Shiro是什么?
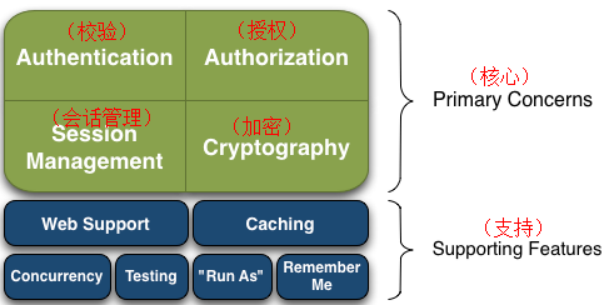
Shiro是一个非常强大的,易于使用的,开源的,权限框架。它包括了权限校验,权限授予,会话管理,安全加密等组件
什么时候使用它呢?
如果你是设计RBAC基础系统,需要编写大量用于权限控制的代码时,使用Shiro开源大大减少工作量。
使用到的包:
下载路径:
http://shiro.apache.org/download.html
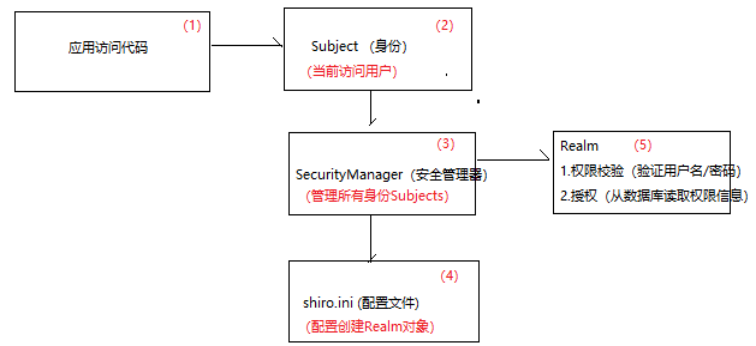
Shiro结构图:
入门配置:
1.配置流程图
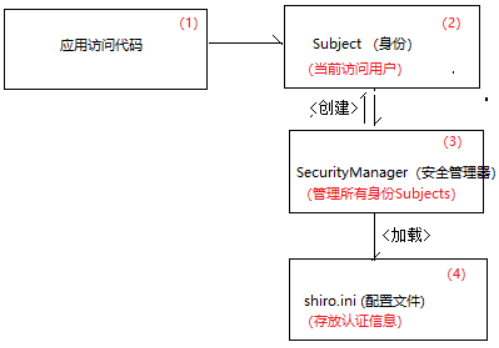
配置文件代码:
注意:配置文件的后缀一定要是 .ini
##[users] #用于配置用户名信息 ## 用户名= 密码, 角色1, 角色2, …, 角色N ##[roles] #用于配置角色信息 ## 角色名= 权限1, 权限2, …, 权限N #全部权限使用 * (星号) [users] admin=123456,role_admin,role_edu [roles] role_admin = user:list,user:create,user:edit,user:delete role_edu = edu:list,edu:create
测试代码:
package cn.gzsxt.shiro; import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken; import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory; import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject; public class ShiroTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //第一步:创建SecurityManager //shiro框架读取配置文件,如果在源码夹下,需要在前缀加上classpath IniSecurityManagerFactory imf=new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini"); SecurityManager securityManager = imf.createInstance(); //第二步:创建一个身份对象Subject SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); UsernamePasswordToken token =new UsernamePasswordToken("admin1","123456"); //第三步:校验参数 try { Subject resultSubject = securityManager.login(subject,token ); // System.out.println(resultSubject.getPrincipal()); // boolean hasRole = resultSubject.hasRole("role_admin"); // System.out.println(hasRole); boolean authenticated = resultSubject.isAuthenticated(); System.out.println(authenticated); } catch (AuthenticationException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Realm机制的必要性:
Shiro是通过Realm机制,实现将配置用户信息存放在数据库等储存系统中
通过Realm可以从数据库里面获得用户的验证信息
配置文件代码:
[main] #声明realm对象 myRealm=cn.gzsxt.realm.MyRealm #指定securityManager的realm对象 securityManager.realms=$myRealm
编写Realm
package cn.gzsxt.realm; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm; import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection; public class MyRealm extends AuthorizingRealm{ /** * 权限校验 */ @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("账号名:"+token.getPrincipal()); if ("admin".equals(token.getPrincipal())) { SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(token.getPrincipal(),"123",this.getName()); return info; } return null; } /** * 权限授权 */ @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection token) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } }
测试代码:
package cn.gzsxt.shiro; import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken; import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory; import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject; public class ShiroTest { public static void main(String[] args) { IniSecurityManagerFactory factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:Shiro.ini"); SecurityManager securityManager = factory.createInstance(); SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); AuthenticationToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("admin","123"); Subject resultSubject = securityManager.login(subject, token ); boolean authenticated = resultSubject.isAuthenticated(); System.out.println(authenticated); } }
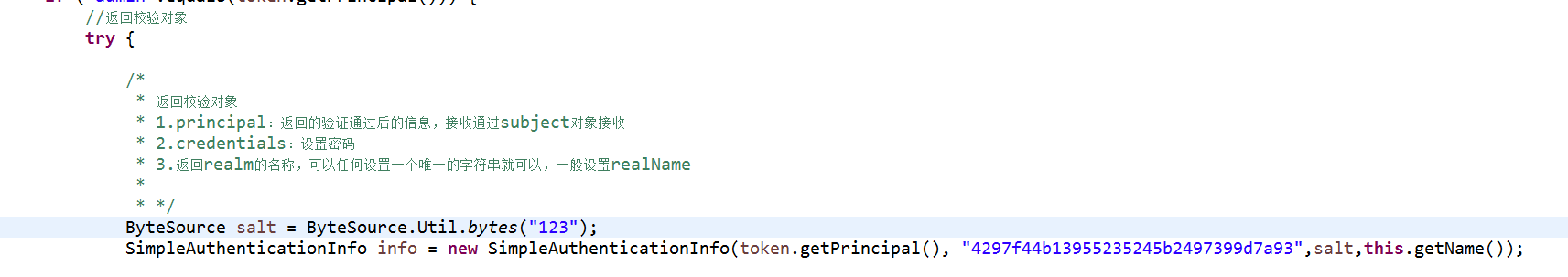
附:加密
先创建一个Md5帮助类,得到加密后的密码,便于测试
md5帮助类代码:
package cn.gzsxt.utils; import org.apache.shiro.crypto.hash.SimpleHash; import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource; public class Md5Util { public static void main(String[] args) { ByteSource salt = ByteSource.Util.bytes("123"); SimpleHash sh = new SimpleHash("md5", "123", salt,1); String target = sh.toString(); System.out.println(target); } }
Realm处代码