Code Implementation of Double link list
1 Construction of a double link list
1.1 Construct the node
typedef struct line{
struct line * prior; // Point to the precursor
int data;
struct line * next; // Point to the subsequence
}line;
1.2 Initialization
line* initLine(line * head){
head=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line)); // Create the first node
head->prior=NULL;
head->next=NULL;
head->data=1;
line * list=head;
for (int i=2;i<=5;i++){ // Initialize and create a node
line * body=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
body->prior=NULL;
body->next=NULL;
body->data=i;
list->next=body; // Subsequence points to the new node
body->prior=list; // New node points to the precursor
list=list->next;
}
return head;
}
1.3 Display the list
void display(line * head){
line * temp=head;
while (temp) {
if (temp->next==NULL) { // If no 'next', means the node is the last one
printf("%d\n",temp->data);
}else{
printf("%d <-> ",temp->data);
}
temp=temp->next;
}
}
int main() {
line * head=NULL; // Create a head pointer
head=initLine(head); // Create the list
display(head);
printf("The 4th's direct precursor in the list is:%d",head->next->next->next->prior->data);
return 0;
}
Output:

2 Basic operations of double link list
2.1 Insert elements
line * insertLine(line * head,int data,int add){
line * temp=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
temp->data=data;
temp->prior=NULL;
temp->next=NULL;
if (add==1) { // Special condition: Insert to the head
temp->next=head;
head->prior=temp;
head=temp;
}else{
line * body=head;
for (int i=1; i<add-1; i++) { // Find the last node of the inserted place
body=body->next;
}
if (body->next==NULL) { // If true, the place is on the tail
body->next=temp;
temp->prior=body;
}else{
body->next->prior=temp;
temp->next=body->next;
body->next=temp;
temp->prior=body;
}
}
return head;
}
2.2 Delete elements
line * delLine(line * head,int data){
line * temp=head;
while (temp) { // Traversal
if (temp->data==data) {
temp->prior->next=temp->next;
temp->next->prior=temp->prior;
free(temp);
return head;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
printf("No such element");
return head;
}
2.3 Find the element
int selectElem(line * head,int elem){
line * t=head; // Initialized as head pointer
int i=1;
while (t) {
if (t->data==elem) {
return i;
}
i++;
t=t->next;
}
return -1; // Failed to find the target
}
2.4 Alter the element
line *amendElem(line * p,int add,int newElem){
line * temp=p;
for (int i=1; i<add; i++) { // Traversed to the deleted node
temp=temp->next;
}
temp->data=newElem;
return p;
}
2.5 Check the code
void display(line * head){
line * temp=head;
while (temp) {
if (temp->next==NULL) {
printf("%d\n",temp->data);
}else{
printf("%d->",temp->data);
}
temp=temp->next;
}
}
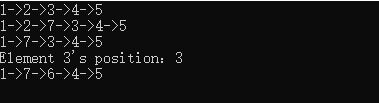
int main() {
line * head=NULL;
head=initLine(head); // Create the list
display(head);
head=insertLine(head, 7, 3); // Insert element 7 at the position 3
display(head);
head=delLine(head, 2); // Delete element 2
display(head);
printf("Element 3's position:%d\n",selectElem(head,3));
head = amendElem(head,3,6); // Change the 3rd node to store number 6
display(head);
return 0;
}
Output: