1.IO流概念
1.1流的概念
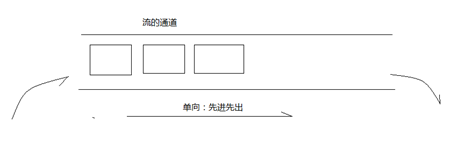
流(stream):流是一连串流动的数据(字节、字符),以先进先出的方式发送的信息的通道中。
1.2输入流和输出流
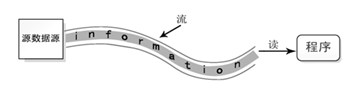
输入流:数据从源数据源流入程序的过程称为输入流,可以理解为从源数据源读取数据到程序的过程。
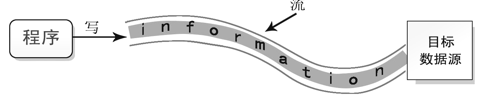
输出流:数据从程序流出到目的地的过程称为输出流,可以理解为把数据从程序写入目的地的过程。
1.3IO流的分类
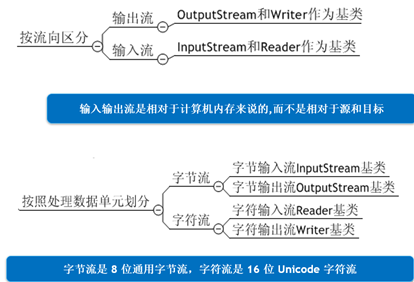
按照流向分为输入流和输出流
按照处理单元分为字节流和字符流
按照功能分为节点流和转换流。
2.InputStream类与OutputStream类
InputStream 是所有字节输入流的抽象父类,提供了read()方法读取一个字节,read(byte[] buf) 方法读取一定量的字节到缓冲区数组 buf中。
OutputStream 是所有字节输出流的抽象父类,提供了write() 方法写入一个字节,write(byte[] buf) 写入一定量的字节到输出流
FileInputStream 文件字节输入流,专门用于从文件中读取字节到程序内存中。
FileOutputStream 文件字节输出流,专门用于从内存中写入字节到文件中。
需求:从文件读取一个字节
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 // 需求:读取一个文件中的一个字节 4 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\a.txt"); 5 6 // 【1】创建管道 7 FileInputStream in = null; 8 9 try { 10 in = new FileInputStream(file); 11 12 // 【2】从管道读取一个字节 13 /* 14 int t; 15 t = in.read(); 16 t = in.read(); 17 t = in.read(); 18 t = in.read(); 19 */ 20 // System.out.println(t); 21 22 // 循环读取一个字节 23 int t; 24 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 25 while( (t=in.read()) != -1 ) { 26 sb.append((char)t); 27 } 28 29 System.out.println(sb.toString()); 30 31 32 33 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } catch(IOException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 39 // 【3】关闭流管道 40 try { 41 in.close(); 42 } catch (IOException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 }
需求:一次读取多个字节
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 // 需求:一次读取多个字节 4 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\a.txt"); 5 6 // 【1】创建管道 7 FileInputStream in = null; 8 9 try { 10 in = new FileInputStream(file); 11 12 // 【2】从管道读取多个字节到缓冲区 13 /* 14 byte[] buf = new byte[5]; 15 int len; 16 len = in.read(buf); 17 len = in.read(buf); 18 len = in.read(buf); 19 len = in.read(buf); 20 21 for(byte b:buf) { 22 System.out.print((char)b+"\t"); 23 } 24 System.out.println(len); 25 */ 26 27 // 通过循环读取文件 28 byte[] buf = new byte[5]; 29 int len; 30 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 31 while( (len=in.read(buf)) != -1 ) { 32 // 读取的内容是原始二进制流,需要根据编码的字符集解码成对于字符 33 String str = new String(buf,0,len); 34 sb.append(str); 35 } 36 System.out.println(sb.toString()); 37 38 39 40 41 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } catch(IOException e) { 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 47 // 【3】关闭流管道 48 try { 49 in.close(); 50 } catch (IOException e) { 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 } 53 }
需求:按照指定编码写入文件:
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 4 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\c.txt"); 5 6 FileOutputStream out = null; 7 8 try { 9 // 【1】创建输出流管道 10 out = new FileOutputStream(file); 11 12 // 【2】写入数据到管道中 13 // 一次写入一个字节 14 /* 15 out.write(97); 16 out.write(98); 17 out.write(99); 18 */ 19 20 // 一次写入多个字节 21 String str = "hello world"; 22 // gbk 23 /* 24 byte[] buf = str.getBytes(); 25 out.write(buf); 26 */ 27 28 byte[] buf = str.getBytes("UTF-8"); 29 out.write(buf); 30 31 System.out.println("写入完成!"); 32 33 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } catch (IOException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 39 // 【3】关闭流 40 try { 41 out.close(); 42 } catch (IOException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 }
需求:请把d:\\javatest\\logo.png 复制到工程目录中,并显示复制进度:
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException { 2 3 4 File oriFile = new File("d:\\javatest\\logo.jpg"); 5 File toFile = new File("logo.jpg"); 6 7 long totalLen = oriFile.length(); // 文件大小 8 long cpyedLen = 0; // 已复制完成的大小 9 float progress = 0.0f; 10 11 FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(oriFile); 12 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(toFile); 13 14 // 一次读取1kb 15 byte[] buf = new byte[512]; 16 int len; 17 while( (len=in.read(buf)) != -1) { 18 out.write(buf, 0, len); 19 cpyedLen += len; 20 progress = cpyedLen*1.0f/totalLen; 21 System.out.println(progress); 22 23 24 } 25 26 in.close(); 27 out.close(); 28 29 System.out.println("复制完成!"); 30 31 }
3.Reader类与Writer类
Reader 是字符输入流的抽象父类,提供了read ()方法一次读取一个字符;提供了read(char[] cbuf) 一次读取多个字符到字符缓冲区cbuf,返回长度表示读取的字符个数。
Writer 是字符输出流的抽象父类,提供了write()方法一次写入一个字符;提供了write(char[] cbuf)一次写入多个字符到字符缓冲区cbuf,返回长度表示读取的字符个数;提供了write(string)方法一次写入字符串。
FileReader 文件字符输入流,专门用于读取默认字符编码文本性文件。
FileWriter 文件字符输出流,专门用于写入默认字符编码的文本性文件。为了提高效率,FileWriter内部存在一个字节缓冲区,用于对待写入的字符进行统一编码到字节缓冲区,一定要在关闭流之前,调用flush方法刷新缓冲区。
需求:一次读取一个字符/多个字符到cbuf:
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\d.txt"); 4 5 FileReader reader = new FileReader(file); 6 7 // 【1】一次读取一个字符 8 /* 9 int c; 10 c = reader.read(); 11 c = reader.read(); 12 c = reader.read(); 13 c = reader.read(); 14 c = reader.read(); 15 System.out.println((char)c); 16 */ 17 18 // 【2】一次读取多个字符到cbuf中 19 /* 20 char[] cbuf = new char[2]; 21 int len; 22 len = reader.read(cbuf); 23 len = reader.read(cbuf); 24 len = reader.read(cbuf); 25 len = reader.read(cbuf); 26 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(cbuf)); 27 System.out.println(len); 28 */ 29 30 char[] cbuf = new char[2]; 31 int len; 32 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 33 while( (len=reader.read(cbuf)) != -1 ) { 34 sb.append(cbuf,0,len); 35 } 36 37 System.out.println(sb); 38 }
需求:写入字符到文件中:
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 4 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\f.txt"); 5 6 FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file); 7 8 // 【1】一次写入一个字符 9 /*writer.write('中'); 10 writer.write('国');*/ 11 12 // 【2】一次写入多个字符 13 /*char[] cbuf = {'h','e','l','l','o','中','国'}; 14 writer.write(cbuf);*/ 15 16 // 【3】一次写入一个字符串 17 String str = "hello你好"; 18 writer.write(str); 19 20 21 // 刷新字节缓冲区 22 writer.flush(); 23 24 // 关闭流通道 25 writer.close(); 26 27 System.out.println("写入完成"); 28 }
