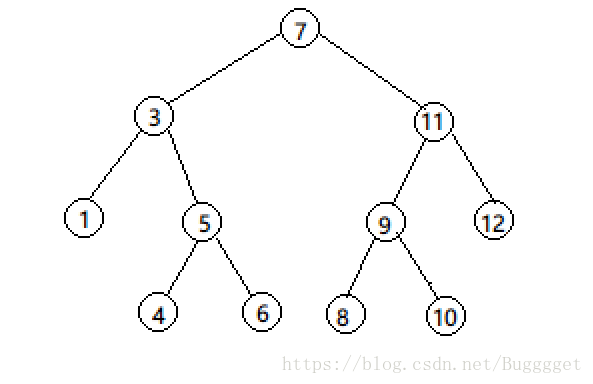
二叉排序树
性质:
二叉排序树又叫二叉搜索树,具有以下性质:
- 若左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于或等于它的根结点的值;
- 若右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于或等于它的根结点的值;
- 左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树;
如下就是一颗二叉排序树:
中序遍历的结果正好是1 3 5 7 8。
结构体定义:
typedef int BSTreeDataType;
// 二叉搜索树(二叉排序树)
typedef struct BSTreeNode {
BSTreeDataType data;
struct BSTreeNode* LChild;
struct BSTreeNode* RChild;
}BSTreeNode;
对于二叉排序树有以下几个操作:
- 插入节点
- 搜索节点
- 删除节点
- 销毁二叉搜索树
- 遍历二叉搜索树
插入节点,时间复杂度:log2(N)(对于非单只树)。
第一步:找到节点
判断当前节点数据(curData)和要插入的节点的数据(insertData)比较,相等不插入,如果
insertData<curData 在左子树找,如果insertData > curData在右子树找。并记录父节点。
第二步:插入
如果小于父节点插入parrent->LChild = insertNode;否则parrent->RChild = insertNode;
代码如下:
递归:
// 插入节点,递归插入
int insertBSTreeNode(BSTreeNode** pRoot, BSTreeDataType data) {
if (*pRoot == NULL) {
*pRoot = buyBSTreeNode(data);
return 1;
}
if ((*pRoot)->data == data)
return 0;
if ((*pRoot)->data > data) {
return insertBSTreeNode(&(*pRoot)->LChild, data);
}
return insertBSTreeNode(&(*pRoot)->RChild, data);
}
非递归:
// 非递归插入节点,返回插入状态
int insertBSTreeNodeNor(BSTreeNode** pRoot, BSTreeDataType data) {
BSTreeNode* insertNode = buyBSTreeNode(data);
if (*pRoot == NULL) {
*pRoot = insertNode;
return 1;
}
BSTreeNode* Cur = *pRoot;
BSTreeNode* preCur = NULL;
while (Cur) {
if (Cur->data == data) {
return 0;
}
else if (data < Cur->data) {
preCur = Cur;
Cur = Cur->LChild;
}
else if (data > Cur->data) {
preCur = Cur;
Cur = Cur->RChild;
}
}
if (data > preCur->data) {
preCur->RChild = insertNode;
}
else {
preCur->LChild = insertNode;
}
}
搜索节点, 时间复杂度:log2(N)
步骤: 判断当前节点数据(curData)和要插入的节点的数据(insertData)比较,相等直接返回,如果
insertData < curData 在左子树找,如果insertData > curData在右子树找。
代码如下:
// 递归搜索节点
BSTreeNode* findBSTreeNode(BSTreeNode* pRoot, BSTreeDataType data) {
if (pRoot == NULL)
return NULL;
if (pRoot->data == data) {
return pRoot;
}
if (data < pRoot->data) {
return findBSTreeNode(pRoot->LChild, data);
}
return findBSTreeNode(pRoot->RChild, data);
}
// 非递归搜索节点
BSTreeNode* findBSTreeNodeNor(BSTreeNode* pRoot, BSTreeDataType data) {
if (pRoot == NULL)
return NULL;
BSTreeNode* Cur = pRoot;
while (Cur) {
if (Cur->data == data) {
return Cur;
}
else if (data > Cur->data) {
Cur = Cur->RChild;
}
else if (data < Cur->data) {
Cur = Cur->LChild;
}
}
return NULL;
}
删除节点,时间复杂度:
删除节点分为以下几个状态:
删除的节点为叶子节点:直接删除
删除的节点为根节点:
|__________根节点只有右孩子
|__________根节点只有左孩子
|__________跟节点左右孩子都有
|______方式1:找到根节点右孩子的最左孩子,将这个节点的值赋值给根节点,删除这个节点
|______方式2:找到根节点左孩子的最右孩子,将这个节点的值赋值给根节点,删除这个节点
删除的节点为父节点的左孩子
如果删除的节点有右孩子,和删除根节点的方式一样。
如果删除的节点无右孩子,让父节点的LChild = delNode->LChild;
删除的节点为父节点的右孩子
如果删除的节点有左孩子,和删除根节点的方式一样。
如果删除的节点无右孩子,让父节点的RChild = delNode->RChild;
代码如下:
// 删除节点
