面向切面编程,有效的降低了代码之间的耦合性,易于维护;例如:我们习惯在代码中加上一些日志信息,在程序出错时方便快速查找找到问题,通常做法是在请求进入方法的时候打印日志,退出前打印日志,还有在出错时打印日志,那么问题就来了,每个方法中都需要打印日志,这些相同的部分就可以当做一个切面,通过配置切点来触发所需要的功能,比如,我需要在请求进入方法的时候打印,即可使用aop当中的前置通知来做到,这样就不需要每个方法中都去写一遍,配置好之后引用即可。
简单的记录一下spring aop的一个示例
基于两种配置方式:
1:基于xml配置
2:基于注解配置
这个例子是模拟对数据库的更改操作添加事物
其实并没有添加,只是简单的输出了一下记录
首先看下整个例子的目录图
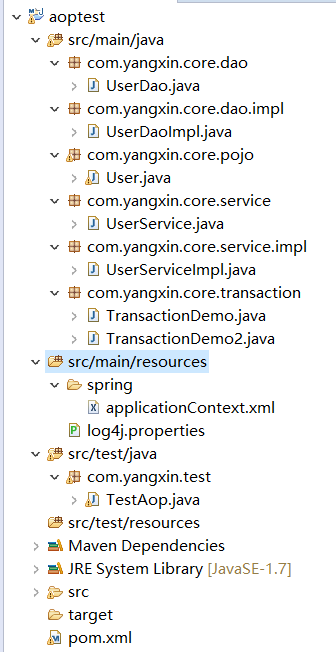
全部代码就不贴了,数目有点多,不过很简单,看一部分就能够明白
第一种配置方式
基于xml方式配置
首先将service,dao注册到spring容器
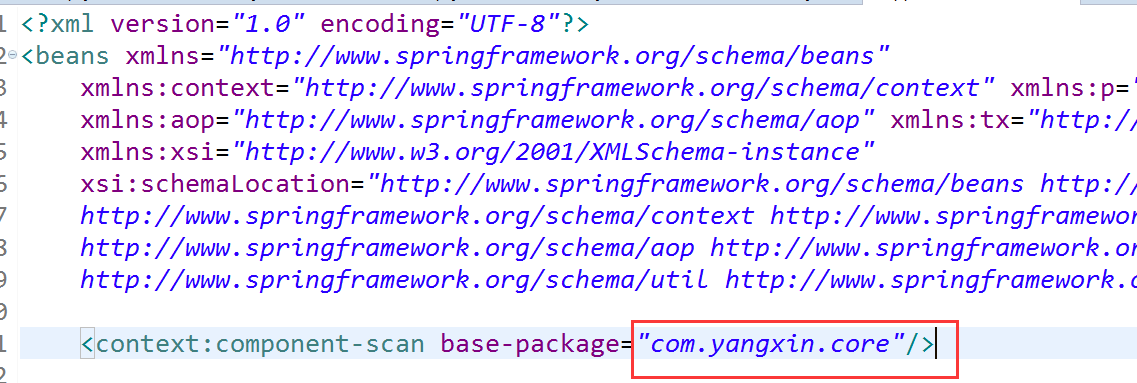
配置一下扫描包还是很方便的
接下来看下service
1 package com.yangxin.core.service.impl;
2
3 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
4 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
5
6 import com.yangxin.core.dao.UserDao;
7 import com.yangxin.core.pojo.User;
8 import com.yangxin.core.service.UserService;
9
10 @Service
11 public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
12
13 @Autowired
14 private UserDao userDao;
15
16 @Override
17 public void addUser(User user) {
18 userDao.insertUser(user);
19 System.out.println("添加成功");
20 }
21
22 @Override
23 public void deleteUser(String name) {
24 userDao.deteleUser(name);
25 System.out.println("删除成功");
26 }
27
28 }
要做的事情很简单,插入一条数据,删除一条数据
接下来看下切面代码
1 package com.yangxin.core.transaction;
2
3 import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
4
5 import com.yangxin.core.pojo.User;
6
7 public class TransactionDemo {
8
9 //前置通知
10 public void startTransaction(){
11 System.out.println("begin transaction ");
12 }
13
14 //后置通知
15 public void commitTransaction(){
16 System.out.println("commit transaction ");
17 }
18
19 //环绕通知
20 public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
21 System.out.println("begin transaction");
22 //调用process()方法才会真正的执行实际被代理的方法
23 joinPoint.proceed();
24
25 System.out.println("commit transaction");
26 }
27
28 }
然后看下这个切面在applicationContext.xml中是如何配置的
![]()
1 <aop:config> 2 <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.yangxin.core.service.*.*.*(..))" id="p1" /> 3 4 <aop:aspect ref = "transactionDemo"> 5 6 <aop:before method="startTransaction" pointcut-ref="p1" /> 7 8 <aop:after-returning method="commitTransaction" pointcut-ref="p1"/> 9 10 </aop:aspect> 11 </aop:config>
这里没有演示环绕通知
好了,运行测试代码
测试代码如下
1 @Test
2 public void test1(){
3 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring/applicationContext.xml");
4
5 UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(UserService.class);
6
7 User user = new User();
8
9 user.setAge(19);
10 user.setName("yangxin");
11
12 userService.addUser(user);
13 userService.deteleUser("yangxin");
1415
16 }
控制台输出如下
begin transaction
添加成功
commit transaction
begin transaction
删除成功
commit transaction
现在来测试一下环绕通知
修改一下applicationContext.xml中的配置切面那一部分
修改后的代码
1 <aop:config> 2 <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.yangxin.core.service.*.*.*(..))" id="p1" /> 3 4 <aop:aspect ref = "transactionDemo"> 5 6 <aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="p1"/> 7 8 </aop:aspect> 9 </aop:config>
运行测试代码
输出如下
begin transaction
添加成功
commit transaction
begin transaction
删除成功
commit transaction
好了,现在贴下如何用注解的方法
贴下基于注解的切面的代码
1 package com.yangxin.core.transaction;
2
3 import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
4 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
5 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
6 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
7 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
8 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
9
10 @Aspect
11 public class TransactionDemo2 {
12
13 @Pointcut(value="execution(* com.yangxin.core.service.*.*.*(..))")
14 public void point(){
15
16 }
17
18 @Before(value="point()")
19 public void before(){
20 System.out.println("transaction begin");
21 }
22
23 @AfterReturning(value = "point()")
24 public void after(){
25 System.out.println("transaction commit");
26 }
27
28 @Around("point()")
29 public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
30 System.out.println("transaction begin");
31 joinPoint.proceed();
32 System.out.println("transaction commit");
33
34 }
35 }
在applicationContext.xml中配置
1 <bean id = "transactionDemo2" class = "com.yangxin.core.transaction.TransactionDemo2" />
1 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
测试步骤和以上一致,这里就不贴了
结合例子我们来看看这些核心的概念:
2.1、切面(Aspect):是一个类,里面定义了通知与切点。
2.2、切点(PointCut):表达式。就是告诉程序要在执行哪些核心业务的时候,执行非核心的业务。
2.3、通知(advice):五种通知方式:
-
@Before:前置通知,在调用目标方法之前执行通知定义的任务@After:后置通知,在目标方法执行结束后,无论执行结果如何都执行通知定义的任务@After-returning:后置通知,在目标方法执行结束后,如果执行成功,则执行通知定义的任务@After-throwing:异常通知,如果目标方法执行过程中抛出异常,则执行通知定义的任务@Around:环绕通知,在目标方法执行前和执行后,都需要执行通知定义的任务。
