文章目录
概述
nginx是一款高性能的http和反向代理服务器,它能够支持高达50000个并发连接数的响应,具有内存、cpu等系统资源消耗低,运行稳定的特点。
在日常的生产过程中nginx主要用于1、读取静态文件充当静态服务器,2、负载功能,3、反向代理的路由功能
nginx的安装
centos下安装nginx
wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.9.0.tar.gz
tar -zxvf nginx-1.9.0.tar.gz
cd nginx-1.9.0
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module
make && make install
–prefix 指定安装目录
–with-http_ssl_module 安装https模块
make 编译
make install 安装
目录结构
conf 配置文件
html 网页文件
logs 日志文件
sbin 二进制程序
nginx常用命令
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx #启动命令
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop #停止命令
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s quit #退出命令
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t #检查配置文件是否正确
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload #重新加载配置文件
#Nginx的信号
kill -TERM pid #快速关闭nginx
kill -QUIT pid #从容关闭nginx
kill -HUP pid #平滑重启,重新加载配置文件
kill -USR1 pid #重新生成(打开)配置文件
kill -USR2 pid #平滑升级可执行程序
kill -9 pid #强制关闭nginx
nginx的日志切割
通过访问日志,你可以得到用户地域来源、跳转来源、使用终端、某个URL访问量等相关信息;通过错误日志,你可以得到系统某个服务或server的性能瓶颈等。因此,将日志好好利用,你可以得到很多有价值的信息。
-
编写切割脚本 nginxLogRotate.sh
#!/bin/bash LOGS_PATH=/usr/local/nginx/logs YESTERDAY=$(date -d "yesterday" +%Y%m%d) mv ${LOGS_PATH}/access.log ${LOGS_PATH}/access_${YESTERDAY}.log mv ${LOGS_PATH}/error.log ${LOGS_PATH}/error_${YESTERDAY}.log kill -USR1 $(cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid) -
建立定时任务
59 23 * * * /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginxLogRotate.sh
nginx的配置详解
nginx.conf配置文件结构
main 全局设置
events设定nginx的工作模式及连接数上限
http 服务器相关属性
server 虚拟主机设置
upstream 上游服务器设置,主要为反向代理、负载均衡相关配置
location URL匹配特定位置后的设置)
内置变量
| 变量 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| $host | http请求头中的(Host)字段,如果请求头中的host不可用或者空,则为请求头中的server名称 |
| $http_HEADER | HTTP请求头中的内容,HEADER为HTTP请求中的内容转为小写,-变为_(破折号变为下划线),例如:$http_user_agent(Uaer-Agent的值) |
| $remote_addr | 客户端的IP地址 |
| $remote_port | 客户端的端口 |
| $request_method | 这个变量是客户端请求的动作,通常为GET或POST |
| $request_uri | 客户端请求的原始URI,带参数 |
| $scheme | 所用的协议,比如http或者是https |
| $server_name | 服务器名称 |
| $server_port | 请求到达服务器的端口号 |
| $server_protocol | 请求使用的协议,通常是HTTP/1.0或HTTP/1.1 |
| $uri | 请求中的当前URI(不带请求参数) |
| $args | 请求中的参数 |
实际使用过程中
访问路径为 : http://192.168.0.207/static/a.html?name=jaye 时
$request_uri 的值为:/static/a.html?name=jaye?name=jaye
$uri的值为/static/a.html?name=jaye
server 虚拟主机
Location规则
-
访问路径分割

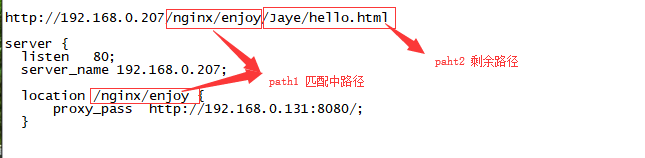
-
Location匹配符
| 匹配符 | 规则说明 |
|---|---|
| = | 精确匹配 : 当匹配路径与 path完全相等时匹配成功 |
| 无前缀 和 ^~ | 一般匹配 : 其中^~也称为非正则匹配 |
| ~ 和 ~* | 正则匹配: ~ 开头表示区分大小写的正则匹配,~* 开头表示不区分大小写的正则匹配 |
| !~ 和 !~* | !~ 和 !~* 分别为区分大小写不匹配及不区分大小写不匹配的正则 |

-
Location下的 root
当在Location{}遇到 root时,会传递过来path(整个路径)
#页面请求路径 http://192.168.0.207:81/static/a.html #实际访问路径 相当于访问html文件夹下的/static/a.html location /static { root html/; } -
Location下的alias
当在Location{}遇到 root时,只会传递path2(剩余路径)
#页面请求路径 http://192.168.0.207:81/target/b.html #实际访问路径 相当于访问 html/static/ 文件夹下的 /b.html location /target { alias html/static/; } -
Location下的proxy_pass
proxy_pass 反向代理,跳转到第三方
#当proxy_pass代理的路径端口后面没有 / 时,传递path(整个路径) #页面请求路径 http://192.168.0.207:81/Jaye/hello.html #实际访问路径 http://192.168.0.131:8080/Jaye/hello.html location /Jaye/hello { proxy_pass http://192.168.0.131:8080; }#当proxy_pass代理的路径端口后面有 / 时,传递path2(剩余路径) #页面请求路径 http://192.168.0.207:81/nginx/Jaye/hello.html #实际访问路径 http://192.168.0.207:8080/Jaye/hello.html location /nginx { proxy_pass http://192.168.0.207:8080/; } -
