1. Characteristics of objectives
S:Specific
M:Measurable
A:Assignable任务分配到个人
R:Realistic
T:Time related
2. Organisational strategy
An expression of how an organization needs to evolve over time to meet its objectives along with a detailed assessment of what needs to be done.
Developing an organizational strategy for a business involves first comparing its present state to its targeted state to define differences, and then stating what is required for the desired changes to take place.
3. stradegy对manager重要的原因
a) Project managers must respond to changes with appropriate decisions about future projects and adjustments to current projects根据长远计划对当前项目做出合理调整,对环境的变化进行回应
b) Project managers who understand their organisation’s strategy can become effective advocates of projects aligned with the firm’s mission符合公司的使命
4. Strategic management( WHAT an organisation is + WHERE the organisation would like to be in the future + HOW to achieve this using the available resources )
a - Review and define the organisational mission
b - Set long-range goals and objectives
c -Analyse and formulate strategies to reach objectives
d - Implement strategies through projects
5. Multi-project challenges
Not able to align with the overall strategies of the organization与公司长期战略不一致
Failure to prioritize the selection of projects by their importance of their contribution to the firm没有根据项目对公司的重要性选择优先项目
Are not integrated throughout the project life cycle没有集成在整个项目周期中
Do not match project planning and controls with the organizational culture to make appropriate adjustments in support of project endeavors项目规划与公司文化不匹配
6.
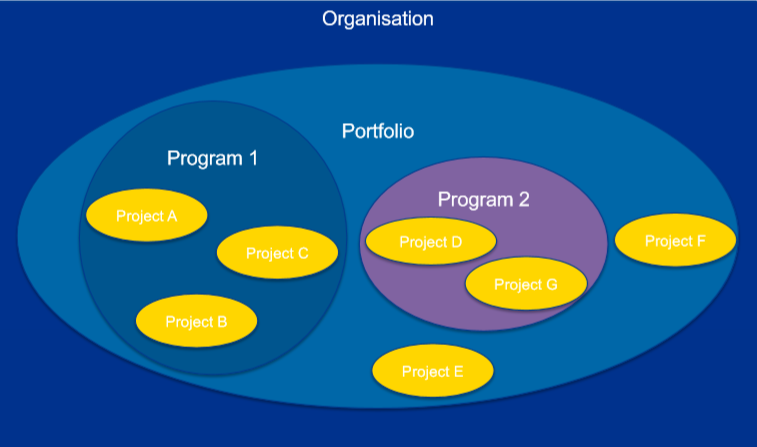

7. Portfolio management system
The aim of a portfolio management system is to ensure that projects are aligned with strategic goals and prioritised appropriately项目组合管理系统的目标是确保项目符合战略目标,并适当地确定优先级
8. Major functions of Portfolio management
a) Oversee project selection
b) Monitor aggregate resource levels and skills监控总体资源水平和技能
c) Encourage use of best practices
d) Balance projects in the portfolio in order to represent a risk level appropriate to the organisation
e) Improve communication among all stakeholders
f) Create a total organisation perspective that goes beyond silo thinking创建一个超越筒仓 (大概就是碎片化) 思维的整体视角
g) Improve the overall management of projects over time
9. Benefits of portfolio management
a) Builds discipline into project selection process在项目选择过程中建立规程
b) Links project selection to strategic metrics将项目选择链接到战略指标
c) Prioritizes project proposals across a common set of criteria, rather than on politics or emotion在同一标准中下考虑项目优先级,而不是政治或情感
d) Allocates resources to projects that align with strategic direction为符合战略方向的项目分配资源
e) Balances risk across all project
f) Justifies killing projects that do not support organization strategy
g) Improves communication and supports agreement on project goals
10.Components of a portfolio management system
Project classification --- Selection criteria --- Proposal sourcing --- Proposal evaluation --- Ongoing management
11. Common types of project management structures
a) Functional项目的不同部分委托给各自的职能部门,通过正常管理渠道保持协调,简单灵活但是对组织的集成不好且低效
b) Dedicated Project Teams /Projectized在全职项目经理的领导下,团队作为独立的单位运作,简单高效跨功能集成,但昂贵且项目接管困难
c) Matrix双链管理,项目参与者同时向职能和项目经理报告,允许在履行正常职能的同时参与多个项目,实现专业知识和项目需求的更大整合,但优先级问题上容易起争议且管理职责不明确
12. Different Matrix forms
a) Weak: The authority of the functional manager predominates and the project manager has indirect authority职能经理的权力占主导地位,项目经理具有间接权力
b) Balanced: The project manager sets the overall plan and the functional manager determines how the work is to be done项目经理制定总体计划,职能经理决定如何完成工作
c) Strong: The project manager has broader control and functional departments act as subcontractors to the project项目经理拥有更广泛的控制权,职能部门作为项目的分包商