版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请声明本博主原创 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39381833/article/details/85330460
d14
归档
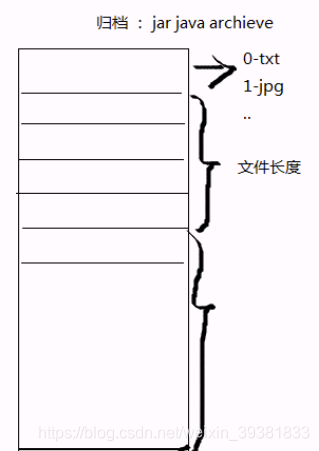
文件长度的获取
int FileInputStream.available()==文件长度
OOP 面向对象
Archive:归档
Archive.java
private static int getFileType(String srcPath) {
//3 得到文件扩展名
srcPath.substring(srcPath.lastIndexOf("."));
return 0;
}
}
app.java
public class app {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "/media/ifeng/_dde_data/iotest/1.jpg";
System.out.println(path.substring(path.lastIndexOf(".")));
}
}
Archive.java
package D14;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Archive {
/*
*
* 创建归档文件
*
*/
public void newArchiveFile(String[] paths,String yarPath){
try {
//创建yar归档文件的输出流
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(yarPath);
//循环添加文件
for(String srcPath : srcPaths){
//向yar归档文件中添加文件
addFile(srcPath,fout);
}
fout.close();
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void addFile(String srcPath, FileOutputStream fout) throws IOException {
try{
// 1.取出srcPath文件的类型和长度
int fType = getFileType(srcPath);
// 2.取出文件的长度
FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(srcPath);
int length = fin.available();
// 3.ftype写入fout
byte bFtype = (byte)fType;
fout.write(new byte[]{bFtype});
// 4.将长度写入到yar中
byte[] bytes = Int2ByteArr(length);
fout.write(bytes);
// 5.写入文件的内容
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 将整数转换为字节数组
*/
private byte[] Int2ByteArr(int i){
byte[] bytes = new byte[4];
bytes[0] = (byte) i;
bytes[1] = (byte) (i>>8);
bytes[2] = (byte) (i>>16);
bytes[3] = (byte) (i>>24);
return null;
}
private int getFileType(String srcPath){
//取出对后一个点以后的位置
String ext = srcPath.substring(srcPath.lastIndexOf(".")).toLowerCase();
int type = -1;
if(".txt".equals(ext)){
type = 0;
}
else if (".jpg".equals(ext)){
type = 1;
}
else if (".avi".equals(ext)){
type = 2;
}
else if (".gif".equals(ext)){
type = 3;
}
else if (".exe".equals(ext)){
type = 4;
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
App.java
package D14;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Archive archiver = new Archive();
String[] srcPaths = {
//"目录"
};
String yarpath = "";
archive.newArchiveFile(srcPaths,yarpath);
System.out.println("over!");
}
}
解归档
private boolean readNextFile(FileInputStream fin){
try {
//文件类型
int type = fin.read();
if (type == -1){
return false;
}
//开始读取文件
//0.构造文件
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(destDir + "/" + fname);
//1.读取文件长度
byte[] bytes = new byte[4];
//2.转换文件数组,成为int
int fileLength = byteArr2Int(bytes);
//3.读取文件总长度
计算文件读取文件的循环次数
//开始循环读取
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while (){
//读取文件并
byte[] buffer = 0;
if(fileLength % buffer.length == 0){
count = fileLength / buffer.length;
}
else {
count = fileLength / buffer.length + i;
}
//开始循环读取
for(int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++){
//不是最后一次
if(i != (count -1)){
fin.read(buffer);
fout.read(buffer);
}
else {
byte[] buf0 = new byte[FileLength - ((count -1) * buffer.length)];
fin.read(buf0);
fout.write(buf0);
}
}
//
fout.close();
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
/**
* 将长度为4字节数组转换成int
*/
private int byteArr2Int(byte[] bytes) {
int i0 = bytes[3] << 24;
int i1 = (bytes[2] & 0xff) << 16;
int i2 = (bytes[1] & 0xff) << 8;
int i3 = (bytes[0] & 0xff);
return (bytes[3] << 24 | (bytes[2] & 0xff) << 16) ;
return 0;
}
/**
* 得到文件扩展名
*/
private int getFileExt(String srcPath){
//取出对后一个点以后的位置
String ext = ".tmp";
switch (type){
case 0:
ext = ".txt";
break;
case 1:
ext = ".jpg";
break;
case 2:
ext = ".avi";
break;
case 3:
ext = ".gif";
case 4:
ext = ".exe";
break;
}
return ext;
}
IO
1.流向
InputStream
OutputStream
2.类型划分
a.字符流(文本文件)
Reader | Writer
FileReader FileWriter
b.字节流(任何文件)
InputStream | OutputStream
FileInoutStream | FileOutputStream
3.性能划分
BufferedWriter:缓冲区流(装饰模式,flush清理)| 分缓冲区流
BufferedReader:缓冲区,read(fill)
readLine() LineNUmberReader
BufferedInputStream.read()
BufferedOutputStream
转换流
InputStreamReader,OutputStreamWriter
转换流的由来
字节流与字符流之间的桥梁
方便了字符流与字节流之间的操作
转换流的应用
字节流中的数据都是字符时,转成字符流操作更高效
将字节流转换成字符流的桥梁,实用特定字符集读取byte并解码成字符。
底层是字节流,如果需要转换成字符内容处理的话,就可用转换流,也是装饰模式实现
1.InputStreamReader//
new InputStramReader(InputStream is , charset);
2.OutputStreamWriter
new OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out,charset);
System.out.println();
-------------------------------------
out为对象 也即是一个流