版权声明:内容记录学习过成文章,仅供参考 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40195958/article/details/84100586
直接缓冲区
// 直接缓冲区,可以根据文件在通道的大小进行读写
@Test
public void test001() throws IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 创建读写管道
FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("F://1.mp4"),
StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("F://2.mp4"),
StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.WRITE,
StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
// 定义映射文件
MappedByteBuffer inMapBatys = inChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0,
inChannel.size());
MappedByteBuffer outMapBatys = outChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0,
inChannel.size());
// 创建缓冲区,大小为读通道大小
byte[] bytes = new byte[inMapBatys.limit()];
inMapBatys.get(bytes);
outMapBatys.put(bytes);
inChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
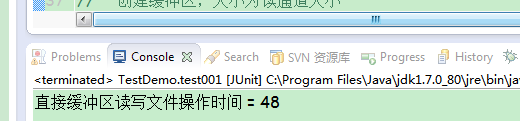
System.out.println("直接缓冲区读写文件操作时间 = " + (endTime - startTime));
}
非直接缓冲区】
// 非直接缓冲区操作
@Test
public void test002() throws IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 创建文件读写流
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("F://1.mp4");
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("F://2.mp4");
// 创建通道
FileChannel inChannel = in.getChannel();
FileChannel outChannel = out.getChannel();
// 创建缓冲区大小,通过通道来读取数据
// 缓冲区大小可以放大,增加缓冲区大小可以提高速度
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (inChannel.read(buffer) != -1) {
// 缓冲区 开启度模式
buffer.flip();
// 将读取的数据写入到通道中
outChannel.write(buffer);
// 每次写完清单缓冲区,否则会造成无限循环
buffer.clear();
}
// 读写结束后,关闭通道
in.close();
out.close();
inChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
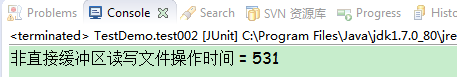
System.out.println("非直接缓冲区读写文件操作时间 = " + (endTime - startTime));
}
结果对比
 、
、
对比结果,直接操作缓冲区进行读写操作,速度提高了很多,
这里直接缓冲区,相当于读取了当前文件的大小,非直接缓冲区可以设置缓冲数据大小来提高读写速度
分散读取,聚集写入
// 分散读取,聚集写入
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 随机访问
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("test1.txt", "rw");
// 获得通道
FileChannel channel1 = raf.getChannel();
// 创建分配缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
ByteBuffer[] bytes = {buffer1,buffer2};
// 数据读取到通道
channel1.read(bytes);
for (ByteBuffer byteBuffer : bytes) {
byteBuffer.flip();
}
System.out.println(new String(bytes[0].array(),"GBK"));
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
System.out.println(new String(bytes[1].array(),"GBK"));
RandomAccessFile raf2 = new RandomAccessFile("test2.txt", "rw");
FileChannel channel2 = raf2.getChannel();
channel2.write(bytes);
raf.close();
raf2.close();
}
```