4.转换流
InputStreamReader 继承于Reader,是字节流通向字符流的桥梁,可以把字节流按照指定编码 解码 成字符流。
OutputStreamWriter 继承于Writer,是字符流通向字节流的桥梁,可以把字符流按照指定的编码 编码 成字节流。
转换流工作原理:
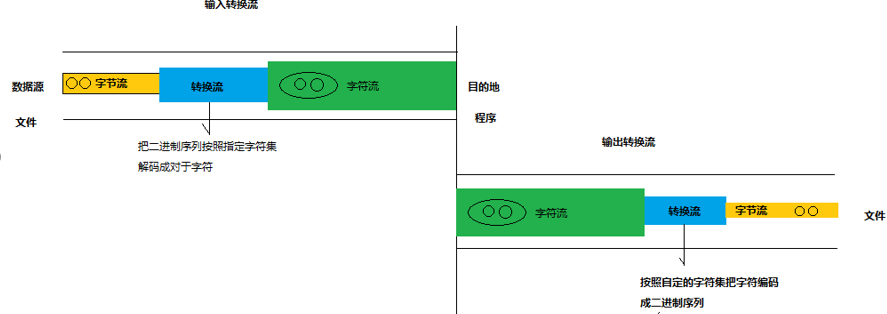
需求:写入utf8文件
1 /** 2 * 把一个字符串以utf8编码写入文件 3 */ 4 public class Test01 { 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 6 7 8 String str = "hello中国"; 9 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\g.txt"); 10 11 // 【1】创建管道 12 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file); 13 OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "utf8"); 14 15 // 【2】写入管道 16 writer.write(str); 17 18 // 【3】刷新缓冲区 19 writer.flush(); 20 21 // 【4】关闭管道 22 out.close(); 23 writer.close(); 24 25 System.out.println("写入完成"); 26 } 27 }
需求:读取utf8文件
1 /** 2 * 读取utf8编码的文本文件 3 */ 4 public class Test01 { 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 6 7 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\g.txt"); 8 9 // 【1】建立管道 10 FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file); 11 InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(in, "UTF-8"); 12 13 char[] cbuf = new char[2]; 14 int len; 15 16 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 17 while( (len=reader.read(cbuf))!=-1 ) { 18 sb.append(cbuf, 0, len); 19 } 20 System.out.println(sb.toString()); 21 22 } 23 }
5.BufferedReader类与BufferedWriter类
BufferedReader 继承于Reader,提供了read()方法,read(char[] cbuf)方法,和readLine() 方法用于读取一行文本,实现对文本的高效读取。BufferedReader 初始化时需要一个reader,本质上BufferedReader在reader的基础上增加readLine()的功能。BufferedWriter继承于Writer,提供了write()方法,write(char[] cbuf)方法,write(string),和newline() 写入一个行分隔符。
需求:读取一首诗:
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 // 按行读取gbk文本性文件 4 5 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\i.txt"); 6 7 // 【1】创建管道 8 FileReader reader = new FileReader(file); 9 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader); 10 11 // 【2】读取一行 12 /* 13 String line = br.readLine(); 14 line = br.readLine(); 15 line = br.readLine(); 16 line = br.readLine(); 17 */ 18 19 String line; 20 while( (line=br.readLine()) != null) { 21 System.out.println(line); 22 } 23 }
需求:以utf8编码高效写入文件
1 /** 2 * 以utf8写入一首诗 3 * @author Administrator 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Test02 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 8 9 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\j-utf8.txt"); 10 11 // 【1】创建utf8管道 12 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file); 13 OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "UTF-8"); 14 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(writer); 15 16 // 【2】写入一行 17 bw.write("窗前明月光,"); 18 bw.newLine(); 19 20 bw.write("疑似地上霜。"); 21 22 // for win 23 bw.write("\r\n"); 24 25 // for unix/linux/mac 26 // bw.write("\n"); 27 28 bw.write("举头望明月,"); 29 bw.newLine(); 30 31 // 【3】flush 32 bw.flush(); 33 34 // 【4】关闭管道 35 bw.close(); 36 writer.close(); 37 } 38 }