一、EL表达式概述
在JSP开发中,为了获取Servlet域对象中存储的数据,经常需要书写很多Java代码,这样的做法会使JSP页面混乱,难以维护。为此,在JSP2.0规范中提供了EL表达式。EL全名为Expression Language,它是一种简单的数据访问语言。EL表达式的目的是替代jsp页面中脚本的编写,使JSP写起来更加简单。
二、EL表达式的11个内置对象
| 分类 |
内置对象名称 |
描述 |
| 作用域 |
pageScope |
page作用域 |
| requestScope |
request作用域 |
|
| sessionScope |
session作用域
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
5451400 查看本文章

|
|
| applicationScope |
application作用域 |
|
| 请求参数 |
param |
获得一个参数 |
| paramValues |
获得一组参数 |
|
| 请求头 |
header |
获得一个请求头 |
| headerValues |
获得一组请求头 |
|
| JSP上下文对象 |
pageContext |
|
| 全局初始化参数 |
initParam |
|
| cookie |
cookie |
【获得指定作用域的数据】
<%--初始化数据--%> <% pageContext.setAttribute("name", "pValue"); request.setAttribute("name", "rValue"); session.setAttribute("name", "sValue"); application.setAttribute("name", "aValue"); %> <%--使用JSP脚本获得--%> <%=pageContext.getAttribute("name")%> <!--如果找不到,返回null--> <%=request.getAttribute("name")%> <%=session.getAttribute("name")%> <%=application.getAttribute("name")%> <hr/> <%--使用EL表达式获得指定作用域的数据--%> ${pageScope.name} ${requestScope.name} ${sessionScope.name} ${applicationScope.name} <hr/> <%--依次获得数据--%> <%--底层使用pageContext.findAttribute("name"),依次从page、request、session、application获得数据,如果都没有返回null--%> ${name}

【请求参数】
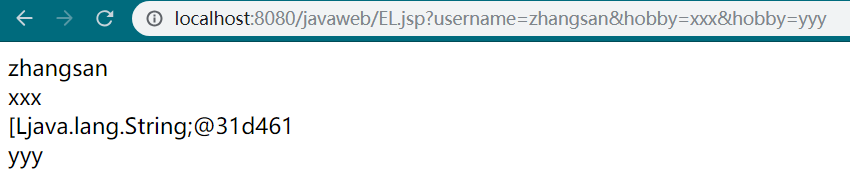
<%--请求路径:javaweb/EL.jsp?username=zhangsan&hobby=xxx&hobby=yyy--%> <%-- param.xxx 对应request.getParameter("xxx") paramValue.xxx 对应request.getParameterValues("xxx") --%> ${param.username}<br/> ${param.hobby}<br/> <!--获得第一个参数--> ${paramValues.hobby}<br/> <!--获得一组数据,使用数组--> ${paramValues.hobby[1]} <!--如果是数组,可以使用下标获得-->
【 请求头】
<%-- header.xxx 对应request.getHeader("xxx") headerValues.xxx 对应request.getHeaders("xxx") --%> ${header.accept}<br/> <%-- ${header.accept-Encoding} 这时非法的,有异常,"-"被解析成减号 --%> ${header['accept-Encoding']}<br/> ${headerValues['accept-Encoding'][0]}

