16281053_杨瑷彤_操作系统第五次实验-文件系统
源代码链接:https://github.com/rdjyat/operating-system/tree/master/操作系统实验五
1.实验简介
本实验要求在模拟的I/O系统之上开发一个简单的文件系统。用户通过create, open, read等命令与文件系统交互。文件系统把磁盘视为顺序编号的逻辑块序列,逻辑块的编号为0至L − 1。I/O系统利用内存中的数组模拟磁盘。
2.程序设计
2.1 数据结构设计
1、模拟磁盘设计:实际物理磁盘的结构是多维的:有柱面、磁道、扇区等概念。系统的任务是隐藏磁盘的结构细节,把磁盘以逻辑块的面目呈现给文件系统。逻辑块顺序编号,编号取值范围为0至L -1 ,其中L表示磁盘的存储块总数。实验中,我们可以利用字符数组disk[L][B]构建磁盘模型,其中B 表示每个存储块的长度。
2、文件结构体设计,使用结构体表示文件,包含文件长度以及分配到的块号数组。
typedef struct FileDescriptor//文件描述符
{
int filelength; //文件长度。单位,字节
int fileblock[Block_Length]; //分配到的块号数组
}FileDescriptor;
3、目录结构体设计
typedef struct directory//目录项结构体,用来描述目录下的每一个文件
{
char filename[Name_Length]; //文件名
int index;
}directory;
2.2 全局变量设计
#define B 512 //定义存储块的长度B字节
#define L 100 //定义磁盘的存储块总数L,逻辑号0-(L-1)
#define K 5 //磁盘的前k 个块是保留区
#define Block_Length 3 //定义文件磁盘块号数组长度为3
#define Name_Length 12 //定义文件名的长度个字节
#define maxopen 20//打开文件表中最多同时存在20个文件
char disk[L][B]; //用字符数组构建磁盘模型
char bitmap[L];
int describ_maxnum; //文件描述符的最大数量,也是文件的最多数量
int file_num;//当前文件数量
int directory_block_num;//目录文件已分得的磁盘块数
int openfile_num;//当前处于打开状态的文件的数量
2.3 主要函数设计
a. I/O系统函数
1、读逻辑块
/*
* 函数名:read_block
* 功能:该函数把逻辑块i 的内容读入到指针p 指向的内存位置,拷贝的字符个数为存储块的长度B
* 参数: int i
* char *p
* 返回值:
* 无
*/
void read_block(int i,char*p)
{
memcpy(p,&disk[i][0],B);
}
2、写入逻辑块
/*
* 函数名:write_block
* 功能:该函数把指针p 指向的内容写入逻辑块i,拷贝的字符个数为存储块的长度B。
* 参数: int i
* char *p
* 返回值:
* 无
*/
void write_block(int i,char*p)
{
memcpy(&disk[i][0],p,B);
}
3、保存至文件,模拟磁盘写
/*
* 函数名:save
* 功能:把数组disk 存储到文件,模拟磁盘写入过程
* 参数:
* 无
* 返回值:
* 无
*/
void save()
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("disk.txt","w");
if(fp == NULL)
{
printf("error,cannot open the file!\n");
}
fwrite(&disk[0][0],sizeof(char),L*B,fp);
fclose(fp);
}
4、文件内容恢复到数组
/*
* 函数名:load
* 功能:把文件内容恢复到数组
* 参数:
* 无
* 返回值:
* 无
*/
void load()
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("disk.txt","r");
if(fp == NULL)
{
printf("error,cannot open the file!\n");
}
for(int i=0;i<(L*B);i++)
fread(&disk[0][0],sizeof(char),L*B,fp);
}
** b.文件系统函数**
1、初始化函数
/*
* 函数名:Init
* 功能:初始化文件系统:
初始化位图(0表示空闲,1表示被占用);
初始化0号文件描述符;
* 参数:
* 无
* 返回值:
* 无
*/
void Init()
{
int i;
//初始化位图
//前k块保留,这里默认被使用
for( i = 0 ; i < K ; ++i )
{
bitmap[i] = '1';
disk[0][i] = '1';//磁盘的前k个单元用来存储对应的bitmap
}
for( i = K ; i < L ; ++i )
{
bitmap[i] = '0';
disk[0][i] = '0';
}
file_num = 0;//初始化时,系统中文件的数量为0
//设置文件描述符
int describ_start = sizeof(bitmap);
pdescrib = (FileDescriptor*)&(disk[0][describ_start]);
//前K块剩下的空间用来村文件描述符
describ_maxnum = (K*B-describ_start)/sizeof(FileDescriptor);
FileDescriptor* temp;
for(temp = pdescrib;temp<pdescrib+describ_maxnum;temp++)
{
temp->filelength = -1;
for( i = 0 ; i < Block_Length ; ++i )
{
//初始化每个文件磁盘块未被使用的
temp->fileblock[i] = -1;
}
}
pdescrib->filelength = 0;//根目录初始化时没有文件
directory_block_num = 0;//初始化时,目录文件并不占有任何磁盘
save();
/*初始化文件打开表,清空表项*/
for(i=0;i<maxopen;i++)
{
openlist[i].index = -1;
openlist[i].rwp = 0;
openlist[i].rw_buffer[0] = '\0';
}
}
根据实验要求,预留K块用于保存位图信息和文件描述信息,先在位图中将前5个单元置1,表示预留5个保留块。其他的磁盘块设为0,表示未被使用。

