文章目录
MyBatis
1.开发dao两种方法:
原始dao开发方法(程序需要编写dao接口和dao实现类)
mybaits的mapper接口(相当于dao接口)代理开发方法
2.特点:
mybatis是一个持久层的框架,是apache下的顶级项目
通过mybatis提供的映射方式,可以自由灵活生成(半自动化,大部分需要程序员编写sql)满足需要sql语句
可以将向 preparedStatement中的输入参数自动进行输入映射,将查询结果集灵活映射成java对象。(输出映射)
3.SSM框架开发:Spring√+SpringMVC√+Mybatis
原生态jdbc程序中的问题
1.数据库连接,使用时就创建,不使用立即释放,对数据库进行频繁连接开启和关闭,造成数据库资源浪费,影响 数据库性能
解决:数据库连接池
2.将sql语句和preparedStatement向占位符号位置和设置参数值,硬编码到java代码中,不利于系统维护
解决:将sql语句及占位符号和参数全部配置在xml中
3.从resutSet中遍历结果集数据时,存在硬编码,将获取表的字段进行硬编码,不利于系统维护
解决:将查询的结果集,自动映射成java对象
mybatis框架原理
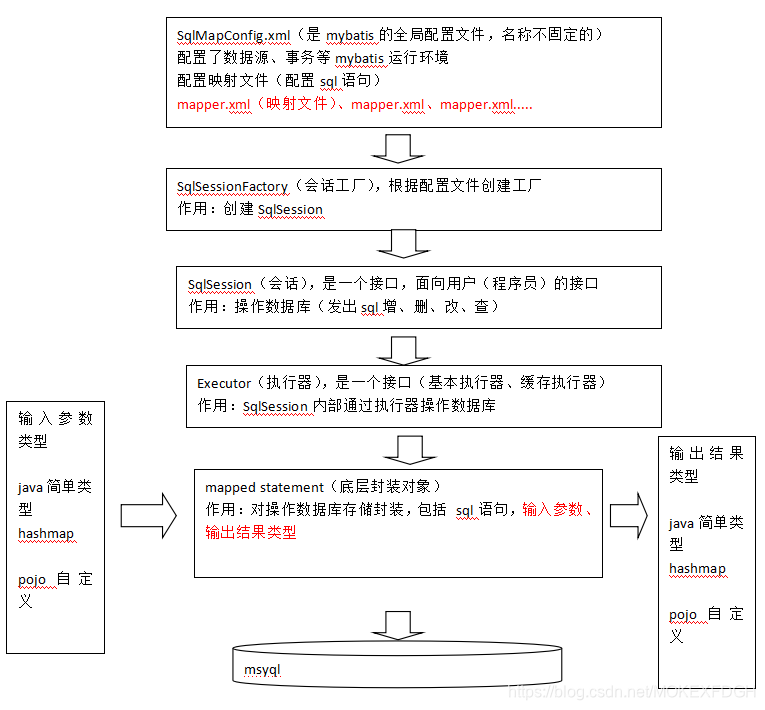
mybatis架构案例
加入mybatis核心包、依赖包、数据驱动包
参照原理,使用案例用户增删改查
解决:原生态jdbc程序中的问题
log4j.properties的使用
# Global logging configuration
# 开发环境下日志级别为DEBUG,生产环境下设置为info
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout
# Console output...
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n
SqlMapConfig.xml的使用
1.配置驱动参数
2.加载映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 和spring整合后 environments配置将废除-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!-- 使用jdbc事务管理-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<!-- 数据库连接池-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf-8" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 加载映射文件 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="sqlmap/User.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
po类和映射文件的使用
1.po类(映射类):
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;// 用户姓名
private String sex;// 性别
private Date birthday;// 生日
private String address;// 地址
...//get、set方法
}
2.User.xml,注:mapper代理开发映射文件名称叫XXXMapper.xml,比如:UserMapper.xml
在映射文件中配置sql语句:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="test"><!-- namespace :命名空间,用于隔离sql语句 -->
<!-- 根据id获取用户信息 -->
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.User">
select * from user where id=#{id}
</select>
<!-- 自定义条件查询用户列表 -->
<select id="findUserByUsername" parameterType="java.lang.String"
resultType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.User">
select * from user where username like '%${value}%'
</select>
<!--
parameterType:定义输入到sql中的映射类型
#{id}表示使用preparedstatement设置占位符号并将输入变量id传到sql
//占位符接收输入参数类型可以为简单类型,pojo(普通javabean),hashmap;可以写成value或者其他名称
resultType:定义结果映射类
${}:表示拼接sql串,将接收到参数的内容不加任何修饰拼接在sql中,有sql注入风险,不建议使用
${value}:如果传入类型是简单类型,${}中只能使用value
-->
<!-- 添加用户 -->
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.User">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
select LAST_INSERT_ID()
<!--
keyProperty:返回的主键存储在pojo中的哪个属性
order:selectKey的执行顺序,是相对与insert语句来说
由于mysql的自增原理执行完insert语句之后才将主键生成,所以这里selectKey的执行顺序为after
resultType:返回的主键是什么类型
LAST_INSERT_ID():是mysql的函数,返回auto_increment自增列新记录id值
-->
</selectKey>
insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
</insert>
<!-- 删除用户 -->
<delete id="deleteUserById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
delete from user where id=#{id}
</delete>
<!-- 更新用户 -->
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.User">
update user set username=#{username},birthday=#{birthday},sex=#{sex},address=#{address} where id=#{id}
</update>
</mapper>
3.非自增主键使用uuid():
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.User">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="java.lang.String" order="BEFORE">
select uuid()
</selectKey>
insert into user(id,username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{id},#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
</insert>
4.通过oracle的序列生成主键:
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="java.lang.Integer" order="BEFORE">
SELECT 自定义序列.NEXTVAL FROM DUAL
</selectKey>
insert into user(id,username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{id},#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
</insert>
创建会话操作数据库
1.根据用户id(主键)查询用户信息
2.根据用户名称模糊查询用户信息
3.添加用户
3.删除用户
public class MybatisFirst {
//根据id查询用户信息
public void fingUserByIdTest() throws IOException {
//加载配置文件
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//创建会话工厂
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//通过工厂得到SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//通过SqlSession操作数据库
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("test.fingUserById",1);//selectOne:查询出一条记录进行映射,单记录也可以使用selectList
//第一个参数为映射文件statement的id(namespqce+"."+id)
// 第二个指定映射文件中所匹配parameterType类型的参数
//结果为映射文件中的resultType类型的对象
System.out.print(user);
sqlSession.close();
}
//根据用户名称模糊查询
public void findUserByNameTest() throws IOException {
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
List<User> userList = sqlSession.selectList("test.findUserByUsername","小明");//selectList:查询多条记录进行映射
System.out.print(userList);
sqlSession.close();
}
//添加用户
public void insertUserTest() throws IOException {
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("张小明");
user.setAddress("河南郑州");
user.setSex("1");
sqlSession.insert("test.insertUser", user);
sqlSession.commit();//提交事务
sqlSession.close();
}
//删除用户
public void deleteUserTest() throws IOException {
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
sqlSession.delete("test.deleteUserById", 35);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
//更新用户
public void updateUserTest() throws IOException {
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("张大明");
user.setAddress("河南郑州");
user.setSex("2");
sqlSession.update("test.updateUser", user);
sqlSession.commit();//提交事务
sqlSession.close();
}
}
mybatis开发dao的方法
mapper代理开发
解决:原始dao开发方法中的问题
SqlSession使用范围
1.SqlSession创建过程:
(1)通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建会话工厂SqlSessionFactory
将SqlSessionFactoryBuilder当成一个工具类使用即可,不需要使用单例管理SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
即,在需要创建SqlSessionFactory时候,就new一次SqlSessionFactoryBuilder即可
(2)通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession,使用单例模式管理sqlSessionFactory(只有一个实例)
2.SqlSession:是一个面向用户(程序员)的接口
提供了很多操作数据库的方法:如:selectOne(返回单个对象)、selectList(返回单个或多个对象)
线程是不安全的,因为在SqlSesion实现类中除了有接口中的方法(操作数据库的方法)还有数据域属性
由以上特点可知,SqlSession最佳应用场合在方法体内,定义成局部变量使用
原始dao开发方法
原始的开发方法:dao接口+dao实现类
过程:
程序员需要写dao接口和dao实现类
需要向dao实现类中注入SqlSessionFactory(Spring),在方法体内通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession
问题:
dao接口实现类方法中存在大量模板方法
调用sqlsession方法时将statement的id硬编码
传入的变量,由于sqlsession方法使用泛型,即使变量类型传入错误,在编译阶段也不报错,不利于程序员开发
mapper动态代理方法
1.需要编写mapper接口(相当 于dao接口),还需要编写mapper.xml映射文件
编写mapper接口需要遵循一些开发规范,mybatis则可以自动生成mapper接口实现类代理对象
1、Mapper.xml文件中的namespace与mapper接口的类路径相同
2、Mapper接口方法名和Mapper.xml中定义的每个statement的id相同
3、Mapper接口方法的输入参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql 的parameterType的类型相同
4、Mapper接口方法的输出参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的resultType的类型相同
2.由开发规范得到案例对应新的映射文件和接口文件
UserMapper.xml(载入):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="cn.moke.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper"><!-- 1 -->
<!-- 根据id获取用户信息 -->
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User">
select * from user where id = #{id}
</select>
<!-- 自定义条件查询用户列表 -->
<select id="findUserByUsername" parameterType="java.lang.String"
resultType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User">
select * from user where username like '%${value}%'
</select>
<!-- 添加用户 -->
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
select LAST_INSERT_ID()
</selectKey>
insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address)
values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
</insert>
</mapper>
接口:
public interface UserMapper {//2,3,4
//根据用户id查询用户信息
public User findUserById(int id) throws Exception;
//查询用户列表
public List<User> findUserByUsername(String username) throws Exception;
//添加用户信息
public void insertUser(User user)throws Exception;
}
mapper接口方法参数只能有一个,系统是否不利于扩展维护:
系统框架中,dao层的代码是被业务层公用的,即使mapper接口只有一个参数,可以使用包装类型的pojo满足不同的业务方法的需求
注:久层方法的参数可以包装类型、map…,service方法中建议不要使用包装类型(不利于业务层的可扩展)
3.通过映射文件和接口实现案例:
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserMapper{
//注入sqlSessionFactory
public UserDaoImpl(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory){
this.setSqlSessionFactory(sqlSessionFactory);
}
Public void testFindUserById() throws Exception {
//获取session
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//获取mapper接口的代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//调用代理对象方法
User user = userMapper.findUserById(1);
/*
如果mapper方法返回单个pojo对象(非集合对象),代理对象内部通过selectOne查询数据库
如果mapper方法返回集合对象,代理对象内部通过selectList查询数据库
*/
System.out.println(user);
//关闭session
session.close();
}
...
