假设在距离Rs上,每个基带脉冲回波在发射后的2Rs/c秒进行采样。
Assume each basebandpulse echo is sampled 2Rs/c seconds after transmission,corresponding to a range Rs .
同时假设目标位于对应整个数据采集时间(mT秒)的范围内,这意味着R(t)保持在[Rs–cτ/2, Rs]的距离间隔内。
Also assume a targetis present within the range bin corresponding to that sample time for theentire data collection time of mT seconds, meaning that R(t) remains in therange interval [Rs–cτ/2, Rs].
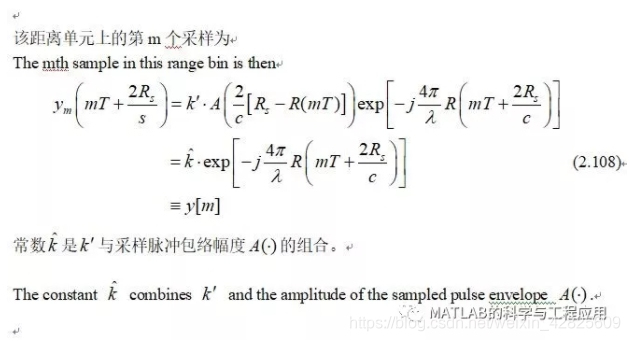
如第3章所述,采样回波序列y[m]构成该距离单元上的慢时间序列。
The series of sampledechoes y[m] forms the slow-time series of samples for that range bin, as willbe described in Chap. 3.
当用于式(2.107)中的一系列脉冲时,式(2.98)中应用的“停止”假设,称为停跳近似。
The "stop"assumption applied in Eq. (2.98), when used across a series of pulses as in(2.107), is called the stop-and-hop approximation.
相对于雷达而言,假设目标在每次脉冲发射时在相应的R(mT)距离内“停止”,然后在下一次脉冲发射时间内“跳”到该距离单元,而不是连续移动。
Relative to theradar, the target is assumed to “stop” at the time of each pulsetransmission at the corresponding range R(mT) and then “hop” to therange at the next pulse transmission time, rather than moving continuously.
考虑一个恒速运动目标R(t) = R0 – vt。
Consider again aconstant velocity target, R(t) = R0 – vt.
则慢时间数据序列变为:
Theslow-time data series becomes
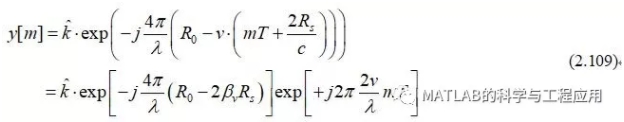
式(2.109)中的第一个指数项是所有慢时间样本y[m]的恒定相移,且影响不大。
The first exponentialin Eq. (2.109) is a constant phase shift for all of the slow-time samples y[m]and is of little consequence.
第二个指数项是一个具有归一化频率2vT/λ周期/样本的离散复正弦波,对应的预期多普勒频率为2v/λ Hz。
The secondexponential is a discrete complex sinusoid with normalized frequency 2vT/λ cycles/sample,corresponding to the expected Doppler frequency of 2v/λ Hz.
因此,使用一串脉冲获得运动目标的相位历史提供了一种方法,能够通过在比单脉冲长得多的观测时间内观测信号,以高精度测量多普勒频移。
Thus, the phasehistory obtained from a moving target using a series of pulses provides a wayto measure the Doppler shift with good precision by observing the signal overan observation time much longer than that of a single pulse.
目标多普勒频移在慢时间相位历史中的表现有时被称为空间多普勒。
The manifestation ofthe target Doppler shift in the slow-time phase history is sometimes referredto as spatial Doppler.
这一术语强调了这样一个事实:多普勒频移不是由脉冲内的频率变化测量的,而是由一系列脉冲上给定距离单元内回波的相位变化测量的。
This terminologyemphasizes the fact that the Doppler shift is measured not from intrapulse frequencychanges, but rather from the change of phase of the echoes at a given range binover a series of pulses.
由于大多数系统无法测量脉内多普勒频移,因此,雷达中的“多普勒处理”一词通常指的是对空间多普勒信息的感知和处理。
Because of theinability to measure intrapulse Doppler frequency shifts in most systems, theterm “Doppler processing” in radar usually refers to sensing andprocessing this spatial Doppler information.
——本文译自Mark A. Richards所著的《Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing(Second edition)》
更多精彩文章请关注微信号: