先序遍历为:1 2 4 5 3 6,中序遍历为:4 2 5 1 6 3
思路:
先序遍历的第一个元素为根节点,在中序遍历中找到这个根节点,从而可以将中序遍历分为左右两个部分,左边部分为左子树的中序遍历,右边部分为右子树的中序遍历,进而也可以将先序遍历除第一个元素以外的剩余部分分为两个部分,第一个部分为左子树的先序遍历,第二个部分为右子树的先序遍历。
由上述分析结果,可以递归调用构建函数,根据左子树、右子树的先序、中序遍历重建左、右子树。
代码:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct TNode
{
int value;
TNode* lchild;
TNode* rchild;
}TNode,*BTree;
//根据先序遍历、中序遍历构建二叉树
BTree rebuild(int preOrder[],int startPre,int endPre,int inOrder[],int startIn,int endIn)
{
//先序遍历和中序遍历长度应相等
if (endPre - startPre != endIn - startIn) return NULL;
//起始位置不应大于末尾位置
if (startPre > endPre) return NULL;
//先序遍历的第一个元素为根节点
BTree tree = (BTree)malloc(sizeof(TNode));
tree->value = preOrder[startPre];
tree->lchild = NULL;
tree->rchild = NULL;
//先序遍历和中序遍历只有一个元素时,返回该节点
if (startPre == endPre) return tree;
//在中序遍历中找到根节点
int index,length;
for (index=startIn;index<=endIn;index++)
{
if (inOrder[index] == preOrder[startPre]) break;
}
//若未找到,返回空
if (index > endIn) return NULL;
//有左子树,递归调用构建左子树
if (index > startIn)
{
length = index-startIn;
tree->lchild = rebuild(preOrder,startPre+1,startPre+1+length-1,inOrder,startIn,startIn+length-1);
}
//有右子树,递归调用构建右子树
if (index < endIn)
{
length = endIn - index;
tree->rchild = rebuild(preOrder,endPre-length+1,endPre,inOrder,endIn-length+1,endIn);
}
return tree;
}
//后序遍历二叉树
void postTraverse(BTree tree)
{
if (tree->lchild != NULL) postTraverse(tree->lchild);
if (tree->rchild != NULL) postTraverse(tree->rchild);
printf("%d ",tree->value);
}
int main()
{
int preOrder[] = {1,2,4,5,3,6};
int inOrder[] = {4,2,5,1,6,3};
BTree tree = rebuild(preOrder,0,5,inOrder,0,5);
postTraverse(tree);
printf("\n");
return 0;
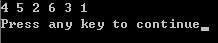
} 重建二叉树后后序遍历的结果如下: