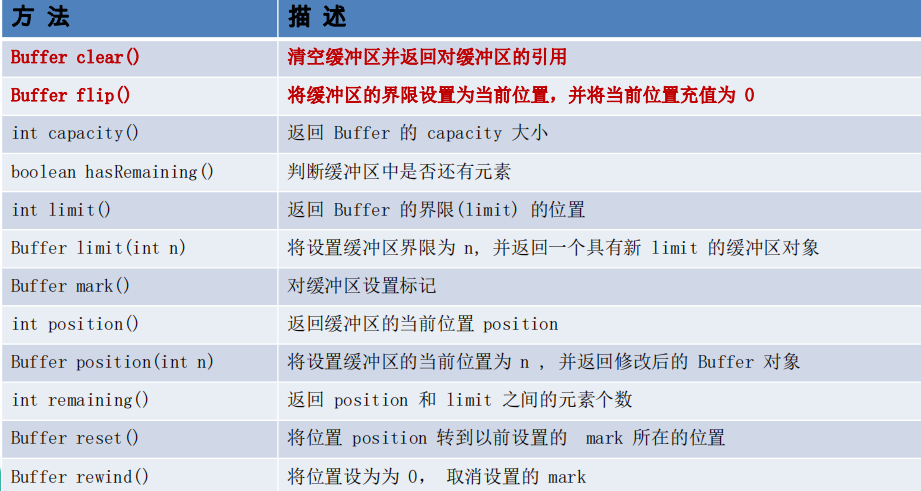
缓冲区(BUffer)
缓冲区(Buffer):一个用于特定基本数据类
型的容器。由 java.nio 包定义的,所有缓冲区
都是 Buffer 抽象类的子类。
Java NIO 中的 Buffer 主要用于与 NIO 通道进行
交互,数据是从通道读入缓冲区,从缓冲区写
入通道中的。
缓冲区:在NIO中负责数据的存取,说白了就是数组用于储存不同类型的数组
根据数据类型不同(boolean类型除外),提供了相应的类型的缓冲区
ByteBuffer
CharBuffer
ShortBuffer
IntBuffer
LongBuffer
FloatBuffer
DoubleBuffer
上述Buffer类他们都采用相拟的方法进行管理数据
只是各自管理的数据类不同而已
的都是通过同一个方法获取Buffer对象:
static XxxBuffer allocate(int capacity) : 创建一个容量为 capacity 的 XxxBuffer 对象
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
缓冲区存取数据的两个核心方法:
1、put():存入数据到缓冲区

2、get():获取缓冲区中的数据
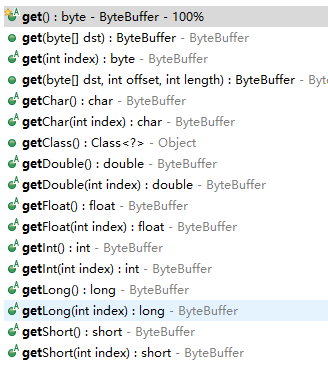
缓冲区中的四个核心属性
public abstract class java.nio.Buffer { // Field descriptor #20 I static final int SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS = 16464; // Field descriptor #20 I private int mark; // Field descriptor #20 I private int position; // Field descriptor #20 I private int limit; // Field descriptor #20 I private int capacity; ...
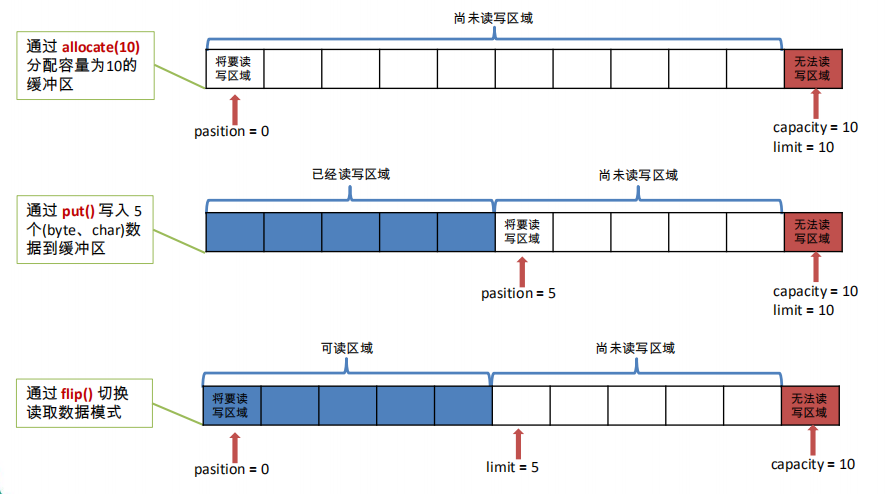
容量 (capacity) :表示 Buffer 最大数据容量,缓冲区容量不能为负,并且创
建后不能更改。
限制 (limit):第一个不应该读取或写入的数据的索引,即位于 limit 后的数据
不可读写。缓冲区的限制不能为负,并且不能大于其容量。
位置 (position):下一个要读取或写入的数据的索引。缓冲区的位置不能为
负,并且不能大于其限制
标记 (mark)与重置 (reset):标记是一个索引,通过 Buffer 中的 mark() 方法
指定 Buffer 中一个特定的 position,之后可以通过调用 reset() 方法恢复到这
个 position.
标记、位置、限制、容量遵守以下不变式: 0 <= mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
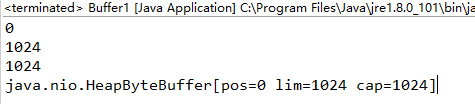
public static void main(String[] args) { //1、分配一个指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); System.out.println(buf.position());//0 System.out.println(buf.limit());//1024 System.out.println(buf.capacity());//1024 System.out.println(buf.mark());//java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=0 lim=1024 cap=1024] }
public static void main(String[] args) { //1、分配一个指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); System.out.println(buf.position());//0 System.out.println(buf.limit());//1024 System.out.println(buf.capacity());//1024 System.out.println(buf.mark());//java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=0 lim=1024 cap=1024] //2、利用put()方法进行存储数据 String str = "hello nio"; buf.put(str.getBytes()); System.out.println(buf.position());//9 System.out.println(buf.limit());//1024 System.out.println(buf.capacity());//1024 System.out.println(buf.mark());//java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=9 lim=1024 cap=1024] }

