版权声明:本人博客欢迎转载,但是请表明原链接和出处! https://blog.csdn.net/Phone_1070333541/article/details/87797366
一、是什么
Spring Cloud Ribbon 是基于 Netflix Ribbon 实现的一套客户端负载均衡的工具。
简单的说,Ribbon 是 Netflix 发布的开源项目,主要功能是提供客户端的软件负载均衡算法,将 Netflix 的中间层服务连接在一起。Ribbon 客户端组件提供一系列完善的配置项如连接超时,重试等。简单的说,就是在配置文件中列出Load Balancer(简称LB)后面所有的机器,Ribbon 会自动的帮助你基于某种规则(如简单轮询,随机连接等)去连接这些机器。我们也很容易使用 Ribbon 实现自定义的负载均衡算法。
二、能干嘛
1. 负载均衡
- LB,即负载均衡(Load Balance),在微服务或分布式集群中经常用的一种应用。
- 负载均衡简单的说就是将用户的请求平摊的分配到多个服务上,从而达到系统的 HA。
- 常见的负载均衡有软件Nginx,LVS,硬件 F5等。
- 相应的在中间件,例如:dubbo和SpringCloud中均给我们提供了负载均衡,SpringCloud的负载均衡算法可以自定义。
2. 集中式 LB
- 即在服务的消费方和提供方之间使用独立的LB设施(可以是硬件,如F5, 也可以是软件,如nginx), 由该设施负责把访问请求通过某种策略转发至服务的提供方
3. 进程内 LB
- 将LB逻辑集成到消费方,消费方从服务注册中心获知有哪些地址可用,然后自己再从这些地址中选择出一个合适的服务器。
- Ribbon就属于进程内LB,它只是一个类库,集成于消费方进程,消费方通过它来获取到服务提供方的地址。
三、架构说明
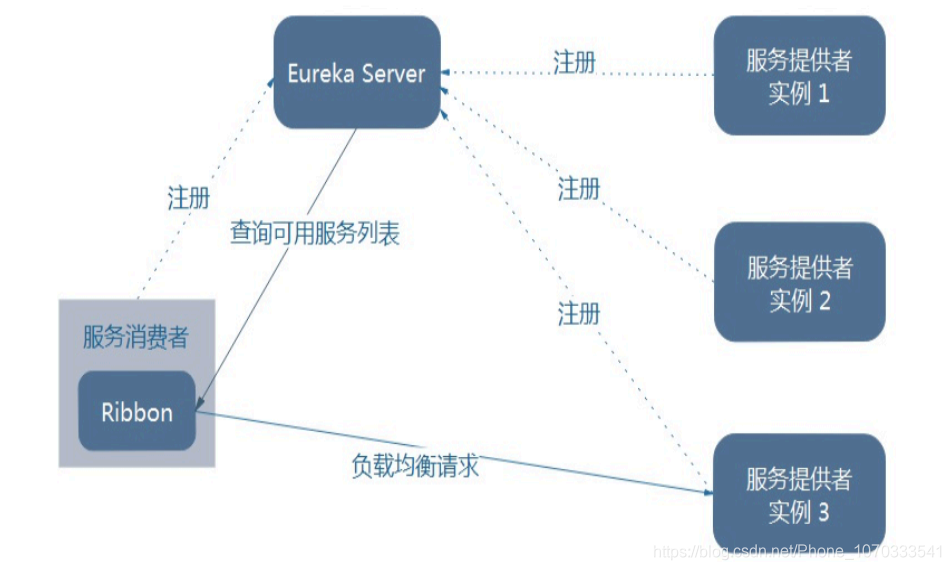
四、Ribbon 工作步骤
- Ribbon 在工作时分成两步
- 第一步先选择 EurekaServer ,它优先选择在同一个区域内负载较少的server。
- 第二步再根据用户指定的策略,在从server取到的服务注册列表中选择一个地址。
- 其中Ribbon提供了多种策略:比如轮询、随机和根据响应时间加权。
五、负载均衡策略
1. 负载均衡算法

2.更换算法方式
@configuration
public class ConfigBean{
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public Restemplate getRestTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
@Bean
public IRule myRule(){
return new RoundRobinRule();
}
}
- 或者:
- 启动类上添加@RibbonClient(name=“服务名称”,configuration=配置类.class)。
- 然后注意:配置类不能放在启动类(带有@ComponentScan)同级的包及其子包下。
- 然后配置类内容如下:
@configuration
public class MySelfRule{
@Bean
public IRule myRule(){
return new RandomRule();// 自定义为随机算法
}
}
3. 例子
- 要求每台服务器被调用5次才能轮询下一个,也就是说以前每台机器一次,现在每台机器5次。
public class RandomRule_my extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {
/**
* Randomly choose from all living servers
*/
@edu.umd.cs.findbugs.annotations.SuppressWarnings(value = "RCN_REDUNDANT_NULLCHECK_OF_NULL_VALUE")
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
return null;
}
Server server = null;
private int total = 0; // 总共被调用的次数,目前要求每台被调用5次
private int currentIndex = 0; // 当前提供服务的机器号
while (server == null) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
return null;
}
List<Server> upList = lb.getReachableServers();
List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers();
int serverCount = allList.size();
if (serverCount == 0) {
/*
* No servers. End regardless of pass, because subsequent passes
* only get more restrictive.
*/
return null;
}
//int index = chooseRandomInt(serverCount);
//server = upList.get(index);
// private int total = 0; // 总共被调用的次数,目前要求每台被调用5次
// private int currentIndex = 0; // 当前提供服务的机器号
if(total < 5){
server = upList.get(currentIndex);
total++;
}else{
total = 0;
currentIndex++;
if(currentIndex >= upList.size()){
currentIndex = 0;
}
}
if (server == null) {
/*
* The only time this should happen is if the server list were
* somehow trimmed. This is a transient condition. Retry after
* yielding.
*/
Thread.yield();
continue;
}
if (server.isAlive()) {
return (server);
}
// Shouldn't actually happen.. but must be transient or a bug.
server = null;
Thread.yield();
}
return server;
}
protected int chooseRandomInt(int serverCount) {
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(serverCount);
}
@Override
public Server choose(Object key) {
return choose(getLoadBalancer(), key);
}
}
定义完这些以后,要在配置类中 new RandomRule_my() ,来使用新的算法。