2、创建新文件
/*
* 函数名:create
* 功能:根据指定的文件名创建新文件
* 参数:
* char* filename
* 返回值:
* int型 : 返回该文件描述符序号
*/
int create(char *filename)
{
//找可用的文件描述符
FileDescriptor* temp;
int isfound = 0;
int index = 0;
for(temp = pdescrib;temp<pdescrib+describ_maxnum;temp++)
{
if(temp->filelength == -1)
{
isfound = 1;
temp->filelength = 0;
pdescrib->filelength = pdescrib->filelength + sizeof(directory);
break;
}
index++;
}
if(isfound == 0)
{
printf("no file descriptor!\n");
return -1;
}
//判断当前目录文件所占有的块是否能够存下创建的文件
if(pdescrib->filelength > B*directory_block_num && directory_block_num < Block_Length)//不能存下,需要申请新的块
{
//找到新的磁盘块
int x = seekfreeOnBitMap();
if(x == -1)
{
printf("There is no room for new file\n");
pdescrib->filelength = pdescrib->filelength - sizeof(directory);
return -1;
}
//修改位图
bitmap[x] = '1';
disk[0][x] = '1';
//修改对应的目录磁盘块
pdescrib->fileblock[directory_block_num] = x;
directory_block_num++;
//将新申请的磁盘块中的所有目录项都初始化为未使用
directory *p = (directory *)(&disk[x][0]);
for( int i = 0 ; i < (B/sizeof(directory)) ; ++i )
{
p = p + i;
p->index = -1;
}
}
directory* available = (directory*)(&disk[pdescrib->fileblock[0]][0]);
while(available->index != -1)
{
available++;
}
//往空闲目录项中添加信息
strcpy(available->filename,filename);//添加新的目录项的相应内容
available->index = index;
//往文件中写内容
printf("please input the content of the file\n");
char input[B * Block_Length]="";
scanf("%s",input);
//修改该文见对应磁盘空间的内容,以块为单位进行修改;
int length = strlen(input);
int nbrofblock = length / B + 1;
for( int i = 0; i < nbrofblock ; ++i )
{
int x = seekfreeOnBitMap();
if(x == -1)
{
printf("there is no enough room for the new file\n");
break;
}
//修改位图
bitmap[x] = '1';
disk[0][x] = '1';
/********
//往目录中加入目录项
**********/
FileDescriptor *newfile = pdescrib + index;
newfile->filelength = length;
newfile->fileblock[i] = x;
//以块为单位拷贝输入内容到磁盘中
memcpy(&disk[x][0],input+B * i , B);
//修改文件数量
file_num++;
save();
}
return index;
}
3、删除文件
/*
* 函数名:destroy
* 功能:根据文件名删除新文件
* 参数:
* char* filename
* 返回值:
* int型 : 返回该文件描述符序号
*/
int destroy(char *filename)
{
//现在目录中找到目录项
directory *pStart = (directory *)(&disk[pdescrib->fileblock[0]][0]);
int destory_index = -1;
for(int i = 0 ; i < file_num ; ++i )
{
if(strcmp(pStart->filename,filename) == 0)
{
destory_index = pStart->index;
break;
}
pStart = pStart + 1;
}
if(destory_index == -1)
{
printf("file not found!\n");
return -1;
}
//检测该文件是否打开
for( i = 0 ; i < maxopen ; ++i )
{
if(openlist[i].index == destory_index)
{
printf("file is opened!\n");
return -1;
}
}
/*删除文件*/
//找到对应的文件描述符
FileDescriptor* destroyfile = pdescrib + destory_index;
//修改位图,将文件占用的所有磁盘均变为空闲
for( i = 0 ; i < Block_Length ; ++i )
{
if(destroyfile->fileblock[i] != -1)
{
bitmap[destroyfile->fileblock[i]] = '0';
disk[0][destroyfile->fileblock[i]] = '0';
memset(&(disk[destroyfile->fileblock[i]][0]),'\0',B);
}
}
//设置文件描述符为空闲
destroyfile->filelength = -1;
for( i = 0 ; i < Block_Length ; ++i )
{
destroyfile->fileblock[i] = -1;
}
//销毁目录项
pStart->index = -1;
