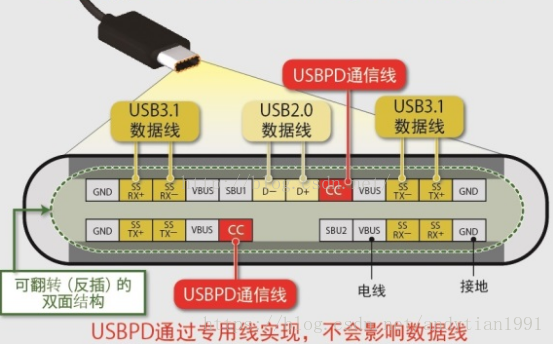
USB Type-C(简称USB-C)的基本特性:
1. 接口插座的尺寸与原来的Micro-USB规格一样小,约为8.3mm X 2.5mm
2. 可承受1万次反复插拔
3. 支持正反均可插入的“正反插”功能
4. 最大传输速度10Gb/s,即是USB 3.1 Gen2标准
5. 配备USB-C连接器的标准规格连接线可通过3A电流,同时还支持超出现有USB供电能力的
USB Power Delivery,可以最大提供100W电力(20V/5V)
Downstream-Facing Port (DFP) 主
Upstream-Facing Port (UFP) 从
Dual-Role Port (DRP)
DRP可以做DFP也可以做UFP。当DPR接到UFP,DRP转化为DFP。当DRP接到DFP,DRP转化为UFP。两个DRP接在一起,这时就是任意一方为DFP,另一方为UFP。(A DRP port is a port that can operate as either a sink or source, or it may alternate between these two states. When a DRP initially operates as a source, the port takes the data role of a DFP. Alternatively, when a DRP initially operates as a sink, the port takes the data role of a UFP.)
Electronically Marked Cable Assembly (EMCA)
VCONNECTOR (VCONN)
USB Type-C bus wire used to power the IC in the EMCA
Configuration Channel (CC)
USB Type-C bus wire used to carry the PD protocol signals.
Sideband Use (SBU)
USB Type-C bus wire used for non-USB control signals
A Provider is a Type-C port that sources power over V BUS ; a Consumer is a Type-C port that sinks power from V BUS
A DFP exposes Rp terminations on its CC pins (CC1 and CC2) and a UFP exposes Rd terminations on its CC pins.
Cable need to expose Ra on its VCONN pin to get power from the DFP.
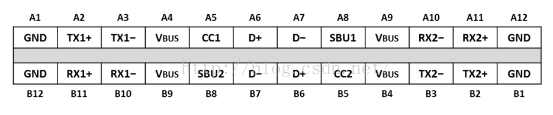
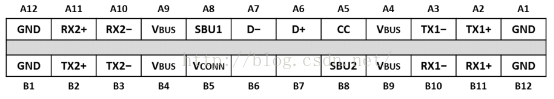
引脚解释,如图2所示:
母口:
公头:
USB 3.1 和 USB Type-C
有时 USB 3.1 和 USB Type-C 这两个词在某些场合下是可以互换的,这就导致了许多人对这两个概念之间的额界限比较模糊。简单的说,USB 3.1 是一个行业标准,同时也是目前标准的修订号。这是一项技术标准,并不是物理产品。但是 USB Type-C 则是一种新型的连接器,有 Type-C 插头和 Type-C 插座组成。
更重要的是,虽然 USB Type-C 是基于 USB 3.1 进行设计的,但是并不意味这使用这种连接方式的设备都支持 USB 3.1 标准,比如诺基亚 N1 平板,尽管使用了 USB Type-C 插头,但是依然还是 USB 2.0 设备。于此同时对于使用 USB 3.0 Type-A 接口的设备来说,这种以蓝色为标志的接口经常出现在笔记本电脑和台式机上,却兼容USB 3.1 标准,所以这么做有什么意义呢?为什么有些设备使用了不兼容 USB 3.1 标准的 USB Type-C 接口呢?没错,就是为了方便。
USB 标准的提出是为了规范计算机和外部设备的连接和通讯,它从最初 1996 年的 1.0 版本普及,到 2008 年的 3.0 版本更新,最终在 2013 年 3.1版本中成为现在的最新状态。第一代的 USB 1.0 大范围商业运用传输速率为 12 Mbps,而随着带宽需求的不断增长,USB 1.0 很快就不能满足实际需求。随后 USB 2.0 带来了传输速率上的显著提高,峰值达到了 480 Mbps。而后来的 USB 3.0 则提升到了 5Gbps,而最新的 USB 3.1 则可以达到 10 Gpbs 速率。而目前比较常见的速率则在 7.2 Gpbs 左右。
USB 除了可以用来传输数据之外,还可以作为电力供应的手段。而最初的 USB 标准由于并不具备电力供应能力,因此 USB 1.0 及 2.0 的电力供应能力仅限于 2.5W(0.5A/5V)。虽然这足以供应手机登小型电子设备,但是对于外界驱动器来说,远远不够。而 USB 3.0 应运而生,它的供应值可达 4.5W(0.9A/5V)。
而在 USB 3.1 标准下的 USB Type-C 接口的供电能力可以达到最高 20A/5V,也就是 100W,不仅可以满足手机充电的要求,还能够满足平板设备和计算机的充电需求,另外,在这种供电能力下,也可以免去其它用电功率较高的外部设备需要另接电源的麻烦。
USB 充(供)电
Battery Charging
定義了 portable device 跟 charger 之間的溝通方式。(主要靠 D+、D-)讓 portable device 得以在插上 USB 的時候辨認接上的是不是 charging port,幫助 portable device 決定從該 USB port 取電的時候允許的電流範圍。這個標準的 1.2 版規範的供電電壓基本上還是維持在 5V,只是把 charging port 的最高允許電流提升到了 5A
USB Power Delivery Specification(USB-PD)
“USB Power Delivery Specification(USB PD)”是一个利用USB接口实现可供给100W电力的标准,旨在为用户提供更强大的电源充电方案。USB 2.0只面向便携终端的驱动和内置充电电池的充电等用途时,“USB Battery Charging”标准虽然提高了供给电力,但供给电力也只有7.5W。
USB Power Delivery offers the following features:
- Increased power levels from existing USB standards up to 100W.
- Power direction is no longer fixed. This enables the product with the power (Host or Peripheral) to provide the power.
- Optimize power management across multiple peripherals by allowing each device to take only the power it requires, and to get more power when required for a given application.
- Intelligent and flexible system level management of power via optional hub communication with the PC.
- Allows low power cases such as headsets to negotiate for only the power they require.
Quick Charge
Qualcomm制定的快速充电标准。
Type-C is a new reversible USB connector specification that can support a number of new standards including USB 3.1, Display Port and USB power delivery. Even though the latest Smartphones, laptops are equipped a USB Type-c port, but that doesn't mean any USB C charger works with any USB C device.
USB Type-C ports supports max 5V/3A. If a USB PD is implemented in a USB Type-C port, it can support the 100W power (5V/20A) defined in the USB PD specification. Thus, not all USB Type-C ports support USB Power Delivery.