BUAAOO 第三单元总结
一. JML语言理论基础及应用工具链情况
(一) JML理论基础
1. 注释结构
-
行注释的表示方式:
//@annotation -
块注释的方式:
/* @ annotation @*/
2. JML表达式
原子表达式:
-
\result表示一个非 void 类型的方法执行所获得的结果,即方法执行后的返回值。
-
\old( expr )用来表示一个表达式 expr 在相应方法执行前的取值。
-
\not_assigned(x,y,...)用来表示括号中的变量是否在方法执行过程中被赋值。
-
\not_modifified(x,y,...)与\not_assigned表达式类似,该表达式限制括号中的变量在方法执行期间的取值未发生变化。
-
\nonnullelements( container )表示 container 对象中存储的对象不会有 null 。
-
\type(type)返回类型type对应的类型(Class)。
-
\typeof(expr)该表达式返回expr对应的准确类型。
量化表达式:
-
\forall全称量词修饰的表达式,表示对于给定范围内的元素,每个元素都满足相应的约束。
-
\exists存在量词修饰的表达式,表示对于给定范围内的元素,存在某个元素满足相应的约束。
-
\sum返回给定范围内的表达式的和。
-
\product返回给定范围内的表达式的连乘结果。
-
\max返回给定范围内的表达式的最大值。
-
\min返回给定范围内的表达式的最小值。
-
\num_of返回指定变量中满足相应条件的取值个数。
集合表达式:
可以在JML规格中构造一个局部的集合(容器),明确集合中可以包含的元素。
集合构造表达式的一般形式为:new ST {T x|R(x)&&P(x)},其中的R(x)对应集合中x的范围,通常是来自于某个既有集合中的元素,如s.has(x),P(x)对应x取值的约束。
操作符:
-
子类型关系操作符
E1<:E2 -
等价关系操作符
b_expr1<==>b_expr2或者b_expr1<=!=>b_expr2 -
等价关系操作符
b_expr1<==>b_expr2或者b_expr1<=!=>b_expr2 -
变量引用操作符
\nothing指示一个空集;\everything指示一个全集。变量引用操作符经常在assignable句子中使用,如assignable \nothing表示当前作用域下每个变量都不可以在方法执行过程中被赋值。
3. 方法规格
-
前置条件
前置条件通过requires子句来表示:
requires P;。其中requires是JML关键词,表达的意思是“要求调用者确保P为真”。 -
后置条件
后置条件通过ensures子句来表示:
ensures P;。其中ensures是JML关键词,表达的意思是“方法实现者确保方法执行返回结果一定满足谓词P的要求,即确保P为真”。 -
副作用范围限定
副作用指方法在执行过程中会修改对象的属性数据或者类的静态成员数据,从而给后续方法的执行带来影响。从方法规格的角度,必须要明确给出副作用范围。
JML提供了副作用约束子句,使用关键词 assignable 或者 modifiable 。
-
signals子句
signals子句的结构为
signals (Exception e) b_expr,意思是当 b_expr 为 true 时,方法会抛出括号中给出的相应异常e
4. 类型规格
-
不变式invariant
不变式是要求在所有可见状态下都必须满足的特性,语法上定义 invariant P ,其中 invariant 为关键词, P 为谓词。
可见状态包括:
-
对象的有状态构造方法(用来初始化对象成员变量初值)的执行结束时刻
-
在调用一个对象回收方法(fifinalize方法)来释放相关资源开始的时刻
-
在调用对象o的非静态、有状态方法(non-helper)的开始和结束时
-
在调用对象o对应的类或父类的静态、有状态方法的开始和结束时刻
-
在未处于对象o的构造方法、回收方法、非静态方法被调用过程中的任意时
-
在未处于对象o对应类或者父类的静态方法被调用过程中的任意时刻
-
-
状态变化约束constraint
对象的状态在变化时往往也许满足一些约束,这种约束本质上也是一种不变式。JML为了简化使用规则,规定invariant只针对可见状态(即当下可见状态)的取值进行约束,而是用constraint来对前序可见状态和当前可见状态的关系进行约束。
(二) 应用工具链情况
-
openJML:JML对实现进行静态的检查。
-
JMLUnitNG:根据JML自动生成对应的测试样例,用于进行单元化测试。
二. 针对Graph接口的实现自动生成测试用例
测试用例及分析
containsNode
@Test
public void containsNode() {
int[] nodesList = {1,2,3,4,5};
Path path1 = new MyPath(nodesList);
Graph graph = new MyGraph();
try {
graph.addPath(path1);
}catch (Exception e){
}
boolean result = graph.containsNode(1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
result = graph.containsNode(0);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
}
分析
由于只是判断图中是否存在这一点,正确测试,错误测试即可。
containsEdge
@Test
public void containsEdge() {
int[] nodesList = {1,2,3,4,5};
Path path1 = new MyPath(nodesList);
int[] nodesList2 = {3,6,7};
Path path2 = new MyPath(nodesList2);
Graph graph = new MyGraph();
try {
graph.addPath(path1);
graph.addPath(path2);
}catch (Exception e){
}
boolean result = graph.containsEdge(1,2);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
result = graph.containsEdge(6,3);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
result = graph.containsEdge(1,3);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
result = graph.containsEdge(1,1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
}
分析
判断图中是否存在边,应进行正确测试,错误测试,相同点测试,反向边测试。
isConnected
@Test
public void isConnected() {
int[] nodesList = {1,2,3,4,5};
Path path1 = new MyPath(nodesList);
int[] nodesList2 = {3,6,7};
Path path2 = new MyPath(nodesList2);
int[] nodesList3 = {8,9};
Path path3 = new MyPath(nodesList3);
Graph graph = new MyGraph();
try {
graph.addPath(path1);
graph.addPath(path2);
graph.addPath(path3);
}catch (Exception e){
}
try {
boolean result = graph.isConnected(1,2);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
result = graph.isConnected(3,7);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
result = graph.isConnected(2,6);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
result = graph.isConnected(5,5);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
result = graph.isConnected(1,8);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
分析
判断是否相连,应进行正确测试,错误测试,相同点测试,反向相连测试。
getShortestPathLength
@Test
public void getShortestPathLength() {
int[] nodesList = {1,2,3,4,5,3};
Path path1 = new MyPath(nodesList);
int[] nodesList2 = {5,1,4};
Path path2 = new MyPath(nodesList2);
Graph graph = new MyGraph();
try {
graph.addPath(path1);
graph.addPath(path2);
}catch (Exception e){
}
try {
int result = graph.getShortestPathLength(1,5);
Assert.assertEquals(result, 1);
result = graph.getShortestPathLength(3,5);
Assert.assertEquals(result, 1);
result = graph.getShortestPathLength(1,1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, 0);
result = graph.getShortestPathLength(3,1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, 2);
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
分析
计算最短路径,应进行正确测试,错误测试,相同点测试,反向相连测试。
size
@Test
public void size() {
int[] nodesList = {1,2,3,4,5};
Path path1 = new MyPath(nodesList);
int[] nodesList2 = {3,6,7};
Path path2 = new MyPath(nodesList2);
int[] nodesList3 = {8,9};
Path path3 = new MyPath(nodesList3);
Graph graph = new MyGraph();
try {
int result = graph.size();
Assert.assertEquals(result, 0);
graph.addPath(path1);
graph.addPath(path2);
graph.addPath(path3);
result = graph.size();
Assert.assertEquals(result, 3);
graph.removePath(path1);
graph.removePathById(2);
result = graph.size();
Assert.assertEquals(result, 1);
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
分析
计算图中路径数量,应在还未开始加入路径的时候测试,加入路径的时候测试,删除路径的时候测试。
containsPath
@Test
public void containsPath() {
int[] nodesList = {1,2,3,4,5};
Path path1 = new MyPath(nodesList);
int[] nodesList2 = {3,6,7};
Path path2 = new MyPath(nodesList2);
int[] nodesList3 = {8,9};
Path path3 = new MyPath(nodesList3);
Graph graph = new MyGraph();
try {
boolean result = graph.containsPath(path1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
graph.addPath(path1);
graph.addPath(path2);
graph.addPath(path3);
result = graph.containsPath(path1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
graph.removePath(path1);
result = graph.containsPath(path1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
graph.removePathById(2);
result = graph.containsPath(path2);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
分析
判断是否包含路径,应在还未开始加入路径的时候测试,加入路径的时候测试,删除路径的时候测试。
containsPathId
@Test
public void containsPathId() {
int[] nodesList = {1,2,3,4,5};
Path path1 = new MyPath(nodesList);
int[] nodesList2 = {3,6,7};
Path path2 = new MyPath(nodesList2);
int[] nodesList3 = {8,9};
Path path3 = new MyPath(nodesList3);
Graph graph = new MyGraph();
try {
boolean result = graph.containsPathId(1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
graph.addPath(path1);
graph.addPath(path2);
graph.addPath(path3);
result = graph.containsPathId(2);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
graph.removePath(path1);
result = graph.containsPathId(1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
graph.removePathById(2);
result = graph.containsPathId(2);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
分析
判断是否包含相应Id的路径,应在还未开始加入路径的时候测试,加入路径的时候测试,删除路径的时候测试。
getPathById
@Test
public void getPathById() {
int[] nodesList = {1,2,3,4,5};
Path path1 = new MyPath(nodesList);
int[] nodesList2 = {3,6,7};
Path path2 = new MyPath(nodesList2);
int[] nodesList3 = {8,9};
Path path3 = new MyPath(nodesList3);
Graph graph = new MyGraph();
try {
graph.addPath(path1);
graph.addPath(path2);
graph.addPath(path3);
}catch (Exception e){
}
try {
Path p = graph.getPathById(1);
Assert.assertTrue(p.equals(path1));
p = graph.getPathById(3);
Assert.assertTrue(p.equals(path3));
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
分析
得到对应Id的路径,在加入路径之后测试即可。
getPathById
@Test
public void getPathId() {
int[] nodesList = {1,2,3,4,5};
Path path1 = new MyPath(nodesList);
int[] nodesList2 = {3,6,7};
Path path2 = new MyPath(nodesList2);
int[] nodesList3 = {8,9};
Path path3 = new MyPath(nodesList3);
Graph graph = new MyGraph();
try {
graph.addPath(path1);
graph.addPath(path2);
graph.addPath(path3);
graph.removePath(path3);
graph.addPath(path3);
}catch (Exception e){
}
try {
Path p = graph.getPathById(1);
Assert.assertTrue(p.equals(path1));
p = graph.getPathById(4);
Assert.assertTrue(p.equals(path3));
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
分析
得到对应路径的Id,在加入路径之后测试即可。
addPath
@Test
public void addPath() {
int[] nodesList = {1,2,3,4,5};
Path path1 = new MyPath(nodesList);
int[] nodesList2 = {3,6,7};
Path path2 = new MyPath(nodesList2);
int[] nodesList3 = {8,9};
Path path3 = new MyPath(nodesList3);
Graph graph = new MyGraph();
try {
int result = graph.size();
Assert.assertEquals(result, 0);
graph.addPath(path1);
graph.addPath(path2);
graph.addPath(path3);
result = graph.size();
Assert.assertEquals(result, 3);
graph.addPath(path1);
result = graph.size();
Assert.assertEquals(result, 3);
graph.removePath(path3);
graph.addPath(path3);
Path p = graph.getPathById(4);
Assert.assertTrue(p.equals(path3));
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
分析
向图中加入路径,应测试是否能正常加入路径,路径序号是否正确,删除后重新添加Id是否正确,重复添加路径是否正确。
removePath
@Test
public void removePath() {
int[] nodesList = {1,2,3,4,5};
Path path1 = new MyPath(nodesList);
int[] nodesList2 = {3,6,7};
Path path2 = new MyPath(nodesList2);
int[] nodesList3 = {8,9};
Path path3 = new MyPath(nodesList3);
Graph graph = new MyGraph();
try {
graph.addPath(path1);
graph.addPath(path2);
graph.addPath(path3);
graph.removePath(path3);
boolean b = graph.containsPath(path3);
Assert.assertEquals(b, false);
graph.removePath(path1);
b = graph.containsPath(path1);
Assert.assertEquals(b, false);
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
分析
从图中以Path直接删除路径,应在加入后测试是否能正常删除路径。
removePathById
@Test
public void removePathById() {
int[] nodesList = {1,2,3,4,5};
Path path1 = new MyPath(nodesList);
int[] nodesList2 = {3,6,7};
Path path2 = new MyPath(nodesList2);
int[] nodesList3 = {8,9};
Path path3 = new MyPath(nodesList3);
Graph graph = new MyGraph();
try {
graph.addPath(path1);
graph.addPath(path2);
graph.addPath(path3);
graph.removePathById(1);
boolean b = graph.containsPath(path1);
Assert.assertEquals(b, false);
graph.removePathById(2);
b = graph.containsPath(path2);
Assert.assertEquals(b, false);
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
分析
从图中以Id删除路径,应在加入后测试是否能正常删除路径。
getDistinctNodeCount
@Test
public void getDistinctNodeCount() {
int[] nodesList = {1,2,3,4,5};
Path path1 = new MyPath(nodesList);
int[] nodesList2 = {3,6,7};
Path path2 = new MyPath(nodesList2);
int[] nodesList3 = {8,9};
Path path3 = new MyPath(nodesList3);
Graph graph = new MyGraph();
try {
int result = graph.getDistinctNodeCount();
Assert.assertEquals(result, 0);
graph.addPath(path1);
graph.addPath(path2);
result = graph.getDistinctNodeCount();
Assert.assertEquals(result, 7);
graph.addPath(path3);
result = graph.getDistinctNodeCount();
Assert.assertEquals(result, 9);
graph.removePath(path3);
result = graph.getDistinctNodeCount();
Assert.assertEquals(result, 7);
graph.removePath(path1);
result = graph.getDistinctNodeCount();
Assert.assertEquals(result, 3);
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
分析
计算不同节点的个数,应在还未开始加入路径的时候测试,加入路径的时候测试,删除路径的时候测试。加入的路径应包含同一个路径中有重复点的情况,不同路径中有重复点的情况。
三. 架构设计
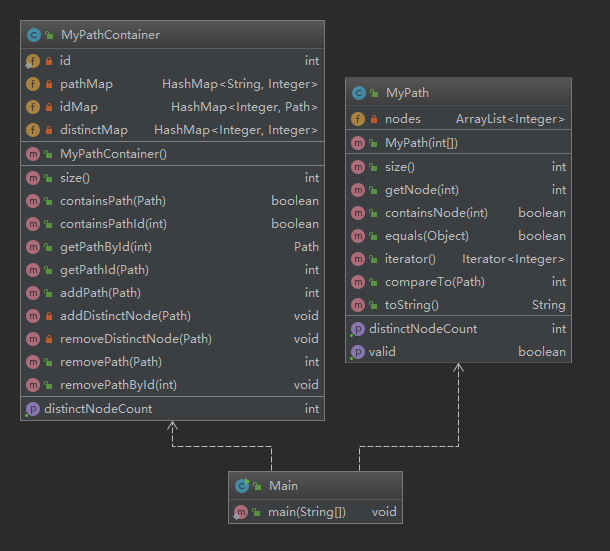
第一次作业
类图

复杂度表
| Method | ev(G) | iv(G) | v(G) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main.main(String[]) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.MyPath(int[]) | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| MyPath.compareTo(Path) | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| MyPath.containsNode(int) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.equals(Object) | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| MyPath.getDistinctNodeCount() | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| MyPath.getNode(int) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.isValid() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.iterator() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.size() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.toString() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPathContainer.MyPathContainer() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPathContainer.addDistinctNode(Path) | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| MyPathContainer.addPath(Path) | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| MyPathContainer.containsPath(Path) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPathContainer.containsPathId(int) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPathContainer.getDistinctNodeCount() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPathContainer.getPathById(int) | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| MyPathContainer.getPathId(Path) | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| MyPathContainer.removeDistinctNode(Path) | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| MyPathContainer.removePath(Path) | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| MyPathContainer.removePathById(int) | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| MyPathContainer.size() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Class | OCavg | WMC |
|---|---|---|
| Main | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath | 1.9 | 19 |
| MyPathContainer | 1.83 | 22 |
分析
这次的复杂度都还比较正常,从架构设计上来说,这次并不需要从其中拆分出单独的对象,就按照题目所要求的架构来就可以和清楚的表达出题目的意思。
第二次作业
类图

复杂度表
| Method | ev(G) | iv(G) | v(G) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main.main(String[]) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyGraph.addDistinctNode(Path) | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| MyGraph.addEdgeMap(Path) | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| MyGraph.addPath(Path) | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| MyGraph.changeEdgeMap(int,int,int) | 1 | 7 | 7 |
| MyGraph.containsEdge(int,int) | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| MyGraph.containsNode(int) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyGraph.containsPath(Path) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyGraph.containsPathId(int) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyGraph.getDistinctNodeCount() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyGraph.getPathById(int) | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| MyGraph.getPathId(Path) | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| MyGraph.getShortestPathLength(int,int) | 4 | 2 | 5 |
| MyGraph.isConnected(int,int) | 3 | 2 | 4 |
| MyGraph.removeDistinctNode(Path) | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| MyGraph.removeEdgeMap(Path) | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| MyGraph.removePath(Path) | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| MyGraph.removePathById(int) | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| MyGraph.setFloydMap() | 1 | 10 | 10 |