}
SqlMapConfig.xml的详解
mybatis的全局配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml
properties属性
即数据库连接池的properties属性
将数据库连接参数单独配置在db.properties中,只需要在SqlMapConfig.xml中加载db.properties的属性值。
在SqlMapConfig.xml中就不需要对数据库连接参数硬编码
1.db.properties:
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123
2.SqlMapConfig.xml引用:
<properties resource="db.properties"/>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
3.properties特性:
MyBatis 将按照下面的顺序来加载属性:
在 properties 元素体内定义的属性首先被读取
然后会读取properties 元素中resource或 url 加载的属性,它会覆盖已读取的同名属性
最后读取parameterType传递的属性,它会覆盖已读取的同名属性
因此,建议不要在properties元素体内添加任何属性值,只将属性值定义在properties文件中
settings(全局参数配置)
mybatis框架在运行时可以调整一些运行参数
比如:开启二级缓存、开启延迟加载…
全局参数将会影响mybatis的运行行为
详细参见“学mybatis-settings.xlsx”文件
typeAliases(重点)
在mapper.xml中,定义很多的statement,statement需要parameterType指定输入参数的类型、需要resultType指定输出结果的映射类型
如果在指定类型时输入类型全路径,则不方便进行开发
可以针对parameterType或resultType指定的类型定义一些别名,在mapper.xml中通过别名定义,方便开发
1.mybatis默认支持别名
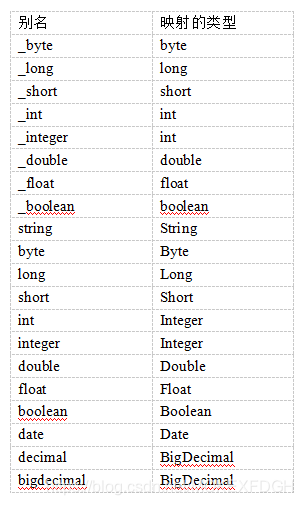
2.自定义别名(针对pojo)
<typeAliases>
<!-- 单个别名定义 -->
<typeAlias alias="user" type="cn.moke.mybatis.po.User"/>
<!-- 批量别名定义,扫描整个包下的类,别名为类名(首字母大写或小写都可以),常用! -->
<package name="cn.moke.mybatis.po"/>
<package name="其它包"/>
</typeAliases>
typeHandlers(类型处理器)
mybatis中通过typeHandlers完成jdbc类型和java类型的转换
通常情况下,mybatis提供的类型处理器满足日常需要,不需要自定义(即无需处理)
mappers(映射配置)
1.通过resource加载单个映射文件
<mapper resource="sqlmap/User.xml" />
2.通过mapper接口加载单个mapper
<mapper class="cn.moke.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper"/>
注:此种方法要求mapper接口名称和mapper映射文件名称相同,且放在同一个目录中
3.批量加载mapper(常用),即指定包下的所有mapper接口
<package name="cn.moke.mybatis.mapper"/>
注:此种方法也要求mapper接口名称和mapper映射文件名称相同,且放在同一个目录中
输入映射
通过parameterType指定输入参数的类型,类型可以是简单类型√、hashmap√、pojo的包装类型√
传递pojo的包装对象
使用自定义的包装类型的pojo,在包装类型的pojo中将复杂的查询条件包装进去
完成用户信息的综合查询,需要传入查询条件很复杂(可能包括用户信息、其它信息,比如商品、订单的)
1.包装类型pojo:
public class UserQueryVo{
//用户信息查询
private UserCustom userCustom;//UserCustom为User的扩展类
public UserCustom getUserCustom(){
return userCustom;
}
public void setUserCustom(UserCustom userCustom){
this.userCustom = userCustom;
}
...//等包装其他的查询条件、订单、商品
}
2.映射文件:
<select id="findUserList" parameterType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.UserQueryVo" resultType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.UserQueryVo">
select * from user where user.sex = #{userCustom.sex} and user.username like '%${userCustom.username}%'
</select>
3.接口文件:
public List<UserCustom> findUserList(UserQueryVo userQueryVo) throws Exception;
4.实现类:
UserQuery userQueryVo = new UserQuery();
UserCustom userCustom = new UserCustom();
userCustom.setSex("1");
userCustom.setUsername("张三丰");
userQueryVo.setUserCustom(userCustom);
List<UserCustom> list = userMapper.findUserList(userQueryVo);
输出映射
resultType
1.特点:
使用resultType进行输出映射,只有查询出来的列名和pojo中的属性名一致,该列才可以映射成功
如果查询出来的列名和pojo中的属性名全部不一致,没有创建pojo对象
只要查询出来的列名和pojo中的属性有一个一致,就会创建pojo对象
2.输出简单类型
<select id="findUserCount" parameterType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.UserQueryVo" resultType="int">
select count(*) from user where user.sex = #{userCustom.sex} and user.username like '%${userCustom.username}%'
</select>
接口文件:
public int findUserCount(UserQueryVo userQueryVo) throws Exception;
注:查询出来的结果集只有一行且一列,才可以使用简单类型进行输出映射
3.输出pojo对象和pojo列表
(1)不管是输出的pojo单个对象还是一个列表(list中包括pojo),在mapper.xml中resultType指定的类型是一样的
(2)在mapper.java指定的方法返回值类型不一样:输出单个pojo对象,方法返回值是单个对象类型;输出pojo对象list,方法返回值是List
注:生成的动态代理对象中是根据mapper方法的返回值类型确定是调用selectOne(返回单个对象调用)还是selectList (返回集合对象调用 )
resultMap
1.概述
mybatis中使用resultMap完成高级输出结果映射
使用场景:
如果查询出来的列名和pojo的属性名不一致,通过定义一个resultMap对列名和pojo属性名之间作一个映射关系
例如:SELECT id id_,username username_ FROM USER WHERE id=#{value}
使用步骤:
(1)定义resultMap
(2)使用resultMap作为statement的输出映射类型
2.定义resultMap
<resultMap type="user" id="userResultMap"><!-- type为最终映射的java对象类型;id为标识 -->
<id column="id_" property="id"/><!-- id用于主键;colume为查询出来的列名;property指定的pojo类型中的属性名 -->
<result column="username_" property="username"/><!-- result对应普通列的映射 -->
</resultMap>
3.使用resultMap
<select id="findUserResultMap" parameterType="int" resultType="userResultMap">
SELECT id id_,username username_ FROM USER WHERE id=#{value}
</select>
4.resultType和resultMap
使用resultType进行输出映射,只有查询出来的列名和pojo中的属性名一致,该列才可以映射成功
如果查询出来的列名和pojo的属性名不一致,通过定义一个resultMap对列名和pojo属性名之间作一个映射关系
动态sql
mybatis核心对sql语句进行灵活操作,通过表达式进行判断,对sql进行灵活拼接、组装
If、Where
对查询条件进行判断,如果输入参数不为空才进行查询条件拼接:
<!-- 传递pojo综合查询用户信息 -->
<select id="findUserList" parameterType="user" resultType="user">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="id!=null and id!=''">
and id=#{id}
</if>
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">
and username like '%${username}%'
</if>
</where>
</select>
sql片段
将上边实现的动态sql判断代码块抽取出来,组成一个sql片段。其它的statement中就可以引用sql片段。
1.定义sql片段(基于单表定义),例如上诉的例子的where语句:sql
<sql id="query_user_where">
<if test="id!=null and id!=''">
and id=#{id}
</if>
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">
and username like '%${username}%'
</if>
</sql>
2.引用sql片段:include
<select id="findUserList" parameterType="user" resultType="user">
select * from user
<where>
<include refid="query_user_where"/>
</where>
</select>
foreach
向sql传递数组或List,mybatis使用foreach解析
例如:在用户查询列表和查询总数的statement中增加多个id输入查询,有两种sql语句:
SELECT * FROM USER WHERE id=1 OR id=10 OR id=16
SELECT * FROM USER WHERE id IN(1,10,16)
1.在输入参数类型中添加List ids传入多个id
private List<Integer> ids;
2.修改mapper.xml
<if test="ids!=null">
<!--
collection:指定输入对象中集合属性
item:每个遍历生成对象
open:开始遍历时拼接的串
close:结束遍历时要拼接的串
separator:遍历的两个对象中需要拼接的串
-->
<foreach collection="ids" item="user_id" open=" and (" close=")" separator="or" >
id=#{user_id}
</foreach>
<!--第二种select语句:
<foreach collection="ids" item="user_id" open=" and id in (" close=")" separator="," >
#{user_id}
</foreach>
-->
</if>
高级映射
数据模型:
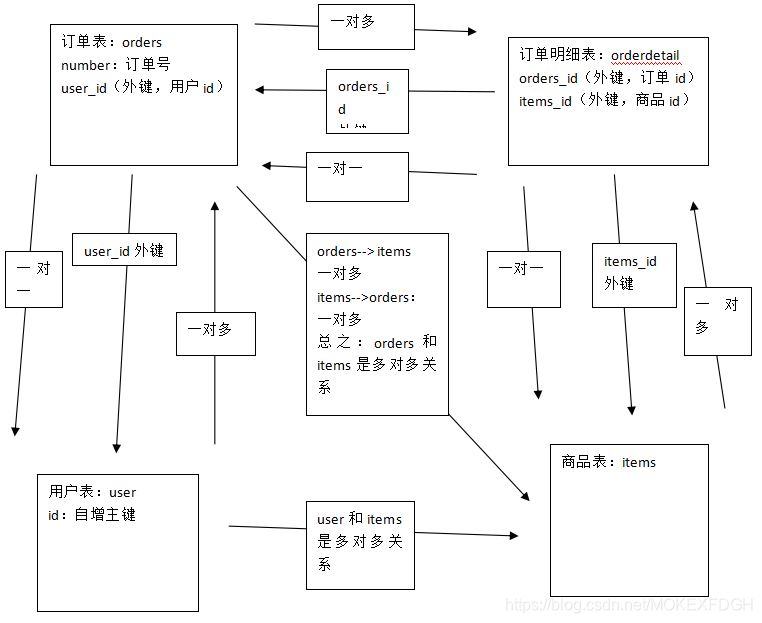
一对一
查询订单信息,关联查询创建订单的用户信息
1.使用resultType
(1)sql语句
SELECT
orders.*, user.username, user.address
FROM
orders, user
WHERE orders.user_id = user.id
(2)创建pojo(原始pojo不包含查询的所有字段):
public class OrdersCustom extends Orders {
private String username;// 用户名称
private String address;// 用户地址
//get/set...
