 版权声明:署名,允许他人基于本文进行创作,且必须基于与原先许可协议相同的许可协议分发本文 (Creative Commons)
版权声明:署名,允许他人基于本文进行创作,且必须基于与原先许可协议相同的许可协议分发本文 (Creative Commons)
部分内容参考了这篇博客 java复制文件的4种方式 - 夏嘻嘻嘻嘻嘻 - 博客园
一、字节流复制文件
这是最经典的方式将一个文件的内容复制到另一个文件中。 使用FileInputStream读取文件A的字节,使用FileOutputStream写入到文件B。 这是第一个方法的代码:
private static void copyFileUsingFileStreams(File source, File dest) throws IOException {
InputStream input = null;
OutputStream output = null;
try {
input = new FileInputStream(source);
output = new FileOutputStream(dest);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = input.read(buf)) != -1) {
output.write(buf, 0, bytesRead);
}
} finally {
input.close();
output.close();
}
}1、直接字节流复制
package cn.scanner.cn.copyFile;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* @author wangyue
* @version 1.0
* @date 2019/7/4 17:10
* @describe: 测试拷贝文件的几种方法
*/
public class TestCopyFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1、创建一个字节输入流,用于读取当前目录下source文件夹中的mp3文件
InputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\\IDEA-IO\\src\\五环之歌.mp3");
//2、创建一个文件字节输出流,用于将读取的数据写入target目录下的文件中
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\\IDEA-IO\\des\\五环之歌.mp3");
int len; // 定义一个int类型的变量len,记住每次读取的一个字节
long begintime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取拷贝文件前的系统时间
//3、读取文件
while ((len = in.read()) != -1) { // 读取一个字节并判断是否读到文件末尾
out.write(len); // 将读到的字节写入文件
}
long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取文件拷贝结束时的系统时间
System.out.println("拷贝文件所消耗的时间是:" + (endtime - begintime) + "毫秒");
//4、释放资源
in.close();
out.close();
}
}
输出
拷贝文件所消耗的时间是:14892毫秒
2、字节流的缓冲区复制文件
当通过流的方式拷贝文件时,为了提高效率也可以定义一个字节数组作为缓冲区,在拷贝文件时,可以一次性读取多个字节的数据,并保存在字节数组中,然后将字节数组中的数据一次性写入文件
package cn.itcast.chapter07.example05;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* 文件的拷贝(使用缓冲区拷贝文件)
*/
public class Example05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\\IDEA-IO\\src\\五环之歌.mp3");
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\\IDEA-IO\\des\\五环之歌.mp3");
byte[] buff = new byte[1024]; // 定义一个字节数组,作为缓冲区
int len;
long begintime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((len = in.read(buff)) != -1) { // 判断是否读到文件末尾 len=读进换取区的字节数量
out.write(buff, 0, len); // 从第一个字节开始,向文件写入len个字节
}
long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("拷贝文件所消耗的时间是:" + (endtime - begintime) + "毫秒");
in.close();
out.close();
}
}
输出
拷贝文件所消耗的时间是:62毫秒
3、字节缓冲流
在IO包中提供两个带缓冲的字节流,分别是BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream,他们的构造方法中分别接受InputStream和OutputStream类型的参数作为对象,在读写数据时提供缓冲功能,
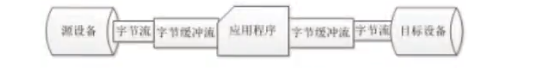
package cn.itcast.chapter07.example06;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
/**
* BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream 这两个流的用法
*/
public class Example06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建一个带缓冲区的输入流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\IDEA-IO\\src\\五环之歌.mp3"));
// 创建一个带缓冲区的输出流
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\IDEA-IO\\des\\五环之歌.mp3"));
long begintime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取拷贝文件前的系统时间
int len;
while ((len = bis.read()) != -1) {
bos.write(len);
}
long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取文件拷贝结束时的系统时间
System.out.println("拷贝文件所消耗的时间是:" + (endtime - begintime) + "毫秒");
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}
输出
拷贝文件所消耗的时间是:94毫秒
4、字节缓冲流+缓冲区(效率最高)
package cn.scanner.cn.copyFile;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
/**
* @author wangyue
* @version 1.0
* @date 2019/7/4 17:10
