1.字符串定义
a = "hello"
b = 'westos'
c = "what's up"
d = 'what\'s up' #用单引号时需要转义\
e = """
用户管理系统
1.添加用户
2.删除用户
3.显示用户
"""print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
print(d)
print(e)
print(type(e)) #查看e的类型
2.字符串的特性
s = 'hello'1)索引: 0,1,2,3,4 索引值默认从0开始
print(s[1])
print(s[0])![]()
2)切片
切片的规则: s[start:end:step] 从start开始,到end-1结束,步长:step
print(s[0:3]) #从第一个字符开始,到第二个字符
print(s[0:4:2]) #从第一个字符开始,到第四个字符,每隔两个取一个![]()
1>显示所有字符
print(s[:])![]()
2>显示前3个字符
print(s[:3])![]()
3>字符串逆序输出
print(s[::-1])![]()
4>除了第一个字符以外,其他全部输出
print(s[1:])![]()
3)重复
print( s * 10)![]()
4)连接
print('hello' + ' ' + 'world')![]()
5)成员操作符(判断一个字符是不是在该字符串内,在返回True,不在返回False)
print('h' in s)
print('q' in s) 
实例:输入一个数字判断是不是回文数(一个数正着写和反着写是一样的)
num = input('Num:')
if num == num[::-1]:
print('是回文数')
else:
print('不是回文数')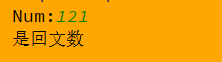
3.字符串判断
1)判断字符串里面每个元素是否为某种类型1>isdigit:数字
print('123'.isdigit())
print('123abc'.isdigit())
2>title:首字母大写,其余小写
print('Hello'.istitle())
print('HeLlo'.istitle())![]()
3>upper:将字符串变成大写
isupper:判断字符串是否是大写
print('hello'.upper())
print('hello'.isupper())
4>lower:将字符串变成小写
islower:判断字符串是否是小写
print('hElLo'.lower())
print('hElLo'.islower())
5>isalnum:判断字符串是否由字母或数字组成
print('hello123'.isalnum())![]()
6>isalpha:判断一个字符串是否为英文字母
print('123'.isalpha())
print('abc'.isalpha())
7>isinstance:判断字符串是否是指定类型
print(isinstance(1,int))
print(isinstance('a',str))
print(isinstance(1,str))
4.字符串去掉开头和结尾
1>
s = ' hello '
a=s.strip()
print(a)![]()
2>
s = ' hello '
b=s.lstrip()
print(b)![]()
3>
s = ' hello '
c=s.rstrip()
print(c)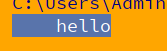
4>
s = ' \nhello '
a=s.strip()
print(a)![]()
5>
s = ' \thello '
b=s.strip()
print(b)![]()
6>去掉h
s = 'helloh'
a=s.strip('h')
print(a)![]()
7>去掉he
s = 'helloh'
a=s.lstrip('he')
print(a)![]()
5.字符串匹配开头和结尾
1)endswith():以......结尾
filename = 'hello.log'
if filename.endswith('.log'):
print(filename)
else:
print('error')![]()
2)startswith():以......开始
url1 = 'file:///mnt'
url2 = 'ftp://172.25.254.250/pub'
url3 = 'http://172.25.254.250/index.html'
if url3.startswith('http://'):
print('爬取该网页')
else:
print('错误网页')![]()
6.字符串的搜索和替换
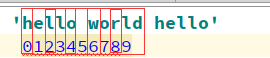
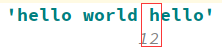
1)find找到子串,并返回最小的索引s = 'hello world hello'print(s.find('hello'))
print(s.find('world'))
2)rfind找到子串,并返回最大的索引值
print(s.rfind('hello'))![]()
3)替换字符串中所有的‘hello’为‘westos’
print(s)
print(s.replace('hello','westos'))
7.字符串的对齐
1)居中
print('学生管理系统'.center(30))
print('学生管理系统'.center(30,'*'))
print('学生管理系统'.center(30,'@'))
2)左对齐
print('学生管理系统'.ljust(30,'*'))![]()
3)右对齐
print('学生管理系统'.rjust(30,'*'))![]()
8.字符串的统计
print('hello'.count('l')) #几个l
print('hello'.count('ll')) #几个ll
print(len('hello')) #字符串长度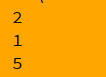
9.字符串的分离和连接
1)分离
s = '172.25.254.250'
s1 = s.split('.')
print(s1)![]()
date = '2019-03-17'
date1 = date.split('-') #以‘-’为分隔符分割
print(date1)![]()
2)连接
date = '2019-03-17'
date1 = date.split('-')
print(''.join(date1)) #以空格连接
print('/'.join(date1)) #以/连接
实例1:
"""
变量名是否合法:
1.变量名只能由字母、数字、下划线组成
2.只能以字母或下划线开头
"""#1.变量名第一个字符是否为字母或者下划线 #2.如果是,继续 --> 4 #3.如果不是,报错 , 退出 #4.依次判断除了第一个字符以外的其他字符 #5.判断是否为字母数字或者下划线
while True:
s = input('变量名:')
if s == 'exit':
print('欢迎下次使用')
break
if s[0].isalpha() or s[0] == '_':
for i in s[1:]:
if not (i.isalnum() or i == '_'):
print('%s变量名不合法' %s)
break
else:
print('%s变量名合法' %s)
else:
print('%s变量名不合法' %s)
实例2:
"""
输入
They are students.
aeiou
输出
Thy r stdnts.
"""s1 = input('s1:')
s2 = input('s2:')
for i in s1:
if i in s2:
s1 = s1.replace(i,'')
print(s1)
实例3:
"""
给定一个字符串来代表一个学生的出勤纪录,这个纪录仅包含以
下三个字符:
'A' : Absent,缺勤
'L' : Late,迟到
'P' : Present,到场
如果一个学生的出勤纪录中不超过一个'A'(缺勤)并且不超过两>个连续的'L'(迟到),
那么这个学生会被奖赏。
你需要根据这个学生的出勤纪录判断他是否会被奖赏。
示例 1:
输入: "PPALLP"
输出: True
示例 2:
输入: "PPALLL"
输出: False
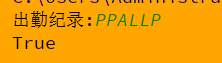
"""a=input('出勤纪录:')
if a.count('A') <=1 and a.count('LLL') ==0:
print('True')
else:
print('False')