react(入门)
-
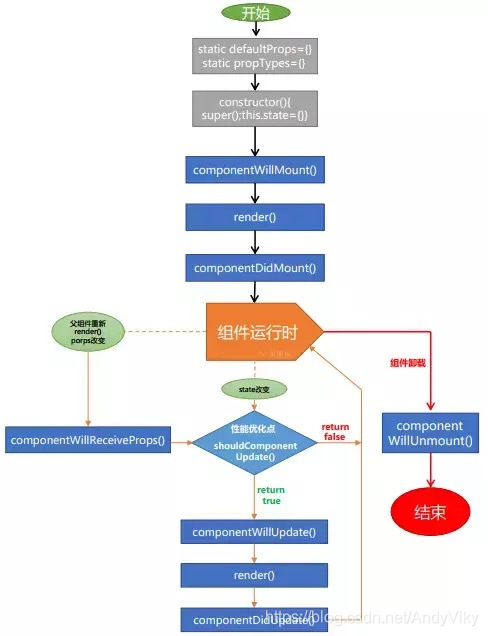
生命周期
-
getDefaultProps()
设置默认的props,也可以用dufaultProps设置组件的默认属性.
-
getInitialState()
在使用es6的class语法时是没有这个钩子函数的,可以直接在constructor中定义this.state。此时可以访问this.props
-
componentWillMount()
组件初始化时只调用,以后组件更新不调用,整个生命周期只调用一次,此时可以修改state。
-
render()
react最重要的步骤,创建虚拟dom,进行diff算法,更新dom树都在此进行。此时就不能更改state了。
-
componentDidMount()
组件渲染之后调用,只调用一次。
-
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps)
组件初始化时不调用,组件接受新的props时调用。
-
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
react性能优化非常重要的一环。组件接受新的state或者props时调用,我们可以设置在此对比前后两个props和state是否相同,如果相同则返回false阻止更新,因为相同的属性状态一定会生成相同的dom树,这样就不需要创造新的dom树和旧的dom树进行diff算法对比,节省大量性能,尤其是在dom结构复杂的时候
-
componentWillUpdata(nextProps, nextState)
组件初始化时不调用,只有在组件将要更新时才调用,此时可以修改state
-
render()
组件渲染
-
componentDidUpdate()
组件初始化时不调用,组件更新完成后调用,此时可以获取dom节点。
-
componentWillUnmount()
组件将要卸载时调用,一些事件监听和定时器需要在此时清除。
-
-
组件 && jsx && 元素渲染
-
组件定义方式
-
函数
function Welcome(props) { return <h1>Hello, {props.name}</h1>; } -
类
class Welcome extends React.Component { render() { return <h1>Hello, {this.props.name}</h1>; } }
-
-
条件渲染
// if条件写在标签外 class Welcome extends React.Component { render() { const test = this.props.test; if(test) return <h1>test</h1> else return <h1>Hello, {this.props.name}</h1>; } } // if条件写在标签内 class Welcome extends React.Component { render() { const test = this.props.test; return ( <h1> { test && <h2>Hello</h2> // react默认不渲染出bool类型变量,当test为true时打印右边标签 } </h1>; ) } } -
列表渲染
// map写在标签外 class Welcome extends React.Component { render() { let lis = this.props.lis.map((content, index) => { return <li key={ index.toString() }>{ content }</li> }) return ( <ul> { lis } </ul> ) } } // map写在标签内 class Welcome extends React.Component { render() { return ( <ul> { this.props.lis.map((content, index) => { return <li key={ index.toString() }>{ content }</li> }) } </ul> ) } } -
表单数据绑定
class Welcome extends React.Components { handleChange(id, e) { this.setData({ inputContent: e.target.value; }) } render() { return ( <input onChange={this.handleChange.bind(this, id)}><input> ) } }
-
-
事件处理
-
绑定自定义事件之
this问题// 直接在构造函数内绑定 class Parent extends React.Components { construct(props) { super(props); this.clickContent = this.clickContent.bind(this); } clickContent(e) { console.log(this); } render() { return ( <h1 onClick={this.clickContent}>Hello</h1> ) } } // 实验性语法 class Parent extends React.Components { construct(props) { super(props); } clickContent = (e) => { console.log(this); } render() { return ( <h1 onClick={this.clickContent}>Hello</h1> ) } } // 直接在onClick内绑定, 避免使用 // 每次相关组件渲染的时候都会创建一个不同的回调函数 // 如果这个回调函数作为一个属性值传入低阶组件,这些组件可能会进行额外的重新渲染 class Parent extends React.Components { construct(props) { super(props); } clickContent(e) { console.log(this); } render() { return ( <h1 onClick={(e) => this.clickContent(e)}>Hello</h1> // <h1 onClick={this.clickContent(this)}>Hello</h1> ) } }
-
-
props && state
props是只读的
// 父向子传递数据 class Welcome extends React.Components { render() { return ( <h1>{this.props.title}</h1> ) } } class Parent extends React.Components { render() { let title = 'test'; return ( <Welcome title={title}></Welcome> ) } } // 子向父传递数据 class Welcome extends React.Components { clickTitle = () => { this.props.onChangeTitle('newTitle'); } render() { return ( <h1 onClick={this.clickTitle}>{this.props.title}</h1> ) } } class Parent extends React.Components { construct(props) { super(props); this.state = { title: 'test' } } changeTitle = (newTitle) => { this.setData({ title: newTitle; }) } render() { return ( <Welcome title={this.state.title} onChangeTitle={this.changeTitle} /> ) } } -
组件的组合
function FancyBorder(props) { return ( <div className={'FancyBorder FancyBorder-' + props.color}> {props.children} // children为默认自元素变量 </div> ); } function WelcomeDialog() { return ( <FancyBorder color="blue"> <h1 className="Dialog-title"> Welcome </h1> <p className="Dialog-message"> Thank you for visiting our spacecraft! </p> </FancyBorder> ); } // 可以使用自定义变量 function FancyBorder(props) { return ( <div className={'FancyBorder FancyBorder-' + props.color}> {props.left} </div> ); } function WelcomeDialog() { return ( <FancyBorder color="blue"> left = { <h1 className="Dialog-title"> Welcome </h1> } </FancyBorder> ); }