一.lucene原理
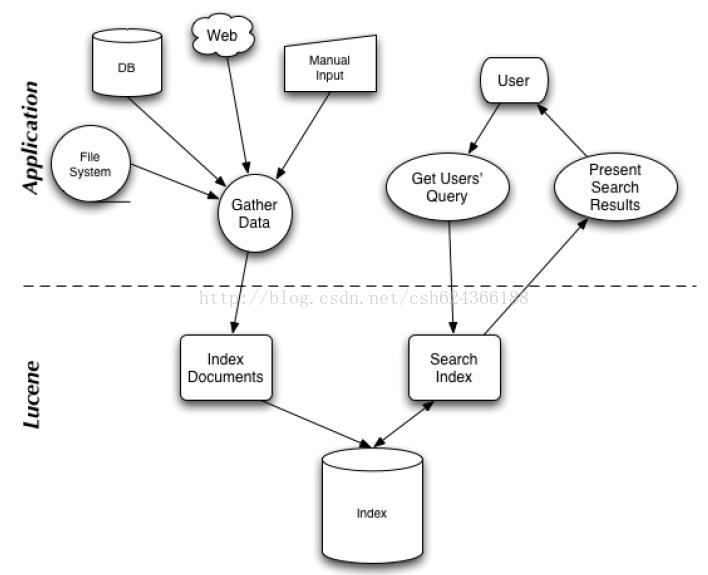
Lucene 是apache软件基金会一个开放源代码的全文检索引擎工具包,是一个全文检索引擎的架构,提供了完整的查询引擎和索引引擎,部分文本分析引擎。它不是一个完整的搜索应用程序,而是为你的应用程序提供索引和搜索功能。lucene 能够为文本类型的数据建立索引,所以你只要能把你要索引的数据格式转化的文本的,Lucene 就能对你的文档进行索引和搜索。比如你要对一些 HTML 文档,PDF 文档进行索引的话你就首先需要把 HTML 文档和 PDF 文档转化成文本格式的,然后将转化后的内容交给 Lucene 进行索引,然后把创建好的索引文件保存到磁盘或者内存中,最后根据用户输入的查询条件在索引文件上进行查询。
搜索应用程序和 Lucene 之间的关系,也反映了利用 Lucene 构建搜索应用程序的流程:
二. 索引和搜索
索引是现代搜索引擎的核心,建立索引的过程就是把源数据处理成非常方便查询的索引文件的过程。为什么索引这么重要呢,试想你现在要在大量的文档中搜索含有某个关键词的文档,那么如果不建立索引的话你就需要把这些文档顺序的读入内存,然后检查这个文章中是不是含有要查找的关键词,这样的话就会耗费非常多的时间,想想搜索引擎可是在毫秒级的时间内查找出要搜索的结果的。这就是由于建立了索引的原因,你可以把索引想象成这样一种数据结构,他能够使你快速的随机访问存储在索引中的关键词,进而找到该关键词所关联的文档。Lucene 采用的是一种称为反向索引(inverted index)的机制。反向索引就是说我们维护了一个词 / 短语表,对于这个表中的每个词 / 短语,都有一个链表描述了有哪些文档包含了这个词 / 短语。这样在用户输入查询条件的时候,就能非常快的得到搜索结果。搜索引擎首先会对搜索的关键词进行解析,然后再在建立好的索引上面进行查找,最终返回和用户输入的关键词相关联的文档。对于中文用户来说,最关心的问题是其是否支持中文的全文检索。由于Lucene良好架构设计,对中文的支持只需对其语言词法分析接口进行扩展就能实现对中文检索的支持。
三. 索引步骤
- 获取内容: Lucene本身没有提供获取内容的工具或者组件,内容是要开发者自己提供相应的程序。这一步包括使用网络爬虫或蜘蛛程序来搜索和界定需要索引的内容。当然,数据来源可能包括数据库、分布式文件系统、本地xml等等。lucene作为一款核心搜索库,不提供任何功能来实现内容获取。目前有大量的开源爬虫软件可以实现这个功能,例如:Solr,lucene的子项;Nutch,apache项目,包含大规模的爬虫工具,抓取和分辨web站点数据;Grub,比较流行的开源web爬虫工具;Heritrix,一款开源的Internet文档搜索程序;Aperture,支持从web站点、文件系统和邮箱中抓取,并解析和索引其中的文本数据。
- 建立文档:获取原始内容后,需要对这些内容进行索引,必须将这些内容转换成部件(文档)。文档主要包括几个带值的域,比如标题,正文,摘要,作者和链接。如果文档和域比较重要的话,还可以添加权值。设计完方案后,需要将原始内容中的文本提取出来写入各个文档,这一步可以使用文档过滤器,开源项目如Tika,实现很好的文档过滤。如果要获取的原始内容存储于数据库中,有一些项目通过无缝链接内容获取步骤和文档建立步骤就能轻易地对数据库表进行航所以操作和搜索操作,例如DBSight,Hibernate Search,LuSQL,Compass和Oracle/Lucene集成项目。
- 文档分析: 搜索引擎不能直接对文本进行索引:必须将文本分割成一系列被称为语汇单元的独立的原子元素。每一个语汇单元能大致与语言中的“单词”对应起来,这个步骤决定文档中的文本域如何分割成语汇单元系列。lucene提供了大量内嵌的分析器可以轻松控制这步操作。
- 文档索引: 将文档加入到索引列表中。Lucene在这一步骤中提供了强档的API,只需简单调用提供的几个方法就可以实现出文档索引的建立。为了提供好的用户体验,索引是必须要处理好的一环:在设计和定制索引程序时必须围绕如何提高用户的搜索体验来进行。
四. 搜索组件
搜索组件即为输入搜索短语,然后进行分词,然从索引中查找单词,从而找到包含该单词的文档。搜索质量由查准率和查全率来衡量。搜索组件主要包括以下内容:
- 用户搜索界面:主要是和用户进行交互的页面,也就是呈现在浏览器中能看到的东西,这里主要考虑的就是页面UI设计了。一个良好的UI设计是吸引用户的重要组成部分。
- 建立查询:建立查询主要是指用户输入所要查询的短语,以普通HTML表单或者ajax的方式提交到后台服务器端。然后把词语传递给后台搜索引擎。这就是一个简单建立查询的过程。
- 搜索查询:即为查询检索索引然后返回与查询词语匹配的文档。然后把返回来的结构按照查询请求来排序。搜索查询组件覆盖了搜索引擎中大部分的复杂内容。
- 展现结果:所谓展现结果,和第一个搜索界面类似。都是一个与用户交互的前端展示页面,作为一个搜索引擎,用户体验永远是第一位。其中前端展示在用户体现上占据了重要地位。
五. 官网实例解析
Lucene的使用主要体现在两个步骤:
- 创建索引,通过IndexWriter对不同的文件进行索引的创建,并将其保存在索引相关文件存储的位置中。
- 通过索引查寻关键字相关文档。
下面针对官网上面给出的一个例子,进行分析:
-
Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT);
-
-
// Store the index in memory:
-
Directory directory = new RAMDirectory();
-
// To store an index on disk, use this instead:
-
//Directory directory = FSDirectory.open("/tmp/testindex");
-
IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, analyzer);
-
IndexWriter iwriter = new IndexWriter(directory, config);
-
Document doc = new Document();
-
String text = "This is the text to be indexed.";
-
doc.add( new Field("fieldname", text, TextField.TYPE_STORED));
-
iwriter.addDocument(doc);
-
iwriter.close();
-
-