| MyGraph.size() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.MyPath(int[]) | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| MyPath.compareTo(Path) | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| MyPath.containsNode(int) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.equals(Object) | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| MyPath.getDistinctNodeCount() | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| MyPath.getNode(int) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.isValid() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.iterator() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.size() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.toString() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Class | OCavg | WMC |
|---|---|---|
| Main | 1 | 1 |
| MyGraph | 2.89 | 55 |
| MyPath | 1.9 | 19 |
分析
这次作业来看,我的MyGraph类的复杂度就有些偏高了。在这次的架构上,我应该拆分出一个结点类,在节点类中储存每个节点对应的邻接表。并且在结点类中进行维护邻接表,查询每个点是否有临边,求出每个点到其他点最短距离的操作,而不应该把这些操作都放在MyGraph类之中,这样会导致MyGraph类显得很累赘,不清楚,在测试找Bug的时候也非常不方便。
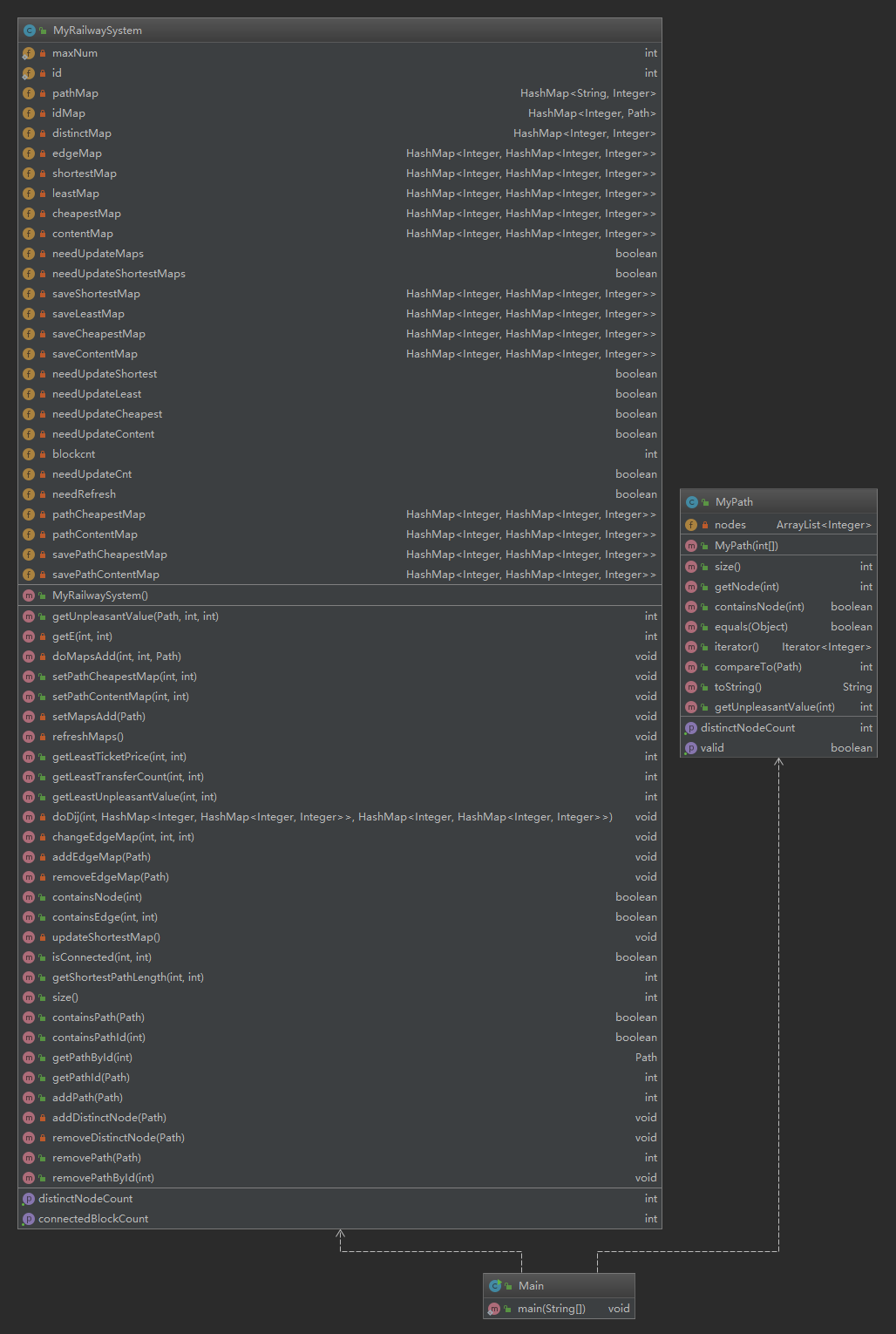
第三次作业
类图

复杂度表
| Method | ev(G) | iv(G) | v(G) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main.main(String[]) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.MyPath(int[]) | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| MyPath.compareTo(Path) | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| MyPath.containsNode(int) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.equals(Object) | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| MyPath.getDistinctNodeCount() | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| MyPath.getNode(int) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.getUnpleasantValue(int) | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| MyPath.isValid() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.iterator() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.size() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath.toString() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyRailwaySystem.MyRailwaySystem() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyRailwaySystem.addDistinctNode(Path) | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| MyRailwaySystem.addEdgeMap(Path) | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| MyRailwaySystem.addPath(Path) | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| MyRailwaySystem.changeEdgeMap(int,int,int) | 1 | 7 | 7 |
| MyRailwaySystem.containsEdge(int,int) | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| MyRailwaySystem.containsNode(int) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyRailwaySystem.containsPath(Path) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyRailwaySystem.containsPathId(int) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyRailwaySystem.doDij(int,HashMap<Integer, HashMap<Integer, Integer>>,HashMap<Integer, HashMap<Integer, Integer>>) | 3 | 11 | 12 |
| MyRailwaySystem.doMapsAdd(int,int,Path) | 1 | 8 | 8 |
| MyRailwaySystem.getConnectedBlockCount() | 5 | 7 | 9 |
| MyRailwaySystem.getDistinctNodeCount() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyRailwaySystem.getE(int,int) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyRailwaySystem.getLeastTicketPrice(int,int) | 5 | 6 | 11 |
| MyRailwaySystem.getLeastTransferCount(int,int) | 5 | 6 | 11 |
| MyRailwaySystem.getLeastUnpleasantValue(int,int) | 5 | 6 | 11 |
| MyRailwaySystem.getPathById(int) | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| MyRailwaySystem.getPathId(Path) | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| MyRailwaySystem.getShortestPathLength(int,int) | 4 | 6 | 10 |
| MyRailwaySystem.getUnpleasantValue(Path,int,int) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyRailwaySystem.isConnected(int,int) | 3 | 6 | 9 |
| MyRailwaySystem.refreshMaps() | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| MyRailwaySystem.removeDistinctNode(Path) | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| MyRailwaySystem.removeEdgeMap(Path) | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| MyRailwaySystem.removePath(Path) | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| MyRailwaySystem.removePathById(int) | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| MyRailwaySystem.setMapsAdd(Path) | 5 | 4 | 6 |
| MyRailwaySystem.setPathCheapestMap(int,int) | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| MyRailwaySystem.setPathContentMap(int,int) | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| MyRailwaySystem.size() | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MyRailwaySystem.updateShortestMap() | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| Class | OCavg | WMC |
|---|---|---|
| Main | 1 | 1 |
| MyPath | 1.91 | 21 |
| MyRailwaySystem | 3.94 | 126 |
分析
可以说,我这次的架构确实做的挺失败的。由于在第二次中没有有效的分出结点类,在时间比较紧的情况之下,我没有重构我的代码,而是把之后的操作又写进了MyRailwaySystem类之中。
有关这次架构设计,由于我没有采用拆点的算法,我认为一个结点类基本能满足我这次的需求,求最短路径的算法可以写在结点类之中,四种不同的最短路径问题只需要一种Dij算法就够了,剩余的就是改变权重的问题。
四. 代码实现的bug和修复情况
第一次作业
这一次的作业中我虽然躲过了强测和互测,但实际上给自己埋了一个非常要命的bug。我的removePath(Path path)函数其实是没有办法正常删除的。但当时由于还不会分模块测试,测试的时候的可能也忽视了这一方面,最终没有测出来这个错误,导致给后面的作业留下了非常大的隐患。
第二次作业
第二次作业中我在强测和互测中也没有出现问题,但我的代码依然隐藏着之前的那个Bug。这次虽然进行了一定的分模块测试,但是还是太盲目自信了,导致没有测之前的模块,而我后面新增的代码也没有用的那个错误的部分,因此又让Bug逃走了一次。
第三次作业
这一次的作业就让我深刻体会到了拥有一个继承下来的bug是一件多么可怕的事情。我在构建图的时候用到了id对应path的Map,而这个Map本身是有问题的,因此他建出来的图本身也是有问题的。然而我却又一次躲过了中测,但是强测迎来了非常全面的爆炸。
这确实让我体会到了模块测试的重要性。因为在一个比较大的工程里面,一些不太容易看出来的错误可能在整体测试的时候很难暴露出来(比如我在强测wa的点也是800+行以后才暴露出来错误),然而却会对于整个工程产生巨大的影响。
五. 心得体会
这次我的对于自己的作业确实不是很满意,主要的心得体会分为两方面:一是对于模块测试重要性的体会,二是对于整体设计架构的体会。
其实在当时自己测试的时候,认为模块测试是一件非常费时费力的事情,而且还不一定能把错误给测出来。但最后结果出来之后,发现自己确实还是栽在了对于模块测试不够重视之上。经过这次的教训,我认为整个工程来看,模块测试和整体测试确实都发挥着非常重要的作用。模块测试可以发现在整理测试中不易察觉的问题,而整体测试则可以测试各模块之间相互配合时的问题,两者都是测试时必不可少的部分,都应该被给予同样的重视。
关于架构设计,这次的架构和之前几次作业比起来可以说是完全不能相比的。究其原因,感觉自己还是在写代码之前缺少了充分的思考,有些过分依赖于已经给了的结构,没有提炼出一些可以单独写的对象。在之后的作业中还是应该先对于架构设计进行充分的思考,而不是太急于代码的实现。
