
前言
之前我们了解了Fiber的数据结构 React 16.7 Fiber源码解读 (一)之数据结构
接下来主要探讨fiber运行的流程。
目录如下:
- Fiber vs Stack
- 关键字Work
- 运行流程图
- 重要函数源码解读
- enqueueSetState
- requestWork
- scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime
- workLoop
- performUnitOfWork
- beginWork
- performUnitOfWork动态图
- commitLifeCycles
- Fiber Debugger
fiber vs stack
上一篇我们介绍了fiber的数据结构,自然产生出几个问题:
- 为什么React 16之前的stack reconciliation无法被中断?
- 为什么fiber的数据结构可以使进行中的work可以被中断?
我打算从stack和fiber数据结构的角度来回答这个问题:
stack无法被中断是因为中断后无法恢复现场,fiber可以被中断是因为中断后可以恢复现场。 听起来像句废话,容我接着分析:
首先来看stack:
// stack node数据结构
export type Node = {
...
children: [...]
...
}
其实是一个树结构,每个node维护一个children保持对子节点的引用。
通过walk来构建虚拟dom:
// stack reconciliation通过递归调用walk生成visual dom
walk(root);
function walk(instance) {
doWork(instance);
const children = instance.render();
children.forEach(walk);
}
function doWork(o) {
console.log(o);
}
我们都知道,递归调用的过程是一层层的入栈,每一层我们称为stack frame,当一个stack frame完成后出栈回到上一级。假设某个子节点还在运行时,由于出现了优先级更高的任务,导致整个walk运行现场被打断了(之前的多层入栈都被清除了),尽管我们也许还保有被中断节点的引用,当高优先级任务运行完成,只凭这个中断节点的引用是无法恢复递归的现场的,我们既无法找到它的兄弟节点,也无法找到它的父亲节点。
再来看fiber:
- 数据结构给力
- 构建visual dom不再使用递归
export type Fiber = {
// ...
// 当前fiber的父级fiber实例
return: Fiber | null,
// 子Fiber
child: Fiber | null,
// 兄弟fiber
sibling: Fiber | null
// ...
}
关键字Work
React在协调阶段(reconciliation)的各项工作诸如运行周期函数,更新ref,都可以认为是一个Work.
对于不同类型的React Element所做的work也不尽相同。在React中我所知道的element类型就有class component,function component, host component,portals等。
