1. 遇到的问题
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <chrono> #include <future> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; class Counter { public: void addCount() { m_count++; } int count() const { return m_count; } Counter() : m_count(0) { } private: int m_count; }; int work(int a) { return a + a; } template<class Iter> void realWork(Counter& c, double &totalValue, Iter b, Iter e) { for (; b != e; ++b) { totalValue += work(*b); c.addCount(); } } int main() { unsigned n = std::thread::hardware_concurrency(); cout << n << " concurrent threads are support.\n"; vector<int> vec; double totalValue = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { vec.push_back(rand() % 100); } Counter counter; realWork(counter, totalValue, vec.begin(), vec.end()); cout << "total times: " << counter.count() << " " << totalValue << endl; totalValue = 0; Counter counter2; auto iter = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3); auto iter2 = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3 * 2); thread b([&counter2, &totalValue, iter, iter2](){ realWork(counter2, totalValue, iter, iter2); }); auto end = vec.end(); thread c([&counter2, &totalValue, iter2, end](){ realWork(counter2, totalValue, iter2, end); }); realWork(counter2, totalValue, vec.begin(), iter); b.join(); c.join(); cout << "total times use multithread: " << counter2.count() << " " << totalValue << endl; return 0; }
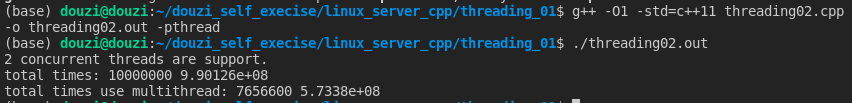
计算结果不一致!三个线程共享一份资源,有的加了有的没加。
2. 解决
2.1 法一:不共享变量
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <chrono> #include <future> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; class Counter { public: void addCount() { m_count++; } int count() const { return m_count; } Counter() : m_count(0) { } private: int m_count; }; int work(int a) { return a + a; } template<class Iter> void realWork(Counter& c, double &totalValue, Iter b, Iter e) { for (; b != e; ++b) { totalValue += work(*b); c.addCount(); } } int main() { unsigned n = std::thread::hardware_concurrency(); cout << n << " concurrent threads are support.\n"; vector<int> vec; double totalValue = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { vec.push_back(rand() % 100); } Counter counter; realWork(counter, totalValue, vec.begin(), vec.end()); cout << "total times: " << counter.count() << " " << totalValue << endl; totalValue = 0; Counter counter2; auto iter = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3); auto iter2 = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3 * 2); double totalC = 0; thread b([&counter2, &totalValue, iter, iter2](){ realWork(counter2, totalValue, iter, iter2); }); auto end = vec.end(); thread c([&counter2, &totalC, iter2, end](){ realWork(counter2, totalC, iter2, end); }); double totalD = 0; realWork(counter2, totalD, vec.begin(), iter); b.join(); c.join(); cout << "total times use multithread: " << counter2.count() << " " << totalValue+totalC+totalD << endl; return 0; }