}
(3)Mapper.xml
<!-- 查询所有订单信息 -->
<select id="findOrdersList" resultType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.OrdersCustom">
SELECT
orders.*, user.username, user.address
FROM
orders, user
WHERE orders.user_id = user.id
</select>
(4)Mapper接口:OrdersCustomMapper.java
public interface OrdersCustomMapper{
public List<OrdersCustom> findOrdersList() throws Exception; }
(5)使用:
public void testfindOrdersList()throws Exception{
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
OrdersCustomMapper ordersCustomMapper = session.getMapper(OrdersCustomMapper.class);
List<OrdersCustom> list = ordersCustomMapper.findOrdersList();
System.out.println(list);
session.close();
}
2.使用resultMap
(1)修改pojo类
在Orders类中加入User属性,user属性中用于存储关联查询的用户信息,因为订单关联查询用户是一对一关系
所以这里使用单个User对象存储关联查询的用户信息
public class Orders{
...
private User user;
}
(2)Mapper.xml
<!-- 定义resultMap -->
<resultMap type="cn.moke.mybatis.po.Orders" id="OrdersUserResultMap">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="user_id" column="user_id"/>
<result property="number" column="number"/>
<association property="user" javaType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.User">
<!--
association:用于映射关联查询单个对象的信息
property:要将关联查询的用户信息映射到Orders中哪个属性
-->
<id property="id" column="user_id"/>
<result property="username" column="username"/>
<result property="address" column="address"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="findOrdersList" resultMap="OrdersUserResultMap">
SELECT
orders.*, user.username, user.address
FROM
orders, user
WHERE orders.user_id = user.id
</select>
(3)Mapper接口:OrdersCustomMapper.java
public interface OrdersCustomMapper{
public List<Orders> findOrdersUserMap throws Exception; }
3.resultType和resultMap实现一对一查询小结:
(1)resultType:使用resultType实现较为简单
如果pojo中没有包括查询出来的列名,需要增加列名对应的属性,即可完成映射
如果没有查询结果的特殊要求建议使用resultType
(2)resultMap:需要单独定义resultMap
如果对查询结果有特殊的要求,使用resultMap可以完成将关联查询映射pojo的属性中
(3)resultMap可以实现延迟加载,resultType无法实现延迟加载
一对多
查询所有订单信息及订单下的订单明细信息
(1)sql语句
SELECT
orders.*,
USER.username,
USER.sex,
USER.address,
orderdetail.id orderdetail_id,
orderdetail.items_id,
orderdetail.items_num,
orderdetail.orders_id
FROM
orders,
USER,
orderdetail
WHERE orders.user_id = user.id AND orderdetail.orders_id=orders.id
注:使用resultType将上边的 查询结果映射到pojo中,订单信息的就是重复,需要使用双重循环遍历,去掉重复记录
(2)修改pojo
在Orders类中加入User属性,在Orders类中加入List orderdetails属性
public class Orders{
...