通过每个fiber,可以看出其所对应的react element有哪些work要做,即一个fiber对应unit of work。fiber的数据结构可以使其对应的work可以被追踪(track),暂停(pause)或者放弃(abort)
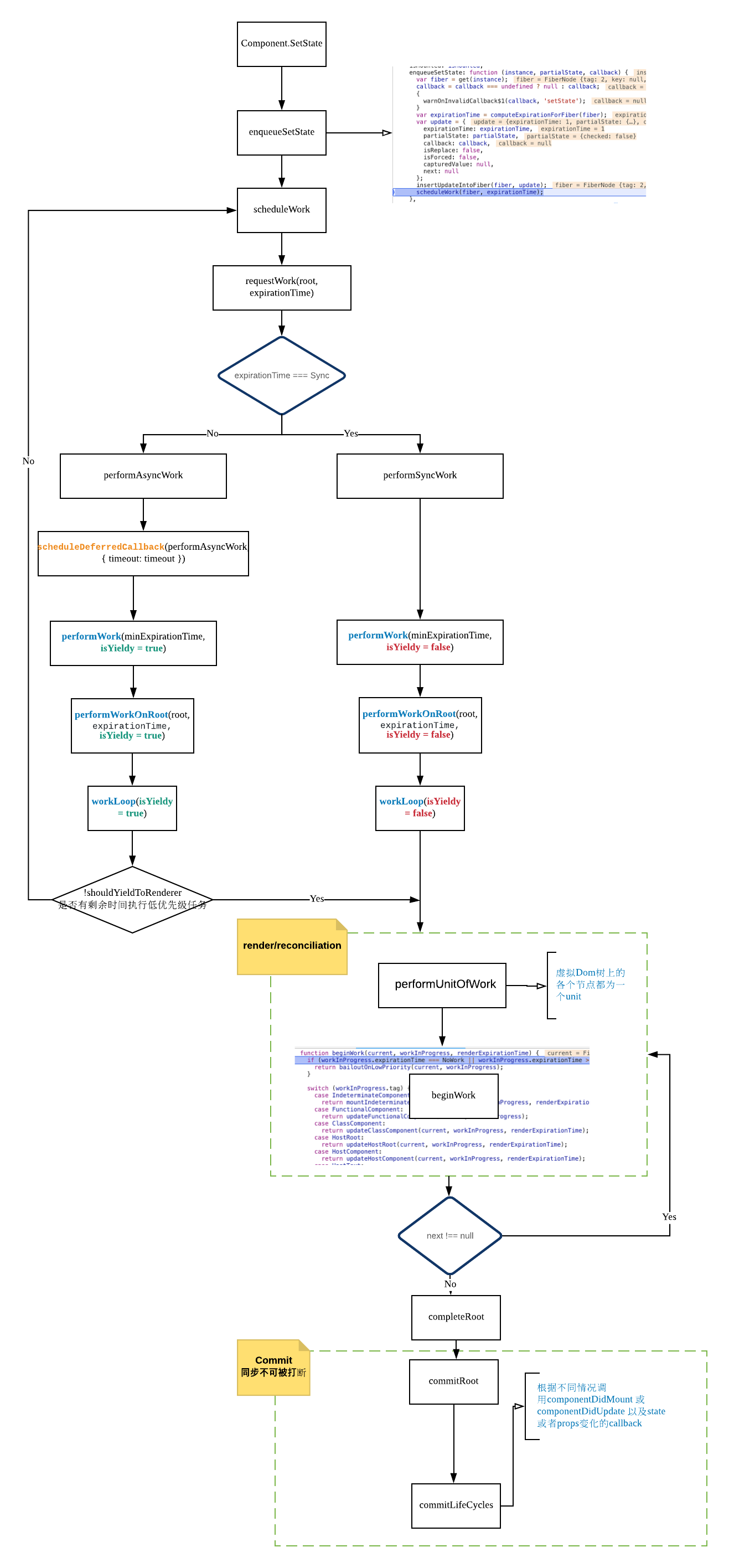
运行流程图
先上一张运行流程图:
重要函数源码解读
接下来会了解运行过程中涉及到的一些重要函数。
enqueueSetState
我们在业务代码中通常用setState来改变组件状态,在调用栈中,我们经常会看到enqueueSetState,代表React接管了之后的工作,即将进入协调(render/reconciliation)阶段。
在React 16.7中,enqueueSetState做了以下几件重要的事情:
- 建立组件对应的fiber
- 将组件的update放入fiber的updateQueue中
- 通过scheduleWork正式开始任务调度
const classComponentUpdater = {
isMounted,
enqueueSetState(inst, payload, callback) {
const fiber = getInstance(inst);
const currentTime = requestCurrentTime();
const expirationTime = computeExpirationForFiber(currentTime, fiber);
const update = createUpdate(expirationTime);
update.payload = payload;
if (callback !== undefined && callback !== null) {
// ...(DEV WARNING)
update.callback = callback;
}
flushPassiveEffects();
// 将组件的新状态更新到该组件对应的fiber.updateQueue中
// 16.3中为 insertUpdateIntoFiber(fiber, update)
enqueueUpdate(fiber, update);
scheduleWork(fiber, expirationTime);
}
...
}
work的调度工作主要在ReactFiberScheduler.js中完成。流程图我们可以找到一条由重要函数组成的调度链:scheduleWork -> requestWork -> performSyncWork / performAsyncWork -> workLoop -> performUnitOfWork -> render
requestWork
function requestWork(root, expirationTime) {
...
if (expirationTime === Sync) {
performSyncWork();
} else {
scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime(root, expirationTime);
}
...