* @describe: 测试拷贝文件的几种方法
*/
public class TestCopyFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建一个带缓冲区的输入流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\IDEA-IO\\src\\五环之歌.mp3"));
// 创建一个带缓冲区的输出流
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\IDEA-IO\\des\\五环之歌.mp3"));
// 定义一个字节数组,作为缓冲区
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
long begintime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取拷贝文件前的系统时间
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(buff)) != -1) {
bos.write(buff, 0, len); // 从第一个字节开始,向文件写入len个字节
}
long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取文件拷贝结束时的系统时间
System.out.println("拷贝文件所消耗的时间是:" + (endtime - begintime) + "毫秒");
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}
输出
拷贝文件所消耗的时间是:16毫秒
二、字符流复制文件
字符流也可以拷贝文本文件,但不推荐使用
因为读取时会把字节转为字符,写出时还要把字符转回字节
1、通过缓冲流完成文件的复制
使用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter完成文件的复制
BufferedReader中的方法
public String readLine() 读一行字符
BufferedWriter中的方法
public void newLine() 写入一个换行符
package cn.itcast.chapter07.example09;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 使用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter完成文件的复制
*
* BufferedReader中的方法
* public String readLine() 读一行字符
*
* BufferedWriter中的方法
* public void newLine() 写入一个换行符
*/
public class Example09 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建一个BufferedReader缓冲对象,用于读取文件数据
BufferedReader in=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\IDEA-IO\\src\\五环之歌.mp3"));
// 创建一个BufferedWriter缓冲对象,用于写文件数据
BufferedWriter out=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\IDEA-IO\\des\\五环之歌.mp3"));
String line=null;
long begintime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 每次读取一行文本,判断是否到文件末尾
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
out.write(line);
out.newLine(); // 写入一个换行符,该方法会根据不同的操作系统生成相应的换行符
out.flush(); //也可以不写,在关闭数据流时,会自动刷新
}
long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("拷贝文件所消耗的时间是:" + (endtime - begintime) + "毫秒");
in.close();
out.close();
}
}
输出
拷贝文件所消耗的时间是:460毫秒
2、通过转换流复制文件
- 前面IO流可以分为字节流和字符流,有时字节流和字符流之间也需要进行转换。在JDK中提供了两个类可以将字节流转换为字符流,分别是InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
- OutputStreamWriter是Writer的子类,它可以将一个字节输出流转换成字符输出流,方便直接写入字符,
- InputStreamReader是Reader的子类,它可以将一个字节输入流转换成字符输入流,

package cn.itcast.example10;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author wangyue
* @version 1.0
* @date 2019/7/3 10:01
* @describe: 转换流:
*/
public class Example10 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//指定输入流
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\\IDEA-IO\\src\\五环之歌.mp3");//创建字节输入流
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(in); //将字节输入流转换成字符输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr); //高效缓冲流包装
//指定输出流
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\\IDEA-IO\\des\\五环之歌.mp3");//创建字节输出流
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(out);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
//读数据
String line = null;
long begintime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { //是否读到文件末尾
//写数据
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("拷贝文件所消耗的时间是:" + (endtime - begintime) + "毫秒");
//关闭流
br.close(); //只要关闭最后的缓冲流即可
bw.close();
}
}
输出
拷贝文件所消耗的时间是:545毫秒
、注意事项
1.字符流也可以拷贝文本文件,但不推荐使用
因为读取时会把字节转为字符,写出时还要把字符转回字节。
2.不可以拷贝非纯文本的文件
因为在读的时候会将字节转换为字符,在转换过程中,可能找不到对应的字符,就会用?代替;写出的时候会将字符转换成字节写出去,如果是?,直接写出,这样写出之后的文件就会产生乱码。
3.使用情况
程序需要读取一段文本,或者需要写出一段文本的时候可以使用字符流
读取的时候是按照字符的大小读取的,不会出现半个中文
写出的时候可以直接将字符串写出,不用转换为字节数组