index执行时机
Root/alias时,若页面请求以/结尾,则认为path只到目录.此时启动index,找目录内的index文件
#当访问的路径是http://192.168.0.207:81/index时返回404页面 #当访问的路径是http://192.168.0.207:81/index/时返回的是index.html页面 #注意index.html前面必须有/,否则不管那个访问路径都是404页面 location /index { root html/; index /index.html; }
Rewrite的使用 - 重写
-
语法格式
rewrite regex replacement [flag]; flag=【break/last/redirect/permanent/不写】
regex : 正则表达式
replacement : 替换的值
flag : 是处理标志 -
regex 正则
正则 ^/ 表示:总是匹配
#访问路径 http://192.168.0.207:82/aa.html #本来应该是在html/static/下寻找aa.html,但实际上是在html/static/下寻找a.html #注意: replacement的值必须是/a.html而不能是a.html,否则会报404找不到页面 server { listen 82; server_name 192.168.0.207; location /aa.html { rewrite ^/ /a.html break; root html/static/; } }rewrite正则匹配命中,则修改为path = /a.html(若不命中呢,不执行)
#访问路径 http://192.168.0.207:82/bb.html #不匹配 /*.js 正则表达式,所以不会执行rewrite重写替换操作 location /bb.html { rewrite /*.js /b.html break; root html/static/; } -
flag详解
当值为 redirect/permanent/,执行后浏览器中显示的访问路径会发生改变,称之为页面重定向
当值为 break/last/,浏览器中显示的访问路径不会发生改变,称之为内部重定向permanent 和redirect的区别
permanent为301状态的永久重定向,redirect为302状态的临时重定向。对浏览器的记忆有区别
break 和 last 的区别
当以last结尾时,会以改写后的路径重新引发Location定位
当以break结尾时,直接执行完当前的Location{}就会结束
在生产环境中应避免使用last,因为容易引发死循环#访问路径为 http://192.168.0.207:82/aa.html #rewrite 重写后的路径为 http://192.168.0.207:82/aa.html , #last结尾会以重写后的路径为基础重新引发Location定位 #页面最终显示内容为 http://192.168.0.207:82/c.html 页面的内容 location /aa.html { rewrite ^/ /a.html last; root html/static/; } location /a.html { rewrite ^/ /c.html break; root html/static/; }
负载均衡
upstream :用以配置负载的策略,并按照对应的策略把请求发到配置的后台tomcat地址 。 nginx自带的策略有:轮询/权重/ip_hash
-
轮询
每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能自动剔除
upstream hello{ server 192.168.0.207:8080; server 192.168.0.131:8080; } server { listen 80; server_name 192.168.0.207; location /Jaye { proxy_pass http://hello; } } -
权重
weight指定轮询几率,weight和访问比率成正比,用于后端服务器性能不均的情况。down掉的服务器 暂时不参与负载
upstream hello{ server 192.168.0.207:8080 weight=2; server 192.168.0.131:8080 weight=1; } server { listen 80; server_name 192.168.0.207; location /Jaye { proxy_pass http://hello; } } -
ip_hash
每个请求按访问ip的hash结果分配,这样同一客户端的请求总是发往同一个后端服务器,可以解决session的问题。
upstream hello{ ip_hash; server 192.168.0.207:8080; server 192.168.0.131:8080; } server { listen 80; server_name 192.168.0.207; location /Jaye { proxy_pass http://hello; } } -
注意事项
proxy_pass http://hello; 的含义是寻找与hello同名的upstream,并将hello字段替换为upstream中server的值,所以proxy_pass的反向代理原则和替换后的路径是一致的。如http://hello替换后为http://192.168.0.207:8080或者http://192.168.0.131:8080这时端口后面是没有斜杠的,location匹配后传递过来的路径将会是path(整个路径)。而proxy_pass的为http://hello/;时,替换后为http://192.168.0.207:8080/或者http://192.168.0.131:8080/这时端口后面是有斜杠的,location匹配后传递过来的路径就会是path2(匹配后剩余路径)。
跨域
-
跨域的解决方案
1、最常用的是,jsonp。此方案需要前后端共同协作来解决。
2、cors跨域,此方式非常优雅,是w3c组织制定的解决方案。为目前主流方案。方案流程 -
nginx中的跨域配置
#是否允许请求带有验证信息 add_header Access-Control-Allow-Credentials true; #允许跨域访问的域名,可以是一个域的列表,也可以是通配符* add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *; #允许脚本访问的返回头 add_header Access-Control-Allow-Headers 'x-requested-with,content-type,Cache-Control,Pragma,Date,x-timestamp'; #允许使用的请求方法,以逗号隔开 add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods 'POST,GET,OPTIONS,PUT,DELETE'; #允许自定义的头部,以逗号隔开,大小写不敏感 add_header Access-Control-Expose-Headers 'WWW-Authenticate,Server-Authorization'; #P3P支持跨域cookie操作 add_header P3P 'policyref="/w3c/p3p.xml", CP="NOI DSP PSAa OUR BUS IND ONL UNI COM NAV INT LOC"'; if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') { return 204; }
