JavaIO流概述
Java中对文件内容的操作需要使用IO流,I : Input 输入,O Output 输出 流: 数据的传输。
IO流的分类
按照数据流的传输方向:分为 输入流,和输出流
Tips:此处的输入输出都是以程序作为参照物的,文件数据读入程序即为输入,程序数据写入内存即为输出。
按照数据流的传输单位: 分为 字节流,字符流
字节流:按照单个字节进行读写,即8个bit。
字符流:按照Unicode字符进行读写该字符集可以描述任意字符,每个字符占2个字节即16个bit位。
不论任何文件,在磁盘中都是将字符转换称为字节,然后将该字节文件存放在磁盘中。虽然单位不同,但传输原理是相同的,而且这两种流可以相互转换。对于纯文本文件,优先使用字符流。其它文件如视频,图片等使用字节流。
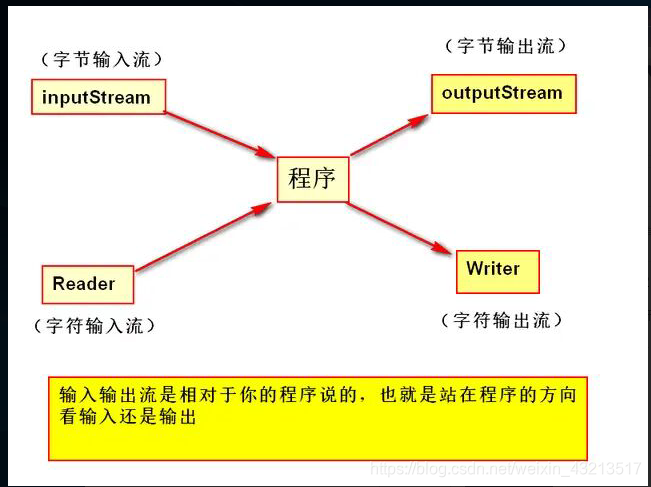
与IO流有关的主要有四个类:
- public abstract class OutputStream implements Closeable, Flushable
- public abstract class InputStream implements Closeable, Flushable
- public abstract class Writer implements Appendable, Closeable, Flushable
- public abstract class Reader implements Appendable, Closeable, Flushable
可以看出这四个类都是抽象类,不能直接实例化对象,因此我们操作的是它们的实现类。
Closeable接口中的close方法用于关闭流,和释放资源(IO操作属于资源处理,资源处理完毕都需要关闭),其中Closeable接口继承了AutoCloseable(自动关闭接口),因此可以借助try--catch实现自动关闭。 Flushable接口中的flush方法用于刷新缓冲区,将缓冲区的内容读入或者写出。
与文件读写有关的Filexxx系列类
FileOutputStream(数据按字节写入文件)
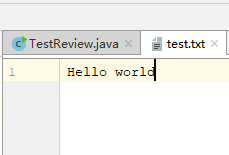
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "test.txt"; // 相对路径
File file = new File(path);
try(OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file)){ // JDK1.7提供的自动关闭
out.write("Hello world".getBytes());
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}运行结果:
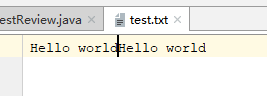
其中该构造方法有一个重载方法,即每次在文件内容后进行追加。只需在后面加一个true即可,不加默认是false。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "test.txt"; // 相对路径
File file = new File(path);
try(OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file,true)){ // JDK1.7提供的自动关闭
out.write("Hello world".getBytes());
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}运行结果:两个helloworld
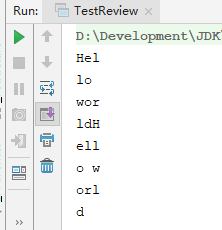
FileInputStream(文件数据按字节读入程序中)
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "test.txt"; // 相对路径
File file = new File(path);
try(InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file)){ // JDK1.7提供的自动关闭
byte[] buff = new byte[3];
int len = -1;
while((len = in.read(buff)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(buff,0,len));
}
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}运行结果:(每三个一组)
其中在对文件进行写入的时候,文件可以不存在,会自动创建,但不会创建目录(文件路径是绝对路径),但对文件进行读入的时候需要确保文件存在。
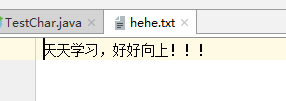
FileWriter(数据按字符写入文件)
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "hehe.txt";
try(Writer out = new FileWriter(path)){
out.write("天天学习,好好向上!!!");
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}运行结果:
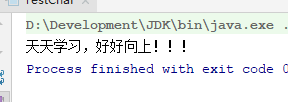
FileReader(文件数据按字符读入程序中)
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "hehe.txt";
try(Reader in = new FileReader(path)){
char[] buff = new char[3];
int len = -1;
while((len = in.read(buff)) != -1){
System.out.print(new String (buff));
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}运行结果:
转换流
OutputStreamWriter(字节输出流----> 字符输出流)
该类定义:public class OutputStreamWriter extends Writer
该类继承了Writer,在构造方法中,传一个OutputStream类型的对象,底层会调用Writer类的构造方法,生成一个Writer类对象,因此会实现转换。
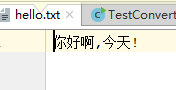
public class TestConvertStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("hello.txt");
try(OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(file);
Writer out = new OutputStreamWriter(output)){ // 字节流转换为字符流
out.write("你好啊,今天!");
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
InputStreamReader(字节输入流----> 字符输入流)
类定义:
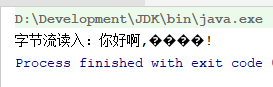
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("hello.txt");
try(InputStream input = new FileInputStream(file);
Reader in = new InputStreamReader(input)){ // 字节流转换为字符流
int len = -1;
char[] buff1 = new char[3];
System.out.print("字符流读入:");
while((len = in.read(buff1)) != -1){
System.out.print(new String(buff1,0,len));
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
用字节流读入则会出现乱码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("hello.txt");
try(InputStream input = new FileInputStream(file);
Reader in = new InputStreamReader(input)){ // 字节流转换为字符流
int len = -1;
byte[] buff2 = new byte[3];
System.out.print("字节流读入:");
while((len = input.read(buff2))!= -1){
System.out.print( new String(buff2,0,len));
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}运行结果:
内存流
内存流的操作发生在内存中,将文件的数据读入内存中,处理完毕写回源文件。
字节内存流ByteArrayOutputStream / ByteArrayInputStream
字符内存流CharArrayWriter / CharArrayReader
通过内存流实现文件的合并:
public class TestMemoryStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file1 = new File("hell.txt");
File file2 = new File("hello.txt");
String str1 = read(file1);
String str2 = read(file2);
System.out.println(str1 + str2);
}
public static String read(File file){
try(InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();){
byte[] buff = new byte[3];
int len = -1;
while((len = in.read(buff)) != -1){
// 将文件内容读进来,存入内存中。
bos.write(buff,0,len);
}
return new String(bos.toByteArray());
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}打印流
因为OutputStream只能输出字节类型,如果要输出,基本类型如int,double等就很不方便。
自定义一个打印流
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* @auther plg
* @date 2019/4/20 10:26
*/
public class TestPrintStream {
private OutputStream out;
public TestPrintStream(OutputStream out){
this.out = out;
}
// 核心方法,任何类型都可以转换为String类型,都可以借助该方法输出
public void print(String str){
try {
this.out.write(str.getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void printInt(int data){
this.print(String.valueOf(data));
}
public void printInt(double data){
this.print(String.valueOf(data));
}
// .......
}打印流属于装饰设计模式,核心依然是某个功能,但针对此功能进行了很多扩展。
字节打印流 public class PrintStream extends FilterOutputStream
使用练习:
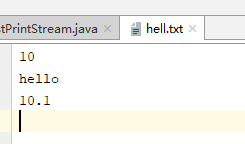
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintStream out = new PrintStream(new File("hell.txt"));
out.println(10);
out.println("hello");
out.println("10.1");
}运行结果:
字符打印流 public class PrintWriter extends Writer
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File("hell.txt"));
out.print("Java");
out.print("C++");
out.print("编程语言");
out.flush(); // 需要刷新缓冲区,负责出不来
}运行结果:

缓冲流
缓冲流和其它的输入输出流本质没有什么不同,只是该流在读取数据的时候提供一个缓冲区,减少与外部设备之间的IO次数,提高效率。