private User user;
private List<orderdetail> orderdetail;
}
(3)mapper.xml
<resultMap type="cn.moke.mybatis.po.Orders" id="userorderdetailmap">
<id property="id"column="id"/>
<result property="user_id" column="user_id"/>
<result property="number" column="number"/>
<association property="user" javaType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.User">
<id property="id" column="user_id"/>
<result property="username" column="username"/>
<result property="address" column="address"/>
</association>
<collection property="orderdetails" ofType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.Orderdetail">
<!--
一个订单关联查询出了多条明细,要使用collection进行映射
collection:对关联查询到多条记录映射到集合对象中
property:将关联查询到多条记录映射到cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orders哪个属性
ofType:指定映射到list集合属性中pojo的类型
-->
<id property="id" column="orderdetail_id"/>
<result property="items_id" column="items_id"/>
<result property="items_num" column="items_num"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
多对多
查询用户及用户购买商品信息
(1)sql语句:
SELECT
orders.*,
USER.username, USER.sex, USER.address,
orderdetail.id orderdetail_id, orderdetail.items_id, orderdetail.items_num, orderdetail.orders_id,
items.name items_name, items.detail items_detail, items.price items_price
FROM
orders, USER, orderdetail, items
WHERE orders.user_id = user.id AND orderdetail.orders_id=orders.id AND orderdetail.items_id = items.id
(2)修改pojo:
将用户信息映射到user中
在user类中添加订单列表属性List orderslist,将用户创建的订单映射到orderslist
在Orders中添加订单明细列表属性Listorderdetials,将订单的明细映射到orderdetials
在OrderDetail中添加Items属性,将订单明细所对应的商品映射到Items
(3)mapper.xml
<resultMap type="cn.moke.mybatis.po.User" id="userOrderListResultMap">
<id column="user_id" property="id"/>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<collection property="orders" ofType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.Orders">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result property="number" column="number"/>
<collection property="orderdetails" ofType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.Orderdetail">
<id column="orderdetail_id" property="id"/>
<result property="ordersId" column="id"/>
<result property="itemsId" column="items_id"/>
<result property="itemsNum" column="items_num"/>
<association property="items" javaType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.Items">
<id column="items_id" property="id"/>
<result column="items_name" property="name"/>
<result column="items_detail" property="detail"/>
</association>
</collection>
</collection>
</resultMap>
(4)多对多查询总结:
使用resultMap是针对那些对查询结果映射有特殊要求的功能,,比如特殊要求映射成list中包括多个list
延迟加载
resultMap可以实现高级映射(使用association、collection实现一对一及一对多映射)
association、collection具备延迟加载功能
例如:如果查询订单并且关联查询用户信息
当我们需要查询用户信息时再查询用户信息,把对用户信息的按需去查询就是延迟加载
特点:延迟加载:先从单表查询、需要时再从关联表去关联查询,大大提高数据库性能
使用association实现延迟加载
1.在SqlMapConfig核心配置文件开启延迟加载:
<settings>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
</settings>
2.resultMap中:
使用association中的select指定延迟加载去执行的statement的id
<resultMap type="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orders" id="userordermap2">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="user_id" column="user_id"/>
<result property="number" column="number"/>
<!--
select:指定延迟加载需要执行的statement的id
column:子查询中链接主表的条件的列名
关联查询的sql理解为:
SELECT orders.*,
(SELECT username FROM USER WHERE orders.user_id = user.id)username,
(SELECT sex FROM USER WHERE orders.user_id = user.id)sex
FROM orders
-->
<association property="user" javaType="cn.moke.mybatis.po.User" select="findUserById" column="user_id"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- 如果findUserById在其它mapper中需要前边加相应mapper的namespace -->
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="user">
select * from user where id=#{value}
</select>
注:collection和association一样在select属性中使用延迟加载
自己实现延迟加载
针对订单和用户两个表定义两个mapper方法:
1、订单查询mapper方法
2、根据用户id查询用户信息mapper方法
默认使用订单查询mapper方法只查询订单信息
当需要关联查询用户信息时再调用根据用户id查询用户信息mapper方法查询用户信息
查询缓存
mybatis提供查询缓存,用于减轻数据压力,提高数据库性能
查询缓存分为一级缓存,和二级缓存,区别如下:
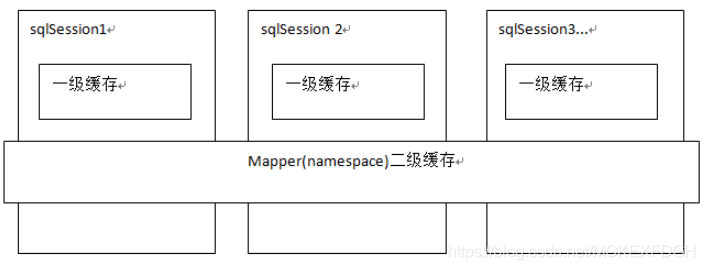
由图可知:
(1)一级缓存是SqlSession级别的缓存
在操作数据库时需要构造 sqlSession对象,在对象中有一个数据结构(HashMap)用于存储缓存数据
不同的sqlSession之间的缓存数据区域(HashMap)是互相不影响的
(2)二级缓存是mapper级别的缓存
多个SqlSession去操作同一个Mapper的sql语句,多个SqlSession可以共用二级缓存,二级缓存是跨SqlSession的
一级缓存
1.一级缓存原理:
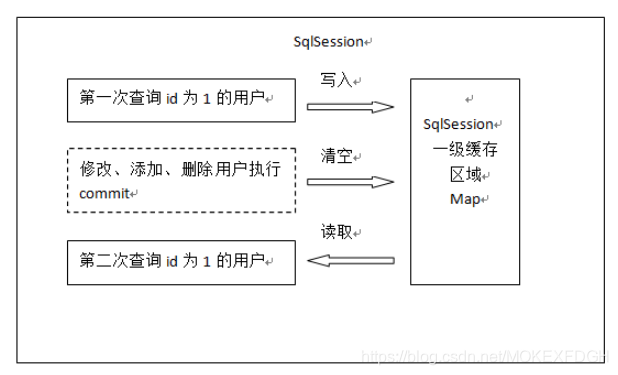
2.一级缓存的应用:
正式开发,是将mybatis和spring进行整合开发,事务控制在service中
一个service方法中包括 很多mapper方法调用
service{
//开始执行时,开启事务,创建SqlSession对象
//第一次调用mapper的方法findUserById(1)
//第二次调用mapper的方法findUserById(1),从一级缓存中取数据
//方法结束,sqlSession关闭
}
注:如果是执行两次service调用查询相同的用户信息,不走一级缓存,因为session方法结束,sqlSession就关闭,一级缓存就清空
二级缓存
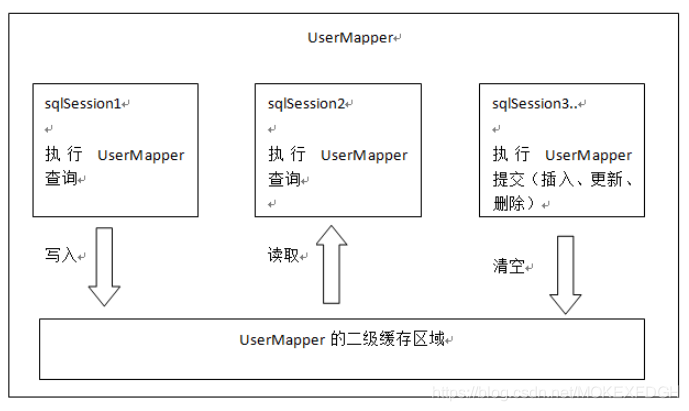
1.多个sqlSession请求UserMapper的二级缓存原理:
2.与一级缓存的区别:
二级缓存的范围更到,多个sqlsession可以恭喜一个二级缓存
每一个namespace的mapper都有一个二缓存区域,两个mapper的namespace如果相同,这两个mapper执行sql查询到数据将存在相同的二级缓存区域中
3.开启二级缓存
mybaits的二级缓存是mapper范围级别,除了在SqlMapConfig.xml设置二级缓存的总开关,还要在具体的mapper.xml中开启二级缓存
(1)在核心配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml中加入
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
(2)在具体mapper中开启,例如UserMapper.xml,直接添加一行
<cache/>
(3)将pojo类实现序列化接口:为了将缓存数据取出执行反序列化操作,因为二级缓存数据不一定全部存储在内存
注:如果存在父类、成员pojo都需要实现序列化接口
public class User implements Serializable{...}
4.useCache
在statement中设置useCache=false可以禁用当前select语句的二级缓存,即每次查询都会发出sql去查询,默认情况是true,即该sql使用二级缓存
<select id="findOrderListResultMap" resultMap="ordersUserMap" useCache="false">
适用场景:针对每次查询都需要最新的数据sql,要设置成useCache=false,禁用二级缓存
5.刷新缓存(清空缓存)
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User" flushCache="true">
默认情况下为true即刷新缓存,如果改成false则不会刷新
般下执行完commit操作都需要刷新缓存,flushCache=true表示刷新缓存,这样可以避免数据库脏读
6.二级缓存应用场景与局限性
(1)应用场景:
对于访问多的查询请求且用户对查询结果实时性要求不高,此时可采用mybatis二级缓存技术降低数据库访问量,提高访问速度
业务场景比如:耗时较高的统计分析sql、电话账单查询sql等
实现方法如下:通过设置刷新间隔时间,由mybatis每隔一段时间自动清空缓存,根据数据变化频率设置缓存刷新间隔flushInterval(cache的参数)
(2)局限性:
mybatis二级缓存对细粒度的数据级别的缓存实现不好
因为mybaits的二级缓存区域以mapper为单位划分,当一个商品信息变化会将所有商品信息的缓存数据全部清空
?解决此类问题需要在业务层根据需求对数据有针对性缓存?