}
scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime
function scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime(root, expirationTime) {
// ...
callbackExpirationTime = expirationTime;
const currentMs = now() - originalStartTimeMs;
const expirationTimeMs = expirationTimeToMs(expirationTime);
const timeout = expirationTimeMs - currentMs;
// 将异步(低优先级)任务放入requestIdleCallback或其polyfill
callbackID = scheduleDeferredCallback(performAsyncWork, {timeout});
}
workLoop
非常简短但是很关键。
循环而不是以递归的方式遍历fiber tree.
isYieldy 为 true, work为异步否则为同步
function workLoop(isYieldy) {
if (!isYieldy) {
// Flush work without yielding
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
} else {
// Flush asynchronous work until there's a higher priority event
// shouldYieldToRenderer()为true代表没有剩余时间执行异步低优先级任务即nextUnitOfWork
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null && !shouldYieldToRenderer()) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
}
}
performUnitOfWork 和 beginWork
performUnitOfWork 调用的核心函数是beginWork,beginWork会遍历当前workInProgress的所有子级fiber,完成单元任务的处理,之后继续处理下一个任务。
// 执行一个workInprogress并且返回下一个可执行的workInProgress(next),直到next不存在,结束本次workloop
function performUnitOfWork(workInProgress) {
var current = workInProgress.alternate;
// ...
// See if beginning this work spawns more work.
// 遍历所有子级fiber,完成单元任务的处理,之后继续处理下一个任务
var next = beginWork(current, workInProgress, nextPriorityLevel);
// ...
if (!next) {
// If this doesn't spawn new work, complete the current work.
next = completeUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
ReactCurrentOwner.current = null;
// ...
return next;
}
function beginWork(current: Fiber | null, workInProgress: Fiber, renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime): Fiber | null {
...
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent: ...
case LazyComponent:...
case FunctionComponent: {