for( i = 0 ; i < Name_Length ; ++i )
{
pStart->filename[i] = '\0';
}
save();
return destory_index;
}
4、打开文件
/*
* 函数名:open
* 功能:根据文件名打开文件。该函数返回的索引号可用于后续的read, write, lseek, 或close 操作。
* 参数:
* char* filename
* 返回值:
* int型 : 返回该文件在文件打开表中的索引号
*/
int open(char *filename)
{
int open_index = findindex(filename);
if(open_index == -1)
{
printf("file not found!\n");
return -1;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < maxopen ; ++i )
{
//检查文件是否已经被打开
if(openlist[i].index == open_index)
{
printf("file already open!\n");
return i;
}
}
for(i = 0 ; i < maxopen ; ++i )
{
if(openlist[i].index == -1)
{
openlist[i].index = open_index;
openlist[i].rwp = 0;
FileDescriptor *f = pdescrib + open_index;
read_block(f->fileblock[0],openlist[i].rw_buffer);
printf("file open successfully!\n");
openfile_num++;
return i;
}
}
printf("cannot open file! openlist is full!\n");
return -1;
}
5、关闭文件
/*
* 函数名:close
* 功能: 根据文件描述符索引号关闭指定文件
* 参数:
* int index
* 返回值:
* int型 : 返回该文件在文件打开表中的索引号
*/
int close(char *filename)
{
int index = findindex(filename);
for(int i = 0 ; i < maxopen ; ++i )
{
//检查文件是否已经被打开
if(openlist[i].index == index)
{
//如果文件指针有改变,要保存修改的内容,即将缓冲区的内容写入磁盘
//确定写到哪一块
int x = openlist[i].rwp / B;
//找到对应的文件描述符
FileDescriptor *f = pdescrib + index;
//将缓冲区的数据写到对应的块中
write_block(f->fileblock[x],openlist[i].rw_buffer);
//在文件打开表中关闭这个文件
openlist[i].index = -1;
openlist[i].rw_buffer[0] = '\0';
openlist[i].rwp = 0;
printf("file has closed!\n");
return i;
}
}
printf("file not found!\n");
return -1;
}
6、读文件
/*
* 函数名:read
* 功能: 从指定文件顺序读入count 个字节memarea 指定的内存位置。读操作从文件的读写指针指示的位置开始。
* 参数:
* int index;
* char *mem_area;
* int count;
* 返回值:
* int型 : 返回读入字节数
*/
int read(char *filename,char *mem_area,int count)
{
int index = open(filename);
if(index == -1)
{
printf("file cannot open!\n");
return -1;
}
//找到对应的文件描述符
FileDescriptor *fd = pdescrib + openlist[index].index;
//判断读写指针最终是否会超过文件长度
char temp[Block_Length * B]="";
int x = openlist[index].rwp / B ;//找到读写指针所在块号
int offset = openlist[index].rwp % B;
if(fd->filelength - openlist[index].rwp < count)//必然读到文件尾部
{
int g = fd->filelength - openlist[index].rwp;
strcat(temp,&openlist[index].rw_buffer[offset]);
x++;
while(x < Block_Length && fd->fileblock[x] != -1)
{
//把对应的块读到缓冲区里
read_block(fd->fileblock[x],openlist[index].rw_buffer);
strcat(temp,openlist[index].rw_buffer);
x++;
}
strcpy(mem_area,temp);
//已经读到文件尾部
openlist[index].rwp = fd->filelength;
return g;
}
else
{
//判断需要读多少块
if(B - offset >= count)//不需要再多地调入块
{
memcpy(temp,&openlist[index].rw_buffer[offset],count);
//达到缓冲区尾部
if(B - offset == count)
{
//将下一块读入磁盘
read_block(fd->fileblock[x+1],openlist[index].rw_buffer);
return count;
}
}
else
{
//需要调入多块
int blocknum;
blocknum = (count - (B - offset)) / B;
strcat(temp,&openlist[index].rw_buffer[offset]);
int i = 0;
while(blocknum != i)
{
x++;
i++;
read_block(fd->fileblock[x],openlist[index].rw_buffer);
strcat(temp,openlist[index].rw_buffer);
}
if(B * blocknum < count - (B - offset))
{
x++;
read_block(fd->fileblock[x],openlist[index].rw_buffer);
memcpy(temp,openlist[index].rw_buffer,count - (B - offset) - B * blocknum);
}
}
strcpy(mem_area,temp);
openlist[index].rwp = openlist[index].rwp + count;
}
return 0;
}
7、写文件
/*
* 函数名:write
* 功能: 把memarea 指定的内存位置开始的count 个字节顺序写入指定文件。写操作从文件的读写指针指示的位置开始。
* 参数:
* char *filename;
* char *mem_area;
* int count;
* 返回值:
* int型 :返回写入字节数
*/
int write(char *filename,char *mem_area,int count)
{
int index = findindex(filename);
int open_index;
int a = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < maxopen ; ++i )
{
if(openlist[i].index == index)
{
open_index = i;
a = 1;
break;
}
}
if(a == 0)
{
open_index = open(filename);
}
if(open_index == -1)
{
printf("no such file!\n");
return -1;
}
FileDescriptor*fd = pdescrib + openlist[open_index].index;
//判断是否有足够空间写入
if(openlist[open_index].rwp + count - 1 > B * 3)
{
printf("write too much!\n");
return -1;
}
//计算写入需要的块数,等于完全写入后的块数减去原来的块数
int blocknum = 0;
for( i = 0 ; i < Block_Length ; ++i )
{
if(fd->fileblock[i] != -1)
{
blocknum ++;
}
}
int blockneed = -1;
int x;
if((fd->filelength + count) % B == 0)
{
x = (fd->filelength + count) / B;
blockneed = x - blocknum;
}
else
{
x = (fd->filelength + count) / B + 1;
blockneed = x - blocknum;
}
for( int j = 0 ; j < blockneed ; ++j )
{
//从磁盘中找到空闲的块
int freeblocknum = seekfreeOnBitMap();
//更新位图
bitmap[freeblocknum] = '1';
disk[0][freeblocknum] = '1';
//fd->fileblock[blocknum+i] = freeblocknum;
for( int i = 0 ; i < Block_Length ; ++i )
{
if(fd->fileblock[i] == -1)
{
fd->fileblock[i] = freeblocknum;
break;
}
}
}
char *pstart = (char *)(&disk[fd->fileblock[0]][0]) + openlist[open_index].rwp;
memcpy(pstart,mem_area,count);
fd->filelength = fd->filelength + count;
openlist[open_index].rwp = openlist[open_index].rwp + count;
read_block(fd->fileblock[x-1],openlist[open_index].rw_buffer);//更新读写缓冲区中的内容
save();
return count;
}
8、 修改文件指针
/*
* 函数名:lseek
* 功能: 把文件的读写指针移动到pos 指定的位置。
* 参数:
* int index;
* int pos;
* 返回值:
* int型 :返回写入字节数
*/
int lseek(char *filename,int pos)
{
int open_index = open(filename);
if(open_index == -1)
{
printf("file not found!\n");
return -1;
}
FileDescriptor *fd = pdescrib + openlist[open_index].index;
if(pos > fd->filelength || pos < 0)
{
printf("the position is OutOfBound!\n");
return -2;
}
openlist[open_index].rwp = pos;
return 0;
}
9、显示目录
/*
* 函数名:show_directory
* 功能: 列表显示所有文件及其长度。
* 参数:
* 无
* 返回值:
* 无
*/
void show_directory()
{
directory*pdir = (directory*)(&disk[pdescrib->fileblock[0]][0]);//pdir 存 第一个目录项的位置
directory*file_pdir = (directory*)malloc(sizeof(directory));
FileDescriptor*file_describ = (FileDescriptor*)malloc(sizeof(FileDescriptor));
printf("文件名 \t文件长度 \t文件描述符序号 \t\n");
for(file_pdir = pdir;file_pdir < (pdir + file_num);file_pdir++)
{
if(file_pdir->index != -1)
{
file_describ = pdescrib + file_pdir->index;
printf("%s\t %d\t %d\t\n",file_pdir->filename,file_describ->filelength,file_pdir->index);
}
}
}
3.主要程序框图
3.1、create函数

3.2、destroy函数

3.3、open函数

3.4、read函数

3.5、write函数

4.实验结果及分析
1、初始化程序
执行程序,进入菜单界面,如下图

此时disk文件中内容如下图
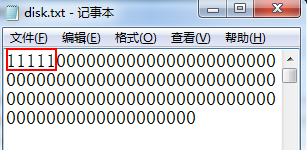
前5位为1,表示预留出的5块内容,其余为为0表示该块未被占用。
2、创建文件

此时再次观察disk文件
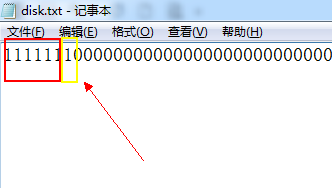
其中第6块用于放置目录文件,第7块用于放置新创建的test.txt文件。且在disk目录文件中出现对于刚刚创建test.txt文件描述,如下图
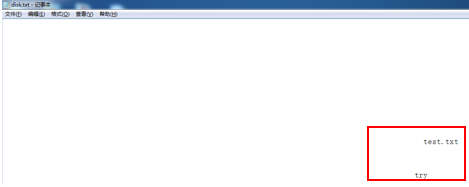
3、删除文件

观察目录文件发现第7块再次空闲,test.txt描述被删除
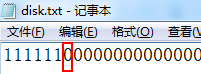
若输入文件名不存在,会产生报错信息
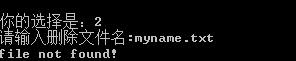
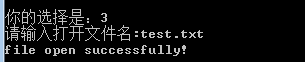
4、打开文件
该函数返回的索引号可用于后续的read, write, lseek, 或close 操作。
若文件不存在,产生报错信息
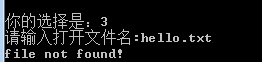
5、关闭文件
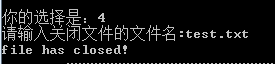
若文件已关闭或不存在,产生报错信息

6、读文件

7、写文件

此时观察目录文件

8、修改读写指针后写文件

观察目录文件,发现从test文件第4字节发生修改

9、显示所有目录与位图信息

可以观察到第7和第8块均为占用
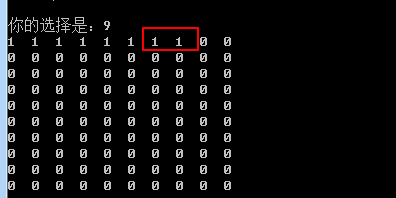
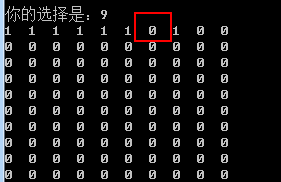
此时,删除test.txt,再次观察,此时第8块为空闲

5.心得体会
由于文件系统的复杂性,我们需要特别注意在对文件进行操作的过程中,相应的位图、文件描述符、目录项、文件打开表等内容的变化,并理清步骤,否则就会出错,使操作不成功或造成更为严重的问题。
完成本次实验,最重要的是明白文件系统的构架,明白位图、文件描述符、目录项、文件打开表等之间的关系,并且在编程之前对文件操作步骤有一个清晰的思路和初步的规划。本次实验涉及到的辅助操作很多,因此就有许多辅助函数,这要求我们要有一个清晰的编程思路,合理调用这些函数。