List<int>> kvp in sort_fuction) { Object[] parameters2 = { kvp.Value }; Thread t = new Thread((ThreadStart)delegate { t1.InvokeMember(kvp.Key, BindingFlags.Static | BindingFlags.InvokeMethod | BindingFlags.Public, null, null, parameters2); }); threads[i] = t; threads[i].Start(); i = i + 1; } Console.ReadLine(); } }
新建一个Dictionary,键值存算法名,值存一个泛型List<int> 这里保存需要进行排序的内容。通过判断泛型类型以及带几个参数,筛选出算法的方法名。用反射去运行每个算法方法。
(开启多线程无法直接调用反射的方法,所以在反射外面再套一层委托来进行。)有2个问题需要探讨一下:
1.这里的Time会不会在线程同时运行的时候互相影响?
private static string time; private List<int> result; public sort(List<int> result) { this.result = result; } public static string Time { get { return time; } } public List<int> Result { get { return result; } set { result = value; } }
2.能否还有其他的优化来提高运行效率??
运行的效果如下;
10000条数据:
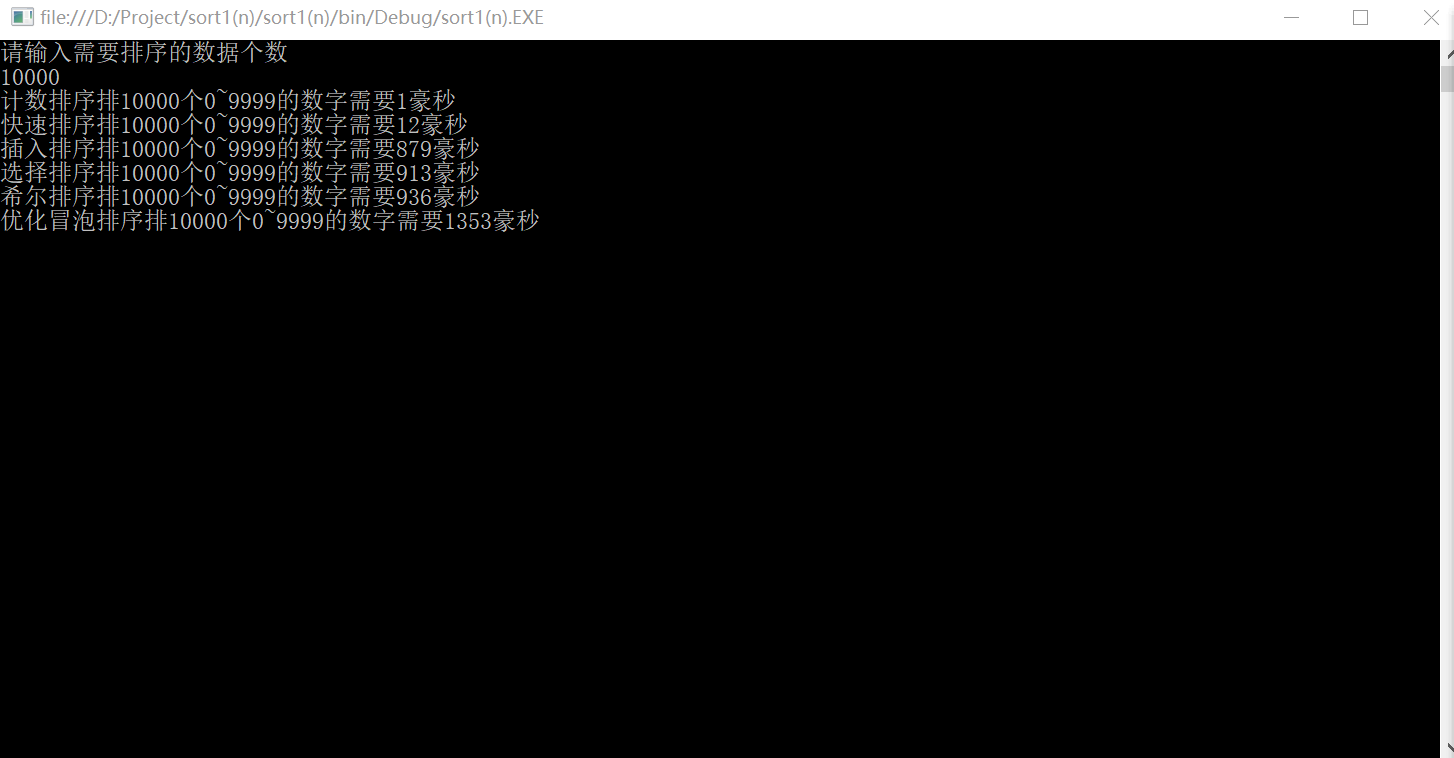
100000条数据:

以上。