...
return updateFunctionComponent(current, workInProgress, Component, resolvedProps, renderExpirationTime);
}
...
}
}
function updateFunctionComponent(workInProgress, ...) {
...
return workInProgress.child
}
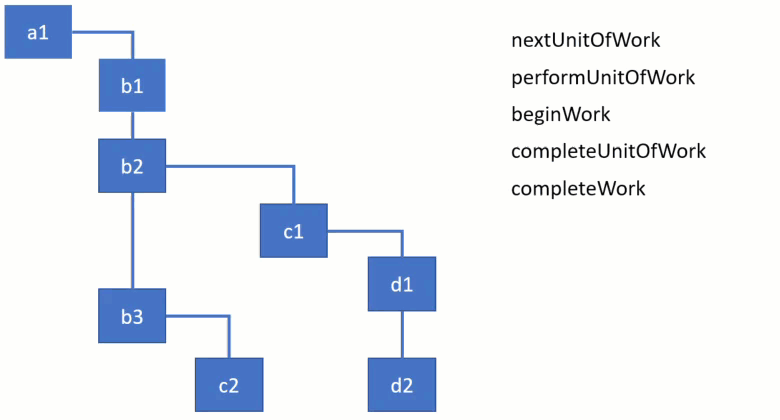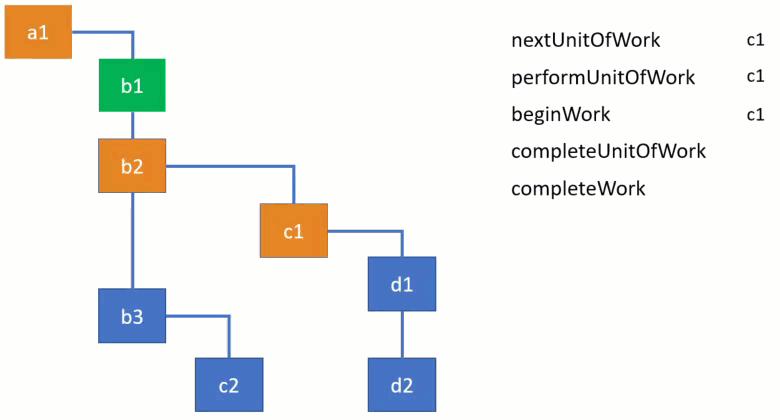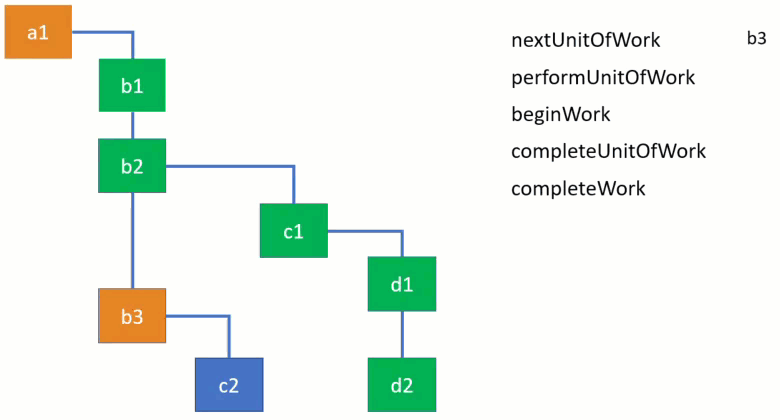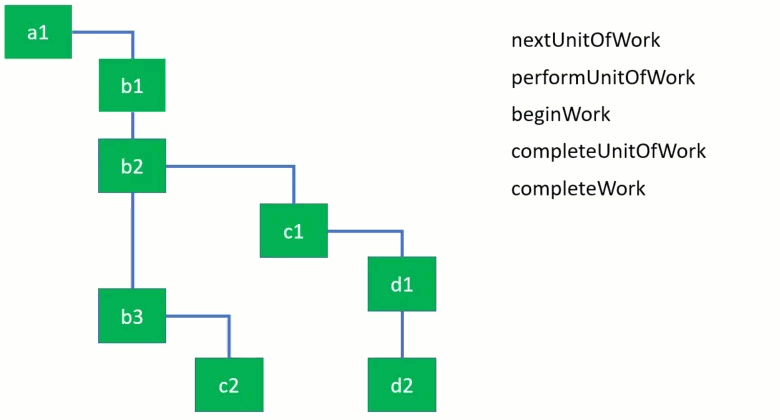
performUnitOfWork动态图
下图fiber结构中a1为root,b1, b2, b3是a1的child。
一个节点(unit work)所有的child完成后该节点即为完成(completeUnitOfWork)
commitLifeCycles
commit阶段的重要函数,在这里会根据不同的情况调用业务代码中的周期函数
// 根据current是否存在判断调用componentDidMount 还是 componentDidUpdate
function commitLifeCycles(
finishedRoot: FiberRoot,
current: Fiber | null,
finishedWork: Fiber,
committedExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): void {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case SimpleMemoComponent: ...
case ClassComponent: {
const instance = finishedWork.stateNode;
if (finishedWork.effectTag & Update) {
if (current === null) {
startPhaseTimer(finishedWork, 'componentDidMount');
instance.componentDidMount();
stopPhaseTimer();
} else {
const prevProps =
finishedWork.elementType === finishedWork.type
? current.memoizedProps
: resolveDefaultProps(finishedWork.type, current.memoizedProps);
const prevState = current.memoizedState;
startPhaseTimer(finishedWork, 'componentDidUpdate');
// We could update instance props and state here,
instance.componentDidUpdate(
prevProps,
prevState,
instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate,
);
stopPhaseTimer();
}
}
const updateQueue = finishedWork.updateQueue;
if (updateQueue !== null) {
// 这里会调用state或props改变的callback函数
commitUpdateQueue(
finishedWork,
updateQueue,
instance,
committedExpirationTime,
);
}
return;
}
case HostRoot: ...
case HostComponent: ...
case HostText: ...
case HostPortal: ...
case Profiler:...
case SuspenseComponent:
...
default: ...
