通过@Async注解实现一个简单的异步任务处理
首先,假设一个全自动化的工厂车间每天需要开启四台互不影响的机器开关来完成生产量,于是车间主任A委派“同步甲”和“异步乙”轮
流完成每天打开机器开关的任务;
“同步甲”是个做事谨慎,认真细心的人,每次进了工厂都是确保一台机器从开启到生产结束无异常后,才开启下一台机器,最后离开车间。
“异步乙”是个做事粗心,好吃懒做的人,每次进了工厂都是一次性打开四台机器,便扬长离开车间。
具体的代码如下:
①Springboot启动类,加入@EnableAsync注解
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; @SpringBootApplication @EnableAsync @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.example") public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); } }
②四台机器Service类,执行异步时,添加@Async注解
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.Random; /** * Created by Administrator on 2019/4/18. */ @Service @Slf4j public class TaskService { public static Random random=new Random(); @Async public void doTaskOne(String i) throws Exception { log.info("机器"+i+"开始生产..."); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000)); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("机器"+i+"停止生产,耗时:" + (end - start) + "毫秒"); } @Async public void doTaskTwo(String i) throws Exception { log.info("机器"+i+"开始生产..."); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000)); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("机器"+i+"停止生产,耗时:" + (end - start) + "毫秒"); } @Async public void doTaskThree(String i) throws Exception { log.info("机器"+i+"开始生产..."); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000)); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("机器"+i+"停止生产,耗时:" + (end - start) + "毫秒"); } @Async public void doTaskFour(String j){ log.info("机器"+j+"开始生产..."); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); long count = 0; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000000; i ++){ count = count + i ; } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("机器"+j+"停止生产,耗时:" + (end - start) + "毫秒"); } }
③Controller
import com.example.service.TaskService; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import java.util.concurrent.Future; /** * Created by Administrator on 2019/4/18. */ @Controller @Slf4j public class TaskController { private TaskService taskService; @Autowired public TaskController(TaskService taskService) { this.taskService = taskService; } @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/test") public String testAsync() throws Exception { log.info("工作人员走进厂房,准备开始一天的工作。。" ); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); taskService.doTaskOne("A"); taskService.doTaskTwo("B"); taskService.doTaskThree("C"); taskService.doTaskFour("D"); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("工作人员离开厂房,耗时" + (end - start) + "毫秒" ); return "执行成功!!!"; } }
④启动springboot,访问http://localhost:8080/test,查看同步与异步的区别。


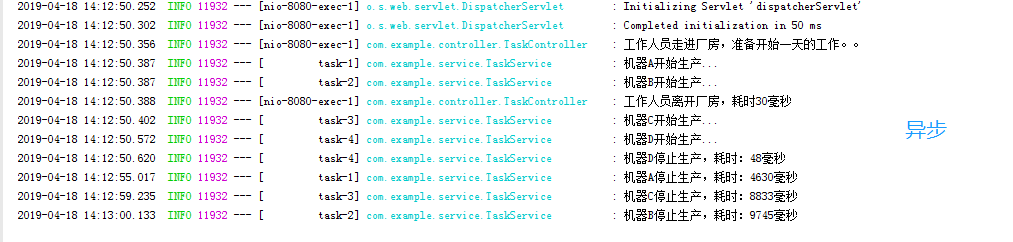

代码地址:https://github.com/liuchunbo24/springboot-async
初步的简单认识,有待继续研究。。。