ehcache
1.ehcache是一个分布式缓存框架,mybatis整合ehcache
2.分布式缓存:
系统为了提高系统并发,性能、一般对系统进行分布式部署(集群部署方式),如下:
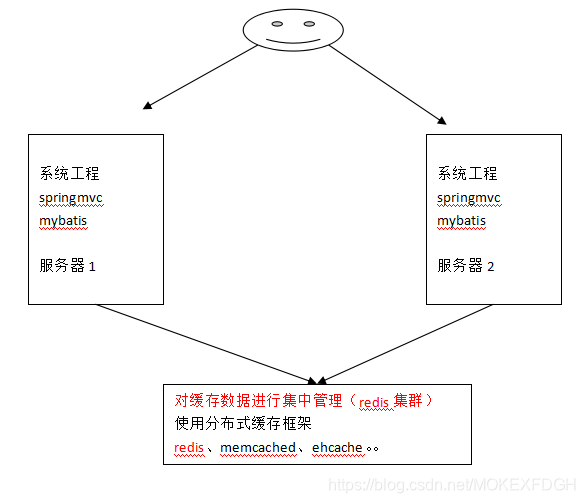
不使用分布缓存,缓存的数据在各各服务单独存储,不方便系统开发;所以要使用分布式缓存对缓存数据进行集中管理
而mybatis无法实现分布式缓存,所以需要和其它分布式缓存框架进行整合
3.整合方法
mybatis和ehcache整合,mybatis和ehcache整合包中提供了一个cache接口的实现类
如果要实现自己的缓存逻辑,实现cache接口开发即可
mybatis默认实现cache类是:PerpetualCache
整合步骤:
(1)加入jar包:ehcache-core、mybatis-enchache
(2)配置mapper中cache中的type为ehcache对cache接口的实现类型
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
(3)创建ehcache的配置文件
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../config/ehcache.xsd">
<diskStore path="F:\develop\ehcache" />
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
</defaultCache>
</ehcache>
mybatis与spring整合
整合步骤:
1.需要spring通过单例方式管理SqlSessionFactory
2.spring和mybatis整合生成代理对象,使用SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession。(spring和mybatis整合自动完成)
3.持久层的mapper都需要由spring进行管理
整合步骤
1.整合环境:mybatis3.2.7的jar包、spring3.2.0的jar包、mybatis和spring的整合包
2.创建配置文件:
(1)mybatis/SqlMapConfig.xml
(2)spring/applicationContext.xml
(3)db.properties:dataSource数据源配置文件
(4)log4j.properties:日志配置文件
3.在applicationContext.xml配置sqlSessionFactory和数据源
注:sqlSessionFactory在mybatis和spring的整合包下
<!-- 加载配置文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" />
<!-- 数据源,使用dbcp -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
<property name="maxActive" value="10" />
<property name="maxIdle" value="5" />
</bean>
<!-- sqlSessinFactory -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!-- 加载mybatis的配置文件 -->
<property name="configLocation" value="mybatis/SqlMapConfig.xml" />
<!-- 数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
原始dao开发(和spring整合后)
1.mapper.xml:User.xml编写->sqlmapconfig加载
2.dao:dao接口+dao实现类
(1)dao实现类继承SqlSessionDaoSupport,通过spring进行注入SqlSessoinFactory
<bean id=" "class="mapper接口的实现">
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
(2)dao实现类获取sqlsession,直接:this.getSqlSession();//SqlSessionDaoSupport
3.通过spring获取dao类的实例,执行方法(实现类会调用sqlsession的操作方法)
mapper代理开发(和spring整合后)
1.创建mapper.xml(映射文件)和mapper.java(mapper接口),sqlMapConfig加载:
<!-- 也可以使用扫描器 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper.xml文件的地址" />
</mappers>
2.spring创建代理对象
(1)通过MapperFactoryBean创建代理对象(需要针对每个mapper进行配置):
<bean id="userMapper" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean">
<property name="mapperInterface" value="mapper接口地址"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
(2)通过MapperScannerConfigurer进行mapper扫描(建议使用)
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="mapper接口包地址"></property>
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
注:basePackage:扫描包路径,中间可以用逗号或分号分隔定义多个包
自动扫描出来的mapper的bean的id为mapper类名(首字母小写),用以获取代理对象
如果将mapper.xml和mapper接口的名称保持一致且放在一个目录 则不用在sqlMapConfig.xml中进行配置(加载映射文件)
逆向工程
mybaits需要程序员自己编写sql语句,mybatis官方提供逆向工程
可以针对单表自动生成mybatis执行所需要的代码(mapper.java,mapper.xml、po…)
即,由数据库的表生成java代码(po类和mapper映射文件)
逆向工程的使用
1.下载逆向工程:mybatis-generator-core-1.3.2-bundle.zip
2.在generatorConfig.xml(index)中配置mapper生成的详细信息:
(1)添加要生成的数据库表
<table tableName="items"></table>
(2)po文件所在包路径
<!-- targetProject:生成PO类的位置 -->
<javaModelGenerator targetPackage="cn.moke.ssm.po"
targetProject=".\src">
<!-- enableSubPackages:是否让schema作为包的后缀 -->
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
<!-- 从数据库返回的值被清理前后的空格 -->
<property name="trimStrings" value="true" />
</javaModelGenerator>
(3)mapper文件(映射文件与接口)所在包路径
<!-- targetProject:mapper映射文件生成的位置 -->
<sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="cn.moke.ssm.mapper" argetProject=".\src">
<!-- enableSubPackages:是否让schema作为包的后缀 -->
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
</sqlMapGenerator>
<!-- targetPackage:mapper接口生成的位置 -->
<javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER" targetPackage="cn.moke.ssm.mapper" targetProject=".\src">
<!-- enableSubPackages:是否让schema作为包的后缀 -->
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
</javaClientGenerator>
配置文件如下:详见generatorSqlmapCustom工程
3.执行生成程序(index),会依据generatorConfig配置文件生成相应的po类、映射文件和mapper接口类
List<String> warnings = new ArrayList<String>();
boolean overwrite = true;
File configFile = new File("generatorConfig.xml");
ConfigurationParser cp = new ConfigurationParser(warnings);
Configuration config = cp.parseConfiguration(configFile);
DefaultShellCallback callback = new DefaultShellCallback(overwrite);
MyBatisGenerator myBatisGenerator = new MyBatisGenerator(config,callback, warnings);
myBatisGenerator.generate(null);
4.将生成工程中所生成的代码拷贝到自己的工程中,即可使用