泛型在Java集合中广泛使用,它是一种未知的数据类型,当不知道使用哪种数据类型的时候,可以使用泛型。泛型可以看做一个变量,用来接收收据类型。如E e:代表Element 元素,T t:代表Type类型。比如ArrayList,定义集合时不知道里面会存储什么数据类型,定义ArrayList类源码中,使用public class ArrayList<E>,里面数据类型为E, 并且里面有两个方法,一个参数类型为E,一个返回数据类型为E,这都是泛型的应用。
public boolean add(E e)
public E get(int index)
创建集合对象的时候,就会确定泛型的数据类型,创建时是什么数据类型,就以什么样的数据类型作为参数传递到E,我们也可以使用泛型,用来自己创建类、方法和接口,感受泛型的优点,并了解泛型的通配符的上下限。
使用泛型优点
集合定义时如果不使用泛型,就默认是Object类型,在做某些子类API调用时,可能不一定都适用集合里所有的数据类型,可能会导致运行期报错。如果创建集合使用泛型,则有效的规避了这样的风险,将运行期出现的错误上升到了编译期。
1 package GenericTest; 2 3 import javax.swing.text.html.HTMLDocument; 4 import java.util.ArrayList; 5 import java.util.Iterator; 6 7 /** 8 * 使用泛型的好处 9 */ 10 public class GenericDemo1 { 11 /** 12 * 创建集合对象如果不使用泛型,默认数据类型为Object 13 * 优点:数据类型为Object,可以存储任意类型的数据 14 * 缺点:由于存储的数据类型可以任意,在调用特有API时可能会引发异常 15 * <p> 16 * 如果创建集合对象的时候使用泛型 17 * 优点:集合对象定义使用什么数据类型,就是什么数据类型,另外将运行期出现的问题上升到了编译期,可以提前发现问题 18 * 缺点:定义数据类型单一,准确来说应该是特点不是缺点 19 */ 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) { 22 //不使用泛型 23 //printArray(); 24 //使用泛型 25 printArrayWithGeneric(); 26 27 } 28 29 //集合不使用泛型 30 public static void printArray() { 31 ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); 32 list.add("hello my future!"); 33 list.add(8848); 34 //遍历集合 35 Iterator it = list.iterator();//集合是什么泛型,迭代器就是什么泛型 36 //打印 OK 37 while (it.hasNext()) { 38 System.out.println(it.next()); 39 } 40 41 //如果想输出集合元素字符串的长度,需要使用String的API,Object需要向下转型为String才可以调用 42 Iterator it1 = list.iterator(); 43 while (it1.hasNext()) { 44 String str = (String) it1.next();//Object向下转型为String 45 int len = str.length(); 46 System.out.println(str + "-->" + len); 47 } 48 /** 49 * 打印输出看出,当打印第一个字符串长度没有问题,但是打印数字时出现了异常,报java.lang.Integer cannot be cast to java.lang.String 50 * 显然是类型转换出来问题,导致的报错,因此如果不使用泛型,可能会出现调用特定API导致不适用而报错 51 */ 52 53 } 54 55 //集合使用泛型 56 public static void printArrayWithGeneric() { 57 ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();//集合对象数据类型为String,则这个数据类型作为参数传递给E 58 list.add("hello my future"); 59 /*list.add(8848);//编译就报错*/ 60 Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); 61 while (it.hasNext()) { 62 System.out.println(it.next()); 63 } 64 65 } 66 67 }
控制台输出结果
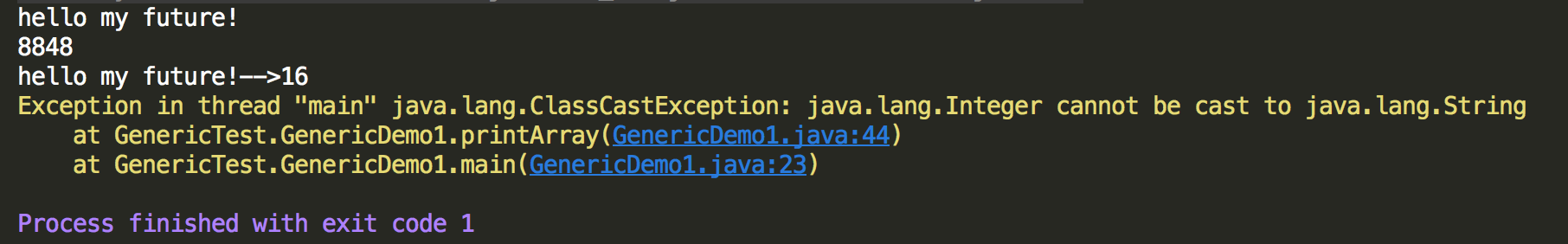
当不使用泛型时,想调用String类型的API,导致数字转换异常报错,这就是不使用泛型的不安全性,当使用泛型其在编译期就报错。
泛型在类中的使用
泛型可以用来定义一个类,对应类中的方法参数和返回值等都要相应变成泛型类型。
1 package GenericTest; 2 3 /** 4 * 定义和使用含有泛型的类,模拟ArrayList集合定义,下面类定义一个参数,刚开始为String,后面在类后面定义泛型后,方法参数全部定义为泛型 5 */ 6 public class GenericClass<E> { 7 8 private E Parameter; 9 10 public E getParameter() { 11 return Parameter; 12 } 13 14 public void setParameter(E parameter) { 15 Parameter = parameter; 16 } 17 }
创建一个实体类来测试数据类型为自定义,上面类方法的调用。

package GenericTest; /** * 自定义测试类,验证定义含有泛型的类 */ public class Student { private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }
测试类,方法使用时调用不同的数据类型,得到不同测试结果。
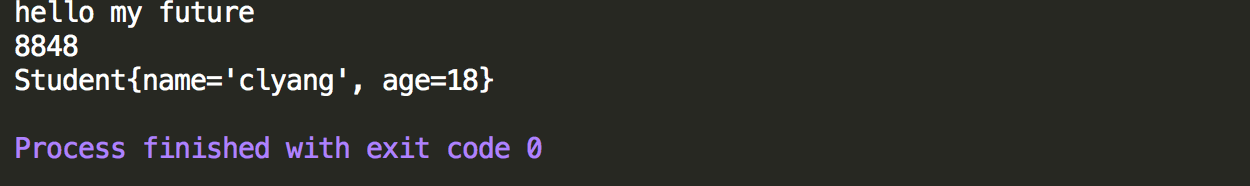
1 package GenericTest; 2 3 /** 4 * 测试定义含有泛型的类 5 */ 6 public class GenericClassTest { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 //创建对象时,泛型类型为String 10 GenericClass<String> col=new GenericClass<>(); 11 col.setParameter("hello my future"); 12 System.out.println(col.getParameter()); 13 //创建对象时,泛型类型为Integer 14 GenericClass<Integer> col1=new GenericClass<>(); 15 col1.setParameter(8848); 16 System.out.println(col1.getParameter()); 17 //创建对象时,泛型类型为自定义 18 GenericClass<Student> col2=new GenericClass<>(); 19 Student stu=new Student(); 20 stu.setName("clyang"); 21 stu.setAge(18); 22 col2.setParameter(stu); 23 System.out.println(col2.getParameter().toString()); 24 } 25 }
控制台输出情况,可以看出当你给方法什么类型的参数它就使用什么类型的参数执行方法,并返回对应的值。
泛型在方法中的使用
定义和使用含有泛型的方法,泛型定义在方法修饰符和返回值之间,含有泛型的方法被调用时,往里传递的是什么参数,则泛型就是什么类型的泛型。
格式:
方法修饰词 <泛型> 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型(定义的泛型) 参数){
方法体
}
1 package GenericTest; 2 3 /** 4 * 定义和使用含有泛型的方法,泛型定义在方法修饰符和返回值之间 5 * 格式: 6 * 方法修饰词 <泛型> 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型(定义的泛型) 参数){ 7 * 方法体 8 * } 9 * 10 * 含有泛型的方法被调用时,传递的是什么参数则泛型就是什么类型的泛型 11 */ 12 public class GenericMethod { 13 //定义一个普通方法 14 public <M> void printMethod1(M m) { 15 System.out.println(m); 16 } 17 18 //定义一个静态方法 19 public static <N> void printMethod2(N n) { 20 System.out.println(n); 21 } 22 }
测试方法中使用泛型。
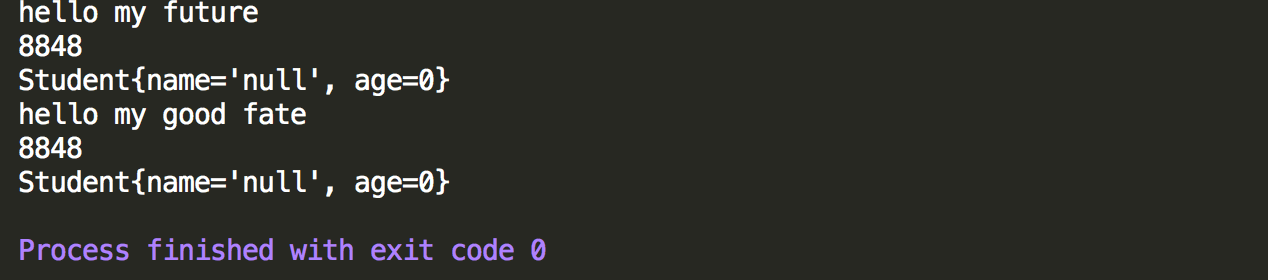
1 package GenericTest; 2 3 /** 4 * 测试方法中定义泛型 5 */ 6 public class GenericMethodTest { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 //测试方法中定义泛型 10 GenericMethod gm = new GenericMethod(); 11 gm.printMethod1("hello my future"); 12 gm.printMethod1(8848); 13 gm.printMethod1(new Student()); 14 15 //测试方法中使用泛型 --静态方法 16 //静态方法调用不建议使用创建对象后使用,直接使用类名.方法名就可以使用 17 GenericMethod.printMethod2("hello my good fate"); 18 GenericMethod.printMethod2(8848); 19 GenericMethod.printMethod2(new Student()); 20 } 21 }
控制台输出情况,普通方法和静态方法都可以实现正常调用。
泛型在接口中的使用
接口中定义泛型,有两种实现方法,一种是在实现类实现接口时,定义接口中泛型类型。另外一种是实现类实现接口,接口是什么泛型实现类就是什么类型泛型,具体参考如下代码。
1 package GenericTest; 2 3 /** 4 * 定义和使用含有泛型的接口 5 * 6 * 第一种实现方法:定义一个含有泛型的接口,再定义一个实现类来实现这个接口,实现时指定接口的泛型 7 * 或者比如Scanner类,public final class Scanner implements Iterator<String>,实现Iterator接口时指定了泛型为String类型, 8 * 因此Scanner对象的Next方法,public String next(String pattern)返回数据类型就是String 9 * 10 * 第二种实现方法:接口使用什么类型,实现类就使用什么泛型,类跟着接口走 11 * 比如ArrayList类,其实现了List接口,可以看到List接口泛型为E,实现类的泛型也为E,其下面的方法参数也相应变成E 12 * 13 */ 14 public interface GenericInterface<T> { 15 //定义一个简单的抽象方法 16 public abstract void printArray(T t); 17 }
第一种方法实现接口中的泛型
1 package GenericTest; 2 3 /** 4 * 第一种实现方法:实现含有泛型的接口,接口实现时指定泛型类型 5 */ 6 public class GenericInterfaceImpl implements GenericInterface<String>{ 7 8 @Override 9 public void printArray(String s) { 10 System.out.println(s); 11 } 12 //可以看到当接口指定泛型类型为String后,方法参数也为String了 13 }
第二种方法实现接口中的泛型
1 package GenericTest; 2 3 /** 4 * 第二种实现方法,接口定义了什么泛型,实现类就是什么泛型,如下所示实现类后面也要加<T> 5 */ 6 public class GenericInterfaceImpl1<T> implements GenericInterface<T>{ 7 8 @Override 9 public void printArray(T t) { 10 System.out.println(t); 11 } 12 //接口类型泛型为T,实现类类型泛型也为T 13 }
测试两种实现
1 package GenericTest; 2 3 /** 4 * 测试类,测试接口中定义泛型 5 */ 6 public class GenericInterfaceImplTest { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 //父类的接口指向子类的对象 10 //第一种实现方法 11 GenericInterface gi=new GenericInterfaceImpl(); 12 gi.printArray("hello my future"); 13 14 //第二种实现方法 15 GenericInterface gi1=new GenericInterfaceImpl1(); 16 gi1.printArray("hello my brother"); 17 gi1.printArray(8848); 18 gi.printArray("is a good phone,you deserve it"); 19 20 } 21 22 }
控制台输出结果,第一种实现其实限定了数据类型,如本例中为String,第二种没有限定。
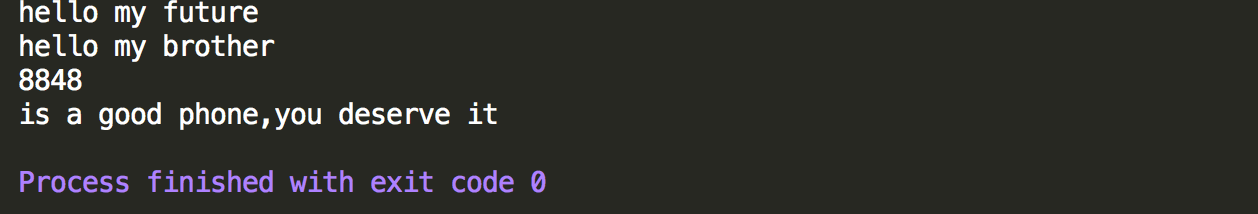
泛型通配符的使用
通配符使用在方法中,当方法参数类型不确定时,可以使用"?"来代替类型,传入的是什么数据类型就是什么类型,注意通配符不能用于创建对象。
package GenericTest; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; /** * 泛型-通配符的使用,用 ?表示,其代表任意数据类型,只能作为方法的参数使用,不能创建对象时使用 * */ public class GenericWildcardCharacter { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建两个不同数据类型的集合,写一个方法实现遍历打印,写方法时不知道需要打印的集合数据类型是什么,因此使用通配符 //第一个集合 ArrayList<String> col1=new ArrayList<String>(); col1.add("you"); col1.add("are"); col1.add("beautiful"); //第二个集合 ArrayList<Integer> col2=new ArrayList<Integer>(); col2.add(8848); col2.add(618); col2.add(1111); //一个方法实现上面两种数据类型集合的遍历打印 printArray(col1); printArray(col2); //通配符不能用来创建对象 /*ArrayList<?> col3=new ArrayList<?>();*/ } //统配符作为参数在方法中 public static void printArray(ArrayList<?> array){ Iterator<?> it=array.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ Object o=it.next();//返回数据类型不确定,使用Object来接收 System.out.println(o); } } }
控制台输出情况
另外通配符还有一个高级的应用,就是通配符的上下限。
1 package GenericTest; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 6 /** 7 * 泛型-通配符高级使用,受限泛型 8 * 泛型的上限限定:? extends E 代表泛类型只能是E类型的子类 9 * 泛型的下限限定:? super E 代表泛类型只能是E类型的父类 10 */ 11 public class GenericWildcardCharacter1 { 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 //创建一些集合,其中Integer是Number的子类,Number是Object的子类,String是Object的子类 15 Collection<Integer> col1=new ArrayList<Integer>(); 16 Collection<String> col2=new ArrayList<String>(); 17 Collection<Number> col3=new ArrayList<Number>(); 18 Collection<Object> col4=new ArrayList<Object>(); 19 20 //调用使用了受限泛型统配符的方法 21 method1(col1); 22 /*method1(col2);//编译失败*/ 23 method1(col3); 24 /*method1(col4);//编译失败*/ 25 26 /*method2(col1);//编译失败*/ 27 /*method2(col2);//编译失败*/ 28 method2(col3); 29 method2(col4); 30 } 31 //上限限定 32 public static void method1(Collection<? extends Number> col){}; 33 //下限限定 34 public static void method2(Collection<? super Number> col){}; 35 }
泛型主要在集合中有广泛使用,可以定义在类、方法和接口中,主要是不知道传入的参数类型是什么才使用了泛型来解决问题。