void deleteBSTreeNode(BSTreeNode** pRoot, BSTreeDataType data) {
// 找到节点
BSTreeNode* Cur = *pRoot;
BSTreeNode* preCur = NULL;
while (Cur) {
if (Cur->data == data)
break;
else if (data < Cur->data) {
preCur = Cur;
Cur = Cur->LChild;
}
else if (data > Cur->data) {
preCur = Cur;
Cur = Cur->RChild;
}
}
if (Cur == NULL)
return;
BSTreeNode* delNode = Cur;
// 如果删除的是叶子节点
if (delNode->RChild == NULL && delNode->LChild == NULL) {
if (delNode == preCur->LChild) {
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
preCur->LChild = NULL;
return;
}
if (delNode == preCur->RChild) {
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
preCur->RChild = NULL;
return;
}
}
//如果删除的节点是根节点
if (delNode == *pRoot) {
if (delNode->LChild == NULL) {
// 如果根节点无左孩子
delNode = *pRoot;
*pRoot = (*pRoot)->RChild;
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
}
else if (delNode->RChild == NULL) {
// 如果根节点无右孩子
delNode = *pRoot;
*pRoot = (*pRoot)->LChild;
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
}
else {
// 如果根节点有左右孩子
// 让根节点和右孩子的最左孩子交换,然后删除这个最左孩子
// 找到右孩子的最左孩子
delNode = (*pRoot)->RChild;
while (delNode->LChild) {
preCur = delNode;
delNode = delNode->LChild;
}
// 将最左孩子值赋值给根节点
(*pRoot)->data = delNode->data;
// 删除这个节点
if (delNode->RChild != NULL) {
// 如果要删除的节点有右孩子
if (preCur != NULL)
preCur->LChild = delNode->RChild;
else {
(*pRoot)->RChild = delNode->RChild;
}
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
}
else {
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
preCur->LChild = NULL;
}
}
}
else if (delNode == preCur->LChild) {
// 如果删除的节点是父节点的左孩子
if (delNode->LChild == NULL) {
// 如果删除的节点无左孩子
preCur->LChild = delNode->RChild;
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
}
else if (delNode->RChild == NULL) {
// 如果删除的节点无右孩子
preCur->LChild = delNode->LChild;
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
}
else {
// 如果删除的节点有左右孩子
// 找到右孩子的最左孩子
delNode = Cur->RChild;
// 如果右孩子无左孩子
if (delNode->LChild == NULL) {
Cur->data = delNode->data;
Cur->RChild = delNode->RChild;
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
return;
}
// 如果右孩子有左孩子,找到最左孩子
while (delNode->LChild) {
preCur = delNode;
delNode = delNode->LChild;
}
// 将最左孩子值赋值给根节点
Cur->data = delNode->data;
// 删除这个节点
if (delNode->RChild != NULL) {
// 如果要删除的节点有右孩子
preCur->LChild = delNode->RChild;
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
}
else {
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
preCur->LChild = NULL;
}
}
}
else if (delNode == preCur->RChild) {
// 如果删除的节点是父节点的右孩子
if (delNode->LChild == NULL) {
// 如果删除的节点无左孩子
preCur->RChild = delNode->RChild;
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
}
else if (delNode->RChild == NULL) {
// 如果删除的节点无右孩子
preCur->RChild = delNode->LChild;
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
}
else {
// 如果删除的节点有左右孩子
// 找到左孩子的最右孩子
delNode = Cur->LChild;
// 如果左孩子无右孩子
if (delNode->RChild == NULL) {
Cur->data = delNode->data;
Cur->LChild = delNode->LChild;
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
return;
}
// 如果左孩子有右孩子,找到最右孩子
while (delNode->RChild) {
preCur = delNode;
delNode = delNode->RChild;
}
// 将最右孩子值赋值给根节点
Cur->data = delNode->data;
// 删除这个节点
if (delNode->LChild != NULL) {
// 如果要删除的节点有左孩子
preCur->RChild = delNode->LChild;
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
}
else {
free(delNode);
delNode = NULL;
preCur->RChild = NULL;
}
}
}
}
中序遍历二叉排序树(和二叉树的操作一样):
// 中序遍历二叉树
void inOrderBSTree(BSTreeNode* pRoot) {
if (pRoot != NULL) {
inOrderBSTree(pRoot->LChild);
printf("%d ", pRoot->data);
inOrderBSTree(pRoot->RChild);
}
}
销毁二叉排序树(和二叉树的操作一样):
// 销毁二叉排序树
void destroyBSTreeNode(BSTreeNode** pRoot) {
// 后续遍历规则
if (*pRoot != NULL) {
destroyBSTreeNode(&(*pRoot)->LChild);
destroyBSTreeNode(&(*pRoot)->RChild);
free(*pRoot);
*pRoot = NULL;
}
}
主函数调用:
int main() {
BSTreeNode* pRoot = NULL;
BSTreeDataType arr[] = {7, 11, 3, 1, 5, 9, 12, 4, 6, 8, 10};
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
insertBSTreeNodeNor(&pRoot, arr[i]);
}
printf("插入所有节点成功!\n");
printf("中序遍历二叉排序树:\n");
inOrderBSTree(pRoot);
// 搜索节点
BSTreeNode* node = findBSTreeNode(pRoot, 7);
printf("\n找到并删除节点%d\n", node->data);
deleteBSTreeNode(&pRoot, node->data);
printf("中序遍历二叉排序树:\n");
inOrderBSTree(pRoot);
// 销毁二叉树
printf("\n销毁之后中序遍历二叉排序树:\n");
destroyBSTreeNode(&pRoot);
inOrderBSTree(pRoot);
return 0;
}
测试用例:
7, 11, 3, 1, 5, 9, 12, 4, 6, 8, 10
运行结果:
二叉排序树应用:
1. 判断一个单词是否拼写正确
步骤:
- 将给的多个单词序列放入二叉排序树(利用strcmp比较两个单词的大小);
- 输入单词,搜索二叉排序树中是否有此单词,有则拼写正确;
结构体定义:
// 二叉树的应用之检测一个单词是否拼写正确
typedef struct BSTreeAppNode {
String word;
struct BSTreeAppNode* LChild;
struct BSTreeAppNode* RChild;
}BSTreeAppNode;
代码实现:
// 获取节点
BSTreeAppNode* buyBSTreeNodeByString(String data) {
BSTreeAppNode* node = (BSTreeAppNode*)malloc(sizeof(BSTreeAppNode));
if (node == NULL)
return NULL;
node->word = data;
node->LChild = NULL;
node->RChild = NULL;
return node;
}
// 中序遍历二叉树
void inOrderBSTreeByString(BSTreeAppNode* pRoot) {
if (pRoot != NULL) {
inOrderBSTreeByString(pRoot->LChild);
printf("%s ", pRoot->word);
inOrderBSTreeByString(pRoot->RChild);
}
}
// 插入节点
int insertBSTreeNodeByString(BSTreeAppNode** pRoot, String word) {
if (*pRoot == NULL) {
*pRoot = buyBSTreeNodeByString(word);
return 1;
}
if (strcmp((*pRoot)->word, word) == 0) // 已经存在了,不能再插入了。
return 0;
if (strcmp((*pRoot)->word, word) > 0) {
return insertBSTreeNodeByString(&(*pRoot)->LChild, word);
}
return insertBSTreeNodeByString(&(*pRoot)->RChild, word);
}
// 判断一个单词是否拼写正确
int isCorrectSpelling(BSTreeAppNode* pRoot, String word) {
if (pRoot == NULL)
return 0;
BSTreeAppNode* Cur = pRoot;
while (Cur) {
if (strcmp(word, Cur->word) == 0)
return 1;
else if (strcmp(word, Cur->word) < 0) {
Cur = Cur->LChild;
}
else if (strcmp(word, Cur->word) > 0) {
Cur = Cur->RChild;
}
}
return 0;
}
测试程序:
// 判断一个单词是否拼写正确
void testIsCorrectSpelling() {
String arr[] = {"hellow", "he", "helloword", "hello"};
int len = sizeof(arr)/ sizeof(arr[0]);
BSTreeAppNode* pRoot = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
insertBSTreeNodeByString(&pRoot, arr[i]);
}
String word = "hello";
int ret = isCorrectSpelling(pRoot, word);
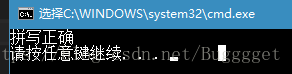
if (ret)
printf("拼写正确\n");
else
printf("拼写错误\n");
}
运行结果:
2. 统计异常(出现次数大于1次)的IP地址,并统计出重复次数最多的K个IP地址
- 将字符串IP转换成unsigned int型的数(点分10进制,转换使用union(共用体));
- 将所有unsigned int类型的IP地址放入二叉排序树。如果树中有次IP,对应的IP出现的次数加1;
- 中序遍历二叉树,并把大于1次的ip存入数组。
- 构建K个元素的小项堆,然后插入数组剩余的元素。
IP地址结构体定义:
// 用于将点分十进制转成无符号整形10进制
typedef union IPCast {
unsigned int ip;
struct {
unsigned char str[4];
}strip;
}IPCast;
typedef struct IP {
unsigned int ip; // ip地址
unsigned int count; // 出现的次数
}IP;
typedef struct IP* IPDataType;
// 二叉搜索树(二叉排序树)
typedef struct BSTreeIPNode {
struct IP ip;
struct BSTreeNode* LChild;
struct BSTreeNode* RChild;
}BSTreeIPNode;
代码如下:
void showHeap(IP* ips, int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
IPCast ipCast;
ipCast.ip = ips[i].ip;
printf("%d.%d.%d.%d 出现次数 %d\n", ipCast.strip.str[3], ipCast.strip.str[2],
ipCast.strip.str[1], ipCast.strip.str[0], ips[i].count);
}
printf("\n");
}
// 字符串IP转整形
unsigned int StringIPCastToInt(String ip) {
IPCast ipCast;
int i = 3;
int j = 0;
String cur = ip;
char preCur[16] = { 0 };
String root = preCur;
while (1) {
if (*cur != '.' && *cur != '\0') {
preCur[j] = *cur;
j++;
}
else {
int a = atoi(preCur);
(ipCast.strip).str[i] = (char)a;
memset(preCur, 0, 16);
j = 0;
i--;
if (*cur == '\0')
break;
}
cur++;
}
return ipCast.ip;
}
// 获取节点
BSTreeIPNode* buyBSTreeNodeByIP(unsigned int ip) {
BSTreeIPNode* node = (BSTreeIPNode*)malloc(sizeof(BSTreeIPNode));
if (node == NULL)
return NULL;
node->ip.ip = ip;
node->ip.count = 0;
node->LChild = NULL;
node->RChild = NULL;
return node;
}
// 中序遍历二叉树,并将遍历的值赋值给结构体数组
void inOrderBSTreeByIP(BSTreeIPNode* pRoot, IP* ips, int* index) {
if (pRoot != NULL) {
(*index)++;
inOrderBSTreeByIP(pRoot->LChild, ips, index);
IPCast ipCast;
ipCast.ip = pRoot->ip.ip;
printf("%d.%d.%d.%d 出现次数 %d\n", ipCast.strip.str[3], ipCast.strip.str[2], ipCast.strip.str[1],
ipCast.strip.str[0], pRoot->ip.count);
if (pRoot->ip.count > 1) {
ips[*index] = pRoot->ip;
(*index)++;
}
inOrderBSTreeByIP(pRoot->RChild, ips, index);
}
}
// 插入IP地址
int insertBSTreeNodeByIP(BSTreeIPNode** pRoot, unsigned int ip) {
if (*pRoot == NULL) {
*pRoot = buyBSTreeNodeByIP(ip);
(*pRoot)->ip.count++;
return 1;
}
if ((*pRoot)->ip.ip == ip) {
(*pRoot)->ip.count++;
return 0;
}
if ((*pRoot)->ip.ip > ip) {
return insertBSTreeNodeByIP(&(*pRoot)->LChild, ip);
}
return insertBSTreeNodeByIP(&(*pRoot)->RChild, ip);
}
void swap(IP* a, IP* b) {
IP tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
// 构建小项堆
void createIPHeap(IP* ips, unsigned int len) {
// 找到临界点
int parrent = 0;
int flag = ((len - 1) / 2);
while (flag >= 0) {
parrent = flag;
while (1) {
int child = parrent * 2 + 1;
if (child + 1 >= len) {
if (ips[parrent].count > ips[child].count) {
swap(&ips[parrent], &ips[child]);
}
break;
}
if (ips[child].count > ips[child + 1].count) {
child++;
}
if (ips[parrent].count > ips[child].count) {
swap(&ips[parrent], &ips[child]);
parrent = child;
}
else {
break;
}
}
flag--;
}
}
// 插入IP地址(向下调整)
void insertIntoHeap(IP* ips, IP insertIP, unsigned int len) {
if (insertIP.count <= ips[0].count)
return;
ips[0] = insertIP;
int parrent = 0;
int child = 0;
//找到孩子中最小的,然后交换
while (1) {
child = parrent * 2 + 1;
if (child >= len)
break;
if (child + 1 >= len) {
if (ips[parrent].count > ips[child].count) {
swap(&ips[parrent], &ips[child]);
break;
}
}
if (ips[child].count > ips[child + 1].count) {
child++;
}
if (ips[parrent].count > ips[child].count) {
swap(&ips[parrent], &ips[child]);
parrent = child;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
// 找到出现次数最多的K个异常IP地址
void getTopKUnusualIP(IP* ips, unsigned int count, unsigned int k) {
if (count <= k) {
createIPHeap(ips, count);
return;
}
createIPHeap(ips, k);
for (int i = k; i < count; i++) {
insertIntoHeap(ips, ips[i], k);
}
showHeap(ips, k);
}
测试程序:
void testCountUnusualIP() {
String ip[] = { "111.168.0.1",
"192.168.0.1" ,
"253.168.0.1" ,
"255.168.0.1" ,
"255.168.0.1",
"192.168.0.1",
"192.168.0.1",
"127.0.0.1",
"0.0.0.1",
"128.98.78.1",
"192.168.0.1" ,
"253.168.0.1" ,
"192.168.0.1" ,
"253.168.0.1" ,
"192.168.0.1" ,
"253.168.0.1" ,
"192.168.0.1" ,
"253.168.0.1" ,
"192.168.0.1" ,
"253.168.0.1" ,
"192.168.0.1" ,
"253.168.0.1" ,
"255.168.0.2" ,
"255.168.0.1",
"192.168.0.1",
"192.168.0.1",
"127.0.0.1",
"0.0.0.1",
"128.98.78.1",
"192.168.0.1" ,
"253.168.0.1" ,
"192.168.0.1" ,
"253.168.0.1" ,
"192.168.0.1" ,
"253.168.0.1" ,
"192.168.0.1" ,
"253.168.0.1" ,
"124.168.0.1",
"124.168.0.1",
"124.168.0.1" };
int len = sizeof(ip) / sizeof(ip[0]);
BSTreeIPNode* pRoot = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
unsigned int ret = StringIPCastToInt(ip[i]);
insertBSTreeNodeByIP(&pRoot, ret);
}
IP ips[40] = {0};
int a = 0;
printf("中序遍历:\n");
inOrderBSTreeByIP(pRoot, ips, &a);
printf("\n出现次数最多的5个元素为:\n");
getTopKUnusualIP(ips, 40, 5);
}
运行结果: