come from ; https://source.android.com/devices/camera
Camera

Android's camera Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) connects the higher level camera framework APIs in Camera 2 to your underlying camera driver and hardware. The camera subsystem includes implementations for camera pipeline components while the camera HAL provides interfaces for use in implementing your version of these components.
Note: If you are implementing the Camera HAL on Android 8.0 and higher, you must use the HIDL interface. For information on the legacy components, see Legacy HAL components.
Architecture
The following figure and list describe the HAL components:
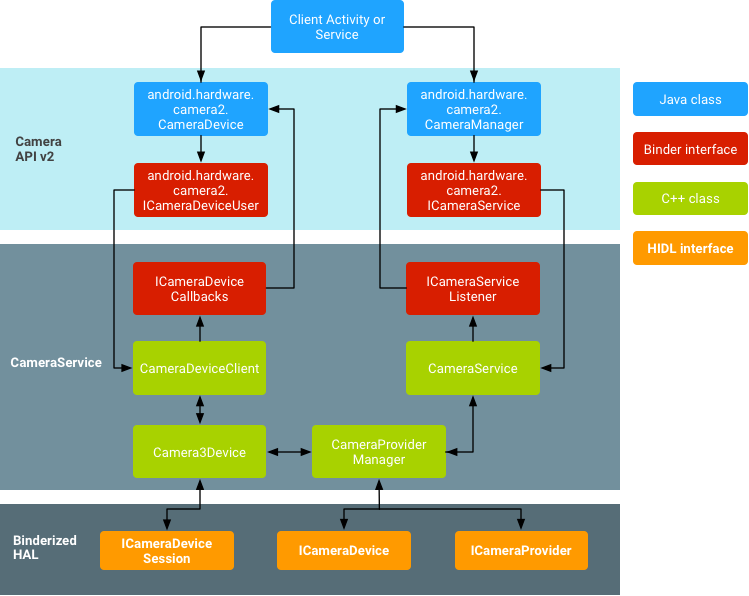
Figure 1. Camera architecture
Application framework
At the application framework level is the app's code, which uses the Camera 2 API to interact with the camera hardware. Internally, this code calls corresponding Binder interfaces to access the native code that interacts with the camera.
AIDL
The binder interface associated with CameraService can be found atframeworks/av/camera/aidl/android/hardware. The generated code calls the lower level native code to obtain access to the physical camera and returns data that is used to create the CameraDevice and eventuallyCameraCaptureSession objects at the framework level.
Native framework
This framework residing in frameworks/av/ provides a native equivalent to the CameraDevice andCameraCaptureSession classes. See also, NDK camera2 reference.
Binder IPC interface
The IPC binder interface facilitates communication over process boundaries. There are several camera binder classes located in the frameworks/av/camera/camera/aidl/android/hardware directory that call into camera service. ICameraService is the interface to the camera service; ICameraDeviceUser is the interface to a specific opened camera device; and ICameraServiceListener and ICameraDeviceCallbacks are the respective CameraService and CameraDevice callbacks to the application framework.
Camera service
The camera service, located in frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/CameraService.cpp, is the actual code that interacts with the HAL.
HAL
The hardware abstraction layer defines the standard interface that the camera service calls into and that you must implement to have your camera hardware function correctly.
Implementing the HAL
The HAL sits between the camera driver and the higher level Android framework and defines an interface you must implement so apps can correctly operate the camera hardware. From Android 8.0, the Camera HAL interface is part of Project Treble and the corresponding HIDL interfaces are defined in hardware/interfaces/camera.
A typical binderized HAL must implement the following HIDL interfaces:
- ICameraProvider: For enumerating individual devices and managing their status.
- ICameraDevice: The camera device interface.
- ICameraDeviceSession: The active camera device session interface.
Reference HIDL implementations are available for CameraProvider.cpp, CameraDevice.cpp andCameraDeviceSession.cpp. The implementation wraps old HALs that still use the legacy API. Starting with Android 8.0, Camera HAL implementations must use the HIDL API; use of the legacy interface is not supported.
For more information on Treble and HAL development, see Treble Resources.
Legacy HAL components
This section describes the architecture of the legacy HAL components and how to implement the HAL. Camera HAL implementations on Android 8.0 and higher must use the HIDL API instead, described above.
Architecture (legacy)
The following figure and list describe the legacy camera HAL components:
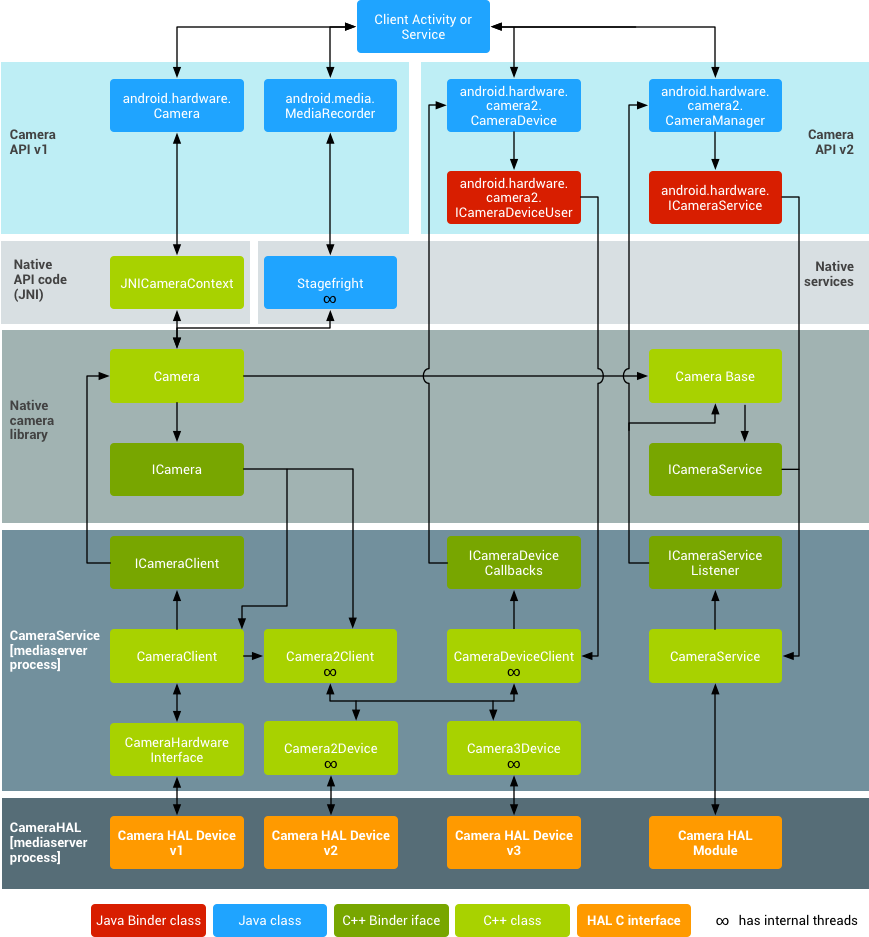
Figure 1. Camera architecture
Application framework
At the application framework level is the app's code, which utilizes the android.hardware.Camera API to interact with the camera hardware. Internally, this code calls a corresponding JNI glue class to access the native code that interacts with the camera.
JNI
The JNI code associated with android.hardware.Camera is located inframeworks/base/core/jni/android_hardware_Camera.cpp. This code calls the lower level native code to obtain access to the physical camera and returns data that is used to create the android.hardware.Camera object at the framework level.
Native framework
The native framework defined in frameworks/av/camera/Camera.cpp provides a native equivalent to theandroid.hardware.Camera class. This class calls the IPC binder proxies to obtain access to the camera service.
Binder IPC proxies
The IPC binder proxies facilitate communication over process boundaries. There are three camera binder classes that are located in frameworks/av/camera directory that calls into camera service. ICameraService is the interface to the camera service, ICamera is the interface to a specific opened camera device, and ICameraClient is the device's interface back to the application framework.
Camera service
The camera service, located in frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/CameraService.cpp, is the actual code that interacts with the HAL.
HAL
The hardware abstraction layer defines the standard interface that the camera service calls into and that you must implement to have your camera hardware function correctly.
Kernel driver
The camera's driver interacts with the actual camera hardware and your implementation of the HAL. The camera and driver must support YV12 and NV21 image formats to provide support for previewing the camera image on the display and video recording.
Implementing the HAL (legacy)
The HAL sits between the camera driver and the higher level Android framework and defines an interface you must implement so apps can correctly operate the camera hardware. The HAL interface is defined in thehardware/libhardware/include/hardware/camera.h andhardware/libhardware/include/hardware/camera_common.h header files.
camera_common.h defines camera_module, a standard structure to obtain general information about the camera, such as the camera ID and properties common to all cameras (i.e., whether it is a front- or back-facing camera).
camera.h contains code that corresponds to android.hardware.Camera. This header file declares a camera_devicestruct that in turn contains a camera_device_ops struct with pointers to functions that implement the HAL interface. For documentation on the camera parameters developers can set, refer to frameworks/av/include/camera/CameraParameters.h. These parameters are set with the function pointed to by int (*set_parameters)(struct camera_device *, const char *parms) in the HAL.
For an example of a HAL implementation, refer to the implementation for the Galaxy Nexus HAL in hardware/ti/omap4xxx/camera.
Configuring the shared library
Set up the Android build system to correctly package the HAL implementation into a shared library and copy it to the appropriate location by creating an Android.mk file:
- Create a
device/<company_name>/<device_name>/cameradirectory to contain your library's source files. - Create an
Android.mkfile to build the shared library. Ensure the Makefile contains the following lines:LOCAL_MODULE := camera.<device_name> LOCAL_MODULE_RELATIVE_PATH := hwYour library must be named
camera.<device_name>(.sois appended automatically), so Android can correctly load the library. For an example, see the Makefile for the Galaxy Nexus camera located inhardware/ti/omap4xxx/Android.mk. - Specify your device has camera features by copying the necessary feature XML files in the
frameworks/native/data/etcdirectory with your device's Makefile. For example, to specify your device has a camera flash and can autofocus, add the following lines in your device's<device>/<company_name>/<device_name>/device.mkMakefile:PRODUCT_COPY_FILES := \ ... PRODUCT_COPY_FILES += \ frameworks/native/data/etc/android.hardware.camera.flash-autofocus.xml:system/etc/permissions/android.hardware.camera.flash-autofocus.xml \For an example of a device Makefile, see
device/samsung/tuna/device.mk. - Declare your camera’s media codec, format, and resolution capabilities in
device/<company_name>/<device_name>/media_profiles.xmlanddevice/<company_name>/<device_name>/media_codecs.xmlXML files. For details, see Exposing codecs to the framework. - Add the following lines in your device's
device/<company_name>/<device_name>/device.mkMakefile to copy themedia_profiles.xmlandmedia_codecs.xmlfiles to the appropriate location:# media config xml file PRODUCT_COPY_FILES += \ <device>/<company>/<device>/media_profiles.xml:system/etc/media_profiles.xml # media codec config xml file PRODUCT_COPY_FILES += \ <device>/<company>/<device>/media_codecs.xml:system/etc/media_codecs.xml - To include the Camera app in your device's system image, specify it in the
PRODUCT_PACKAGESvariable in your device'sdevice/<company>/<device>/device.mkMakefile:PRODUCT_PACKAGES := \ Gallery2 \ ...