}
}
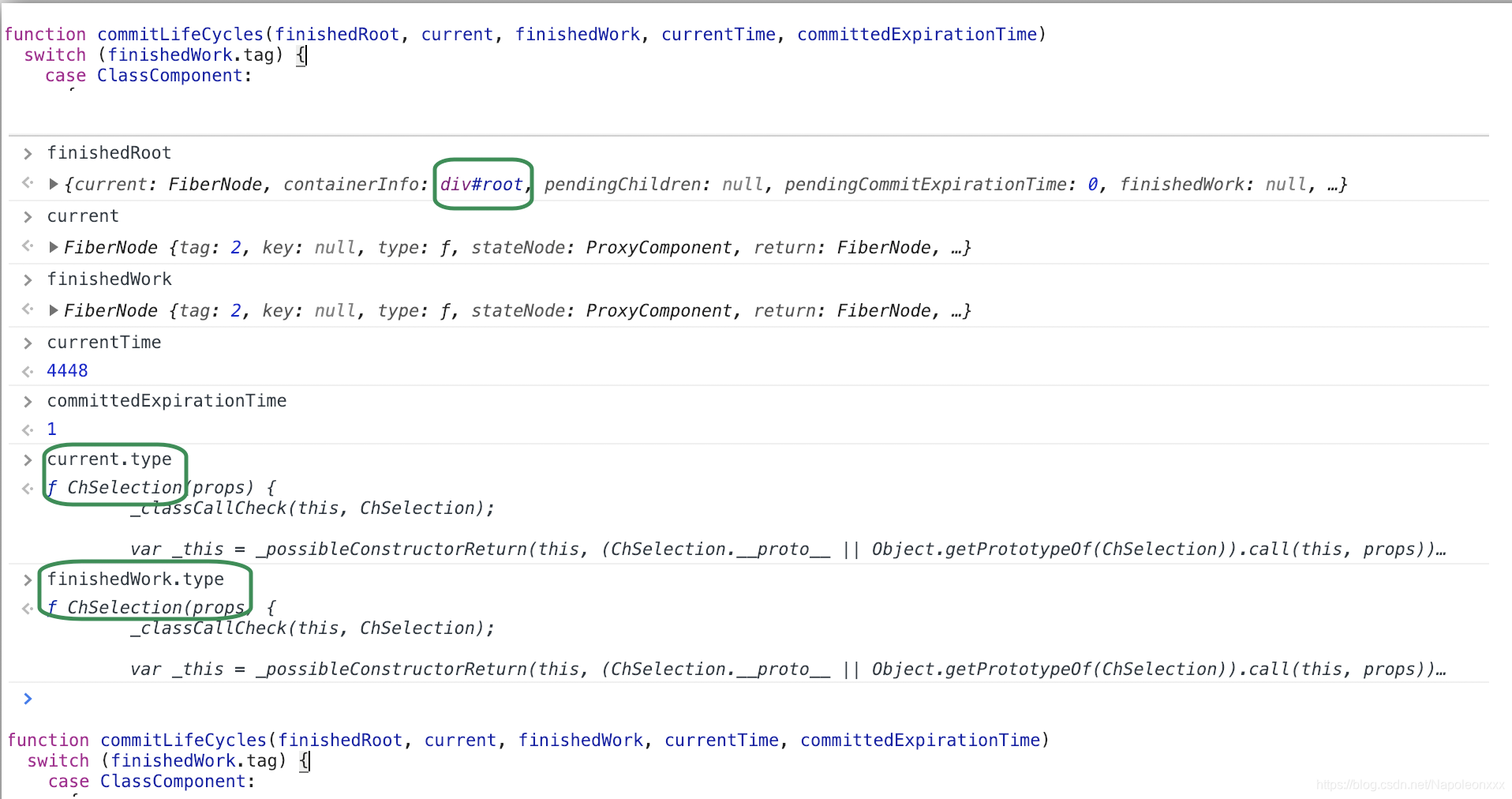
commitLifeCycles 运行实例:
Fiber Debugger
Fiber Debugger是React官方的一个图形化展示fiber运行过程的动态demo.
点击Edit按钮,可将以下代码复制到编辑框,点击运行Run即可查看
log('Render <div>Hello</div>');
ReactNoop.render(<div>Hello</div>);
ReactNoop.flush();
log('Render <h1>Goodbye</h1>');
ReactNoop.render(<h1>Goodbye</h1>);
ReactNoop.flush();
React Fiber源码就先看到这里,代码非常浩繁复杂,难免有理解不对的地方,如有大牛偶尔路过,希望不吝赐教:)