// Now search the index:
-
DirectoryReader ireader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
-
IndexSearcher isearcher = new IndexSearcher(ireader);
-
// Parse a simple query that searches for "text":
-
QueryParser parser = new QueryParser(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, "fieldname", analyzer);
-
Query query = parser.parse( "text");
-
ScoreDoc[] hits = isearcher.search(query, null, 1000).scoreDocs;
-
assertEquals( 1, hits.length);
-
// Iterate through the results:
-
for (int i = 0; i < hits.length; i++) {
-
Document hitDoc = isearcher.doc(hits[i].doc);
-
assertEquals( "This is the text to be indexed.", hitDoc.get("fieldname"));
-
}
-
ireader.close();
-
directory.close();
索引的创建
首先,我们需要定义一个词法分析器。
比如一句话,“我爱我们的中国!”,如何对他拆分,扣掉停顿词“的”,提取关键字“我”“我们”“中国”等等。这就要借助的词法分析器Analyzer来实现。这里面使用的是标准的词法分析器,如果专门针对汉语,还可以搭配paoding,进行使用。
1 Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT);
参数中的Version.LUCENE_CURRENT,代表使用当前的Lucene版本,本文环境中也可以写成Version.LUCENE_40。
第二步,确定索引文件存储的位置,Lucene提供给我们两种方式:
1 本地文件存储
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open("/tmp/testindex");
2 内存存储
Directory directory = new RAMDirectory();
可以根据自己的需要进行设定。
第三步,创建IndexWriter,进行索引文件的写入。
IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, analyzer); IndexWriter iwriter = new IndexWriter(directory, config);
这里的IndexWriterConfig,据官方文档介绍,是对indexWriter的配置,其中包含了两个参数,第一个是目前的版本,第二个是词法分析器Analyzer。
第四步,内容提取,进行索引的存储。
Document doc = new Document();
String text = "This is the text to be indexed.";
doc.add(new Field("fieldname", text, TextField.TYPE_STORED));
iwriter.addDocument(doc);
iwriter.close();
第一行,申请了一个document对象,这个类似于数据库中的表中的一行。
第二行,是我们即将索引的字符串。
第三行,把字符串存储起来(因为设置了TextField.TYPE_STORED,如果不想存储,可以使用其他参数,详情参考官方文档),并存储“表明”为"fieldname".
第四行,把doc对象加入到索引创建中。
第五行,关闭IndexWriter,提交创建内容。
这就是索引创建的过程。
关键字查询:
第一步,打开存储位置
DirectoryReader ireader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
第二步,创建搜索器
IndexSearcher isearcher = new IndexSearcher(ireader);
第三步,类似SQL,进行关键字查询
QueryParser parser = new QueryParser(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, "fieldname", analyzer);
Query query = parser.parse("text");
ScoreDoc[] hits = isearcher.search(query, null, 1000).scoreDocs;
assertEquals(1, hits.length);
for (int i = 0; i < hits.length; i++) {
Document hitDoc = isearcher.doc(hits[i].doc);
assertEquals("This is the text to be indexed.",hitDoc.get("fieldname"));
}
这里,我们创建了一个查询器,并设置其词法分析器,以及查询的“表名“为”fieldname“。查询结果会返回一个集合,类似SQL的ResultSet,我们可以提取其中存储的内容。
关于各种不同的查询方式,可以参考官方手册,或者推荐的PPT
第四步,关闭查询器等。
ireader.close(); directory.close();
自己实现的一个小实例:对一个文件夹内的内容进行索引的创建,并根据关键字筛选文件,并读取其中的内容。
-
package cn.lnu.edu.yxk;
-
import java.io.BufferedReader;
-
import java.io.File;
-
import java.io.FileInputStream;
-
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
-
import java.io.FileReader;
-
import java.io.IOException;
-
import java.util.ArrayList;
-
import java.util.Date;