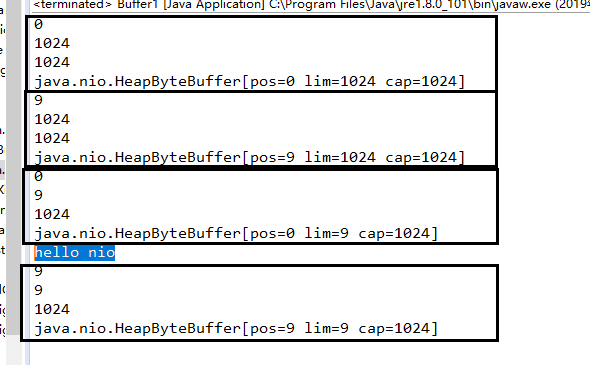
public static void main(String[] args) { //1、分配一个指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); System.out.println(buf.position());//0 System.out.println(buf.limit());//1024 System.out.println(buf.capacity());//1024 System.out.println(buf.mark());//java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=0 lim=1024 cap=1024] //2、利用put()方法进行存储数据 String str = "hello nio";//9字节 buf.put(str.getBytes()); System.out.println(buf.position());//9 System.out.println(buf.limit());//1024 System.out.println(buf.capacity());//1024 System.out.println(buf.mark());//java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=9 lim=1024 cap=1024] //3、切换读取数据的模式 buf.flip(); System.out.println(buf.position());//0 System.out.println(buf.limit());//9 System.out.println(buf.capacity());//1024 System.out.println(buf.mark());//java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=0 lim=9 cap=1024] //4、利用get()方法读取数据 byte dst [] = new byte[buf.limit()]; buf.get(dst); System.out.println(new String(dst,0,dst.length));//hello nio System.out.println(buf.position());//9 System.out.println(buf.limit());//9 System.out.println(buf.capacity());//1024 System.out.println(buf.mark());//java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=9 lim=9 cap=1024]
}
public static void main(String[] args) { //1、分配一个指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); System.out.println(buf.position());//0 System.out.println(buf.limit());//1024 System.out.println(buf.capacity());//1024 System.out.println(buf.mark());//java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=0 lim=1024 cap=1024] //2、利用put()方法进行存储数据 String str = "hello nio"; buf.put(str.getBytes()); System.out.println(buf.position());//9 System.out.println(buf.limit());//1024 System.out.println(buf.capacity());//1024 System.out.println(buf.mark());//java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=9 lim=1024 cap=1024] //3、切换读取数据的模式 buf.flip(); System.out.println(buf.position());//0 System.out.println(buf.limit());//9 System.out.println(buf.capacity());//1024 System.out.println(buf.mark());//java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=0 lim=9 cap=1024] //4、利用get()方法读取数据 byte dst [] = new byte[buf.limit()]; buf.get(dst); System.out.println(new String(dst,0,dst.length));//hello nio System.out.println(buf.position());//9 System.out.println(buf.limit());//9 System.out.println(buf.capacity());//1024 System.out.println(buf.mark());//java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=9 lim=9 cap=1024] //5、rewind()回到读模式(可重复读数据) buf.rewind(); System.out.println(buf.position());//0 System.out.println(buf.limit());//9 System.out.println(buf.capacity());//1024 System.out.println(buf.mark());//java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=0 lim=9 cap=1024] }
rewind():回到读模式(可重复读取数据)
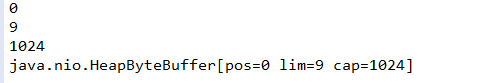
继上述代码继续添加代码:
//6、清空缓冲区 buf.clear(); System.out.println(buf.position());//0 System.out.println(buf.limit());//1024 System.out.println(buf.capacity());//1024 System.out.println(buf.mark());//java.nio.HeapByteBuffer[pos=0 lim=1024 cap=1024]
清空缓冲区之后将会回到初始化状态
缓冲区的数据依然存在,但是处于“被遗忘的数据”(位置界限等都变了)
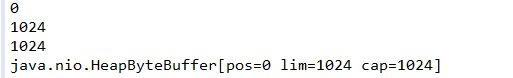
再次进行添加代码:
buf.get(dst); System.out.println(new String(dst,0,dst.length));//hello nio

关于标记和重置的使用
@Test public void test(){ ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); String str="abcde"; buf.put(str.getBytes()); //切换到读取数据模式 buf.flip(); //读取数据 byte dst [] = new byte[buf.limit()]; buf.get(dst,0,2); System.out.println("第一次打印操作"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(new String(dst,0,2)); //进行标记 buf.mark(); //再次进行读取数据 buf.get(dst,2,2); System.out.println("第二次打印操作"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(new String(dst,2,2)); //恢复到之前的位置 buf.reset(); System.out.println("恢复到第一次操作备份的位置"); System.out.println(buf.position()); }

再次添加新的代码:
//判断缓冲区是否还有剩余数据 if(buf.hasRemaining()){ //获取缓冲区可操作的数据的数量 System.out.println(buf.remaining()); }
此前有一个恢复到第一次操作数据的位置
所以此时可以操作的数据剩余量为3

图解缓冲区的基本属性(position、capacity、limit)
缓冲区常常使用的方法