防盗链
- 原理
当html页面中通过url访问图片等资源时,会携带访问当前html页面的url,保持在referers字段中
nginx可以通过相关配置校验referers是否符合条件,如果不符合条件返回404.即可阻止资源的访问 - 配置
location ^~ /img { valid_referers *.Jaye.com if($valid_referers){ return 404; } root html/img; }
缓存
- 配置
使用expires命令:配置过期时间
location ^~ /qq.png { expires 2s; #缓存2秒 expires 2m; #缓存2分钟 expires 2h; #缓存2小时 expires 2d; #缓存2天 root html/img; }
压缩
压缩资源后在进行传输可以节省带宽(压缩和解压消耗cpu)
-
原理
1.浏览器在进行url请求时会携带支持的压缩方式
2.nginx通过压缩方式压缩文件后进行(传输)返回 -
配置
location ~ /(.*)\.(html|js|css) { gzip on; #启用gzip压缩 gzip_types application/javascript text/css; #对js,css 文件启用压缩功能 gzip_min_length 1024; #所压缩文件的最小值,小于该值不会压缩 gzip_buffers 4 1k; #设置压缩响应的缓存块的大小和个数 gzip_comp_level 1; #压缩水平,默认1. 取值范围1-9,值越大压缩比率越大,但越耗cpu时间 root html/gzip; }
使用https
-
创建证书和key
在实际生产过程中证书和key是需要购买的
# 1、创建服务器私钥,命令会让你输入一个口令: openssl genrsa -des3 -out server.key 1024 # 2、创建签名请求的证书(CSR): openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr # 3、在加载SSL支持的Nginx并使用上述私钥时除去必须的口令: openssl rsa -in server.key -out server_nopass.key # 4、最后标记证书使用上述私钥和CSR: openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in server.csr -signkey server_nopass.key -out server.crt -
conf配置
server { listen 84; server_name 192.168.0.207; rewrite ^/ https://192.168.0.207:443$uri redirect; } server { listen 443 ssl; server_name 192.168.0.207; ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/conf.d/server.crt; ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/conf.d/server_nopass.key; location /static { root html; index index.html; } }
nginx的主从 - keepalived
-
安装
下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1G7sLL-YkZGSMu8G76yz1Rw 密码:adbw
prefix :程序安装目录 /data/program/keepalived
默认配置文件目录 /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
网盘下的keepalived在centos6下测试通过./configure --prefix=/data/program/keepalived --sysconf=/etc make && make install -
主机配置
! Configuration File for keepalived global_defs { router_id LVS_DEVEL } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state MASTER interface eno16777736 virtual_router_id 51 priority 200 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.0.200 } } -
从机配置
! Configuration File for keepalived global_defs { router_id LVS_DEVEL } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state BACKUP interface eno16777736 virtual_router_id 51 priority 100 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.0.200 } } -
keepalived监控nginx
#监控脚本 #!/bin/bash A=`ps -C nginx --no-header |wc -l` if [ $A -eq 0 ];then /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx #重启nginx if [ `ps -C nginx --no-header |wc -l` -eq 0 ];then #nginx重启失败,则停掉keepalived服务,进行VIP转移 killall keepalived #杀掉,vip就漫游到另一台机器 fi fi#修改主机配置 调用监控脚本 ! Configuration File for keepalived global_defs { router_id LVS_1 } vrrp_script chk_http_port { script "/usr/local/src/chk_nginx_pid.sh" #心跳执行的监控脚本 interval 2 #(检测脚本执行的间隔,单位是秒) weight 2 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state MASTER interface eno16777736 #系统网卡 virtual_router_id 51 #主备两机器一致 priority 100 #值大的机器,胜出 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } track_script { chk_http_port #(调用检测脚本) } virtual_ipaddress { #可虚拟多个ip 192.168.0.200 } }