-
import java.util.List;
-
-
import jxl.Cell;
-
import jxl.Sheet;
-
import jxl.Workbook;
-
import jxl.read.biff.BiffException;
-
-
import org.apache.lucene.analysis.Analyzer;
-
import org.apache.lucene.analysis.standard.StandardAnalyzer;
-
import org.apache.lucene.document.Document;
-
import org.apache.lucene.document.Field;
-
import org.apache.lucene.index.DirectoryReader;
-
import org.apache.lucene.index.IndexWriter;
-
import org.apache.lucene.index.IndexWriterConfig;
-
import org.apache.lucene.queryparser.classic.ParseException;
-
import org.apache.lucene.queryparser.classic.QueryParser;
-
import org.apache.lucene.search.IndexSearcher;
-
import org.apache.lucene.search.Query;
-
import org.apache.lucene.search.ScoreDoc;
-
import org.apache.lucene.store.Directory;
-
import org.apache.lucene.store.FSDirectory;
-
import org.apache.poi.hwpf.HWPFDocument;
-
import org.apache.poi.hwpf.usermodel.Range;
-
/**
-
* 对一个文件夹内的内容进行索引的创建,并根据关键字筛选文件,读取其中的内容。
-
* @author yxk
-
*
-
*/
-
public class IndexManager {
-
-
private static String content = "";//文件里面的内容
-
private static String INDEX_DIR = "D:\\test\\luceneIndex";//索引创建的存储目录
-
private static String DATA_DIR = "D:\\test\\luceneData";//文件夹的目录
-
-
private static Analyzer analyzer = null;//词法分析器
-
private static Directory directory = null;//索引文件存储的位置
-
private static IndexWriter indexWriter = null;//创建索引器,索引文件的写入
-
-
/**
-
* 创建当前文件目录的索引
-
* @param path当前目录的文件
-
* @return 返回是否创建成功
-
*/
-
public static Boolean createIndex(String path) {
-
Date date1 = new Date();//创建需要的时间
-
-
List<File> files = listFile(path); // 获取指定目录下得所有符合条件的文件
-
-
// 获取文件的内容
-
for (File file : files) {
-
content = "";
-
//通过文件类型获取文件的内容
-
String type = file.getName().substring(
-
file.getName().lastIndexOf( ".") + 1);
-
-
if ("txt".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
-
content += txt2String(file);
-
} else if ("doc".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
-
content += doc2String(file);
-
} else if ("xls".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
-
content += xls2String(file);
-
}
-
-
System.out.println( "name"+file.getName());
-
System.out.println( "path"+file.getPath());
-
//System.out.println(file.getName().getBytes().toString());
-
System.out.println();
-
-
try {
-
analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer();//词法分析器
-
-
directory = FSDirectory.open( new File(INDEX_DIR).toPath());//索引创建存储的位置
-
// System.out.println("ssss"
-
// + new File(INDEX_DIR).toPath().toString());
-
-
//自动创建索引目录
-
File indexFile = new File(INDEX_DIR);
-
if (!indexFile.exists()) {
-
indexFile.mkdirs();
-
}
-
-
//索引文件的写入
-
IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
-
indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory, config);
-
-
/*
-
* 内容提取,进行索引的存储
-
*/
-
//申请了一个document对象,这个类似于数据库中的表中的一行。
-
Document document = new Document();
-
-
