1、一般树
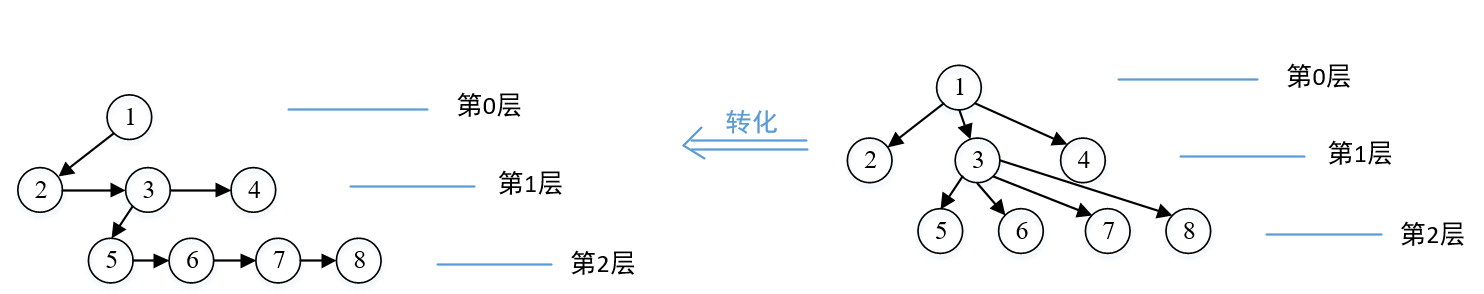
将这种一般的树转化成我们熟悉的单链表形式,这有三层,每一层都可以看成单链表或者多个分散的单链表
数据节点如下:
struct tree {
int elem;
struct tree *FirstChild;
struct tree *NextBro;
};
每个节点和第一个孩子还有下一个兄弟链接
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct tree { int elem; struct tree *FirstChild; struct tree *NextBro; }; struct tree *root_ptr = NULL; /* 知道第一个孩子的位置,将要添加的节点放到链尾 */ int register_child(struct tree **first, struct tree *tree_ptr) { struct tree *ptr = *first; while (ptr->NextBro) ptr = ptr->NextBro; ptr->NextBro = tree_ptr; return 0; } /* 3层树 * floor: 要添加的链表位于第几层 * FirstFa: 是第一层第几个节点的孩子 * num:节点的值 */ int add_tree(int floor, int FirstFa, int num) { struct tree *tree_ptr = (struct tree *)calloc(1, sizeof(struct tree)); if (!tree_ptr) { printf("calloc error\n"); return -1; } if (!root_ptr) { if (floor == 0) root_ptr = tree_ptr; } else { if (floor == 0) { printf("root really exist\n"); goto error; } else if (floor == 1) { if (!(root_ptr->FirstChild)) root_ptr->FirstChild = tree_ptr; else register_child(&(root_ptr->FirstChild), tree_ptr); } else if (floor == 2) { int i; struct tree *last_fa = root_ptr->FirstChild; if (!last_fa) { printf("no first floor\n"); //第1层没有 goto error; } for (i = 0; i < FirstFa; i++) last_fa = last_fa->NextBro; if (!last_fa) { printf("your father No exist\n"); //对应的父节点没有 goto error; } if (!(last_fa->FirstChild)) last_fa->FirstChild = tree_ptr; else register_child(&(last_fa->FirstChild), tree_ptr); } } tree_ptr->elem = num; tree_ptr->FirstChild = NULL; tree_ptr->NextBro = NULL; return 0; error: free(tree_ptr); return -1; } /* 输出该节点和节点下的所以数据 */ int output_fa_and_child(struct tree *fa) { static int cnt = 0; printf("data %d : %d\n", cnt++, fa->elem); struct tree *vy = fa->FirstChild; while (vy) { output_fa_and_child(vy); //递归调用 vy = vy->NextBro; } return 0; } /* 输出树中的所有数据 */ int output_tree_data(void) { if (!root_ptr) { printf("no data\n"); return -1; } output_fa_and_child(root_ptr); return 0; } int main() { int i; int ret; /* 向树中添加10个节点 */ int num[20] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0,10,11 }; ret = add_tree(0, 0, num[0]); if (ret < 0) { printf("add_tree error\n"); } for (i = 1; i < 5; i++) { ret = add_tree(1, 0, num[i]); if (ret < 0) { printf("add_tree error\n"); } } for (i = 1; i < 6; i++) { ret = add_tree(2, 1, num[4 + i]); if (ret < 0) { printf("add_tree error\n"); } } /* 输出所有节点中的数据 */ ret = output_tree_data(); if (ret < 0) printf("output_tree_data error\n"); return 0; }
填充树后的图如下:

输出数据顺序是1、2、3、6、7、8、9、0、4、5

扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
5467591 查看本文章