.和[]的区别
1)[]用于有下标的数据(数组、list集合) .用于有属性的数据(map,对象)
2)如果属性名中包含有特殊的字符,必须使用[]
【pageContext】
<%--pageContext对应pageContext对象--%> jsp:<%=((HttpServletRequest)pageContext.getRequest()).getContextPath()%><br/> el:${pageContext.request.contextPath}
![]()
【全局初始化参数】
<%-- web.xml的配置 <context-param> <param-name>person</param-name> <param-value>张三</param-value> </context-param> --%> <%--initParam对应ServletContext.getInitParameter("person")--%> ${initParam.person}
【cookie】
setCookie.jsp
<% response.addCookie(new Cookie("username", "zhangsan")); response.addCookie(new Cookie("password", "123")); %>
getCookie.jsp
<body> <%-- cookie没有对应API。底层使用request.getCookies()获得所有cookies,然后遍历并存放到Map中(Map<name,obj>) --%> ${cookie}<br/> <%--使用Map获得所有cookie,Map<名称,对象>--%> ${cookie.username.name}:${cookie.username.value}<br> ${cookie.password.name}:${cookie.password.value} </body>
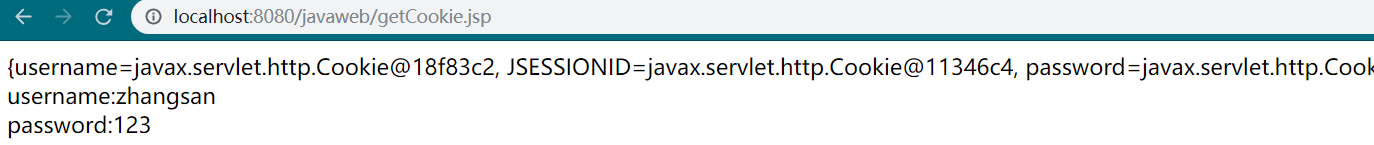
注意:需要先访问setCookie.jsp,然后再访问getCookie.jsp
三、EL的使用
3.1 获得数据
【获得指定作用域数据】(重要)
见上面
【获取字符串、对象、集合的数据】
<% pageContext.setAttribute("city", "北京"); // 存储字符串 request.setAttribute("city", "上海"); // 存储一个对象 User user = new User(); user.setId(1); user.setUsername("zhangsan"); user.setPassword("123"); session.setAttribute("user", user); // 存储一个集合 List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>(); User user1 = new User(); user1.setId(2); user1.setUsername("lisi"); user1.setPassword("123"); list.add(user1); User user2 = new User(); user2.setId(3); user2.setUsername("wangwu"); user2.setPassword("123"); list.add(user2); application.setAttribute("list", list); %> <%--JSP脚本获取数据--%> <%=request.getAttribute("city")%> <% User sessionUser = (User) session.getAttribute("user"); out.write(sessionUser.getUsername()); %> <%--EL获取数据--%> ${requestScope.city} ${sessionScope.user.username} ${applicationScope.list[1].username} <%--使用EL表达式全域查找--%> ${city} ${user.username} ${list[1].username}
3.2 执行运算
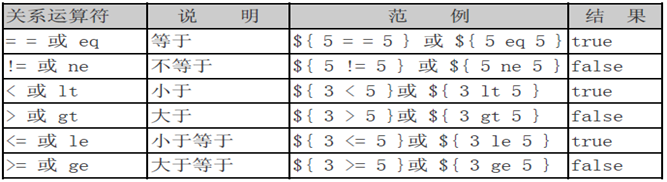
语法:${运算表达式},EL表达式支持如下运算符:
【关系运算符】
【逻辑运算符】
【empty运算符】
检查对象是否为null(空)
【二元表达式】
${user!=null?user.name :""}
四、EL函数库
4.1 EL函数库介绍
由于在JSP页面中显示数据时,经常需要对显示的字符串进行处理,SUN公司针对于一些常见处理定义了一套EL函数库供开发者使用。
这些EL函数在JSTL开发包中进行描述,因此在JSP页面中使用SUN公司的EL函数库,需要导入JSTL开发包,并在页面中使用taglib指令导入EL函数库
<%@ taglib prefix="fn" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/functions" %>
4.2 常用函数
-
String toUpperCase(String input):把参数转换成大写
-
String toLowerCase(String input):把参数转换成小写
-
int indexOf(String input, String substring):从大串中输出小串的位置
-
boolean contains(String input, String substring):查看大串中是否包含小串
-
boolean containsIgnoreCase(String input, String substring):忽略大小写的,是否包含
-
boolean startsWith(String input, String substring):是否以小串为前缀
-
boolean endsWith(String input, String substring):是否以小串为后缀
-
String substring(String input, int beginIndex, int endIndex):截取子串
-
String substringAfter(String input, String substring):获取大串中,小串所在位置后面的字符串
-
substringBefore(String input, String substring):获取大串中,小串所在位置前面的字符串
-
String escapeXml(String input):把input中“<”、">"、"&"、"'"、""",进行转义
-
String trim(String input):去除前后空格
-
String replace(String input, String substringBefore, String substringAfter):替换
-
String[] split(String input, String delimiters):分割字符串,得到字符串数组
-
int length(Object obj):可以获取字符串、数组、各种集合的长度
-
String join(String array[], String separator):联合字符串数组
<%@taglib prefix="fn" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/functions" %> … String[] strs = {"a", "b","c"}; List list = new ArrayList(); list.add("a"); pageContext.setAttribute("arr", strs); pageContext.setAttribute("list", list); %> ${fn:length(arr) }<br/><!--3--> ${fn:length(list) }<br/><!--1--> ${fn:toLowerCase("Hello") }<br/> <!-- hello --> ${fn:toUpperCase("Hello") }<br/> <!-- HELLO --> ${fn:contains("abc", "a")}<br/><!-- true --> ${fn:containsIgnoreCase("abc", "Ab")}<br/><!-- true --> ${fn:contains(arr, "a")}<br/><!-- true --> ${fn:containsIgnoreCase(list, "A")}<br/><!-- true --> ${fn:endsWith("Hello.java", ".java")}<br/><!-- true --> ${fn:startsWith("Hello.java", "Hell")}<br/><!-- true --> ${fn:indexOf("Hello-World", "-")}<br/><!-- 5 --> ${fn:join(arr, ";")}<br/><!-- a;b;c --> ${fn:replace("Hello-World", "-", "+")}<br/><!-- Hello+World --> ${fn:join(fn:split("a;b;c;", ";"), "-")}<br/><!-- a-b-c --> ${fn:substring("0123456789", 6, 9)}<br/><!-- 678 --> ${fn:substring("0123456789", 5, -1)}<br/><!-- 56789 --> ${fn:substringAfter("Hello-World", "-")}<br/><!-- World --> ${fn:substringBefore("Hello-World", "-")}<br/><!-- Hello --> ${fn:trim(" a b c ")}<br/><!-- a b c --> ${fn:escapeXml("<html></html>")}<br/> <!-- <html></html> -->
4.3 自定义EL函数库
- 写一个类,写一个有返回值的静态方法;
- 编写itcast.tld文件,可以参数fn.tld文件来写,把itcast.tld文件放到/WEB-INF目录下;
- 在页面中添加taglib指令,导入自定义标签库。
ItcastFuncations.java
package cn.itcast.el.funcations; public class ItcastFuncations { public static String test() { return "传智播客自定义EL函数库测试"; } }
itcast.tld(放到classes下)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <taglib xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-jsptaglibrary_2_0.xsd" version="2.0"> <tlib-version>1.0</tlib-version> <short-name>itcast</short-name> <uri>http://www.itcast.cn/jsp/functions</uri> <function> <name>test</name> <function-class>cn.itcast.el.funcations.ItcastFuncations</function-class> <function-signature>String test()</function-signature> </function> </taglib>
index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib prefix="itcast" uri="/WEB-INF/itcast.tld" %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <body> <h1>${itcast:test() }</h1> </body> </html>