//把字符串存储起来(因为设置了TextField.TYPE_STORED,如果不想存储,可以使用其他参数,详情参考官方文档),并存储“表明”为"fieldname".
-
document.add( new org.apache.lucene.document.TextField(
-
"filename", file.getName(), Field.Store.YES));//文件名索引创建
-
document.add( new org.apache.lucene.document.TextField(
-
"content", content, Field.Store.YES));//文件内容索引创建
-
document.add( new org.apache.lucene.document.TextField("path",
-
file.getPath(), Field.Store.YES)); //文件路径索引的创建
-
-
//把document对象加入到索引创建中
-
indexWriter.addDocument(document);
-
-
//关闭IndexWriter,提交创建内容。
-
indexWriter.commit();
-
closeWriter();
-
-
} catch (IOException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
content = "";
-
}
-
Date date2 = new Date();
-
System.out.println( "创建索引-----耗时:" + (date2.getTime() - date1.getTime())
-
+ "ms\n");
-
return true;
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 查询索引,返回符合条件的文件
-
*
-
* @param 查询的字符串
-
* @return 符合条件的结果
-
* @throws IOException
-
*/
-
public static void serarchIndex(String text) {
-
Date date1 = new Date();
-
try {
-
//打开存储位置
-
directory = FSDirectory.open( new File(INDEX_DIR).toPath());
-
analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer();
-
DirectoryReader ireader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
-
-
//创建搜索器
-
IndexSearcher isearcher = new IndexSearcher(ireader);
-
-
/*
-
* 类似SQL,进行关键字查询
-
*/
-
QueryParser parser = new QueryParser("content", analyzer);
-
Query query = parser.parse(text);
-
//创建了一个查询器,并设置其词法分析器,以及查询的“表名“为”fieldname“。查询结果会返回一个集合,类似SQL的ResultSet,我们可以提取其中存储的内容。
-
ScoreDoc[] hits = isearcher.search(query, 1000).scoreDocs;
-
-
for (int i = 0; i < hits.length; i++) {
-
Document hitDoc = isearcher.doc(hits[i].doc);
-
System.out.println( "-----------");
-
System.out.println(hitDoc.get( "filename"));
-
System.out.println(hitDoc.get( "content"));
-
System.out.println(hitDoc.get( "path"));
-
System.out.println( "------------");
-
}
-
-
//关闭查询器
-
ireader.close();
-
directory.close();
-
-
} catch (IOException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
} catch (ParseException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
Date date2 = new Date();
-
System.out.println( "关键字查询-----耗时:" + (date2.getTime() - date1.getTime())
-
+ "ms\n");
-
}
-
-
/**
-
*
-
* @throws IOException
-
*/
-
private static void closeWriter() throws IOException {
-
if (indexWriter != null)
-
indexWriter.close();
-
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 读取xls文件内容,引入jxl.jar类型的包
-
* @param file
-
* @return 返回内容
-
*/
-
private static String xls2String(File file) {
-
String result = "";
-
try {
-
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
-
-
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
-
-
jxl.Workbook rwb = Workbook.getWorkbook(fis);
-
Sheet[] sheet = rwb.getSheets();
-
-
for (int i = 0; i < sheet.length; i++) {
-
Sheet rs = rwb.getSheet(i);
-
for (int j = 0; i < rs.getRows(); j++) {
-
Cell[] cells = rs.getRow(j);
-
for (int k = 0; k < cells.length; k++) {
-
sb.append(cells[k].getContents());
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
-
fis.close();
-
-
result += sb.toString();
-
-
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
} catch (BiffException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
} catch (IOException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
return result;
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 读取doc类型文件的内容,通过poi.jar
-
* @param file的类型
-
* @return 返回文件的内容
-
*/
-
private static String doc2String(File file) {
-
String result = "";
-
try {
-
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);//文件输入流
-
-
HWPFDocument document = new HWPFDocument(fis);
-
Range range = document.getRange();
-
result += range.text();
-
-
fis.close();
-
-
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
} catch (IOException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
return result;
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 读取txt文件的内容
-
*
-
* @param file想要读取的文件类型
-
* @return 返回文件内容
-
*/
-
private static String txt2String(File file) {
-
String result = "";
-
-
try {
-
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
-
String s = "";
-
while ((s = reader.readLine()) != null) {
-
result += result + "\n" + s;
-
}
-
-
reader.close();
-
-
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
} catch (IOException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
return result;
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 过滤当前目录下得文件
-
* @param path 当前目录下得文件
-
* @return 返回符合条件的文件
-
*/
-
private static List<File> listFile(String path) {
-
File[] files = new File(path).listFiles();
-
List<File> fileList = new ArrayList<File>();
-
for (File file : files) {
-
if (isTxtFile(file.getName())) {
-
fileList.add(file);
-
}
-
}
-
return fileList;
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 判断是否为目标文件,支持的格式为.txt,.doc,.xls文件格式 如果是文件类型满足过滤条件,返回true;否则返回false
-
* @param name 根据文件名的后缀
-
* @return 是否符合格式规范
-
*/
-
private static boolean isTxtFile(String name) {
-
if (name.lastIndexOf(".txt") > 0)
-
return true;
-
else if (name.lastIndexOf(".doc") > 0)
-
return true;
-
else if (name.lastIndexOf(".xls") > 0)
-
return true;
-
return false;
-
}
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
//创建索引目录,运行一次,重新创建一次
-
File fileIndex = new File(INDEX_DIR);
-
if (deleteIndex(fileIndex)) {
-
fileIndex.mkdir();
-
} else {
-
fileIndex.mkdir();
-
}
-
-
//创建索引文件
-
createIndex(DATA_DIR);
-
-
//通过关键字查询
-
serarchIndex( "中华");
-
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 删除文件目录下得所有文件
-
*
-
* @param fileIndex 当前索引目录下得文件
-
* @return 返回是否删除重新创建
-
*/
-
private static boolean deleteIndex(File fileIndex) {
-
if (fileIndex.isDirectory()) {
-
File[] files = fileIndex.listFiles();
-
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
-
deleteIndex(files[i]);
-
}
-
}
-
fileIndex.delete();
-
return true;
-
}
-
-
}