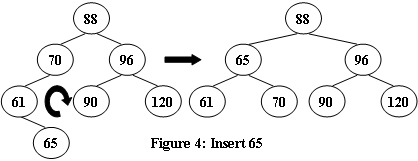
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
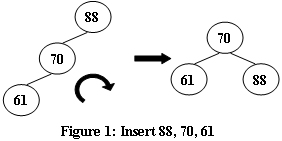
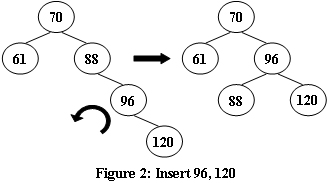
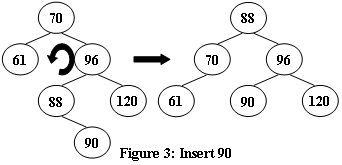
Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to tell the root of the resulting AVL tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤) which is the total number of keys to be inserted. Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the root of the resulting AVL tree in one line.
Sample Input 1:
5 88 70 61 96 120
Sample Output 1:
70
Sample Input 2:
7 88 70 61 96 120 90 65
Sample Output 2:
88
标准的模板题,为方便记忆,对7个函数的返回类型归纳如下:
1个node* (newNode)
2个int(getHeight, getBalance)
4个void (updateHeight,L,R,insert )
#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; struct node{ int data,height; node *left,*right; }*root; node* newNode(int x){ node *ret=new node; ret->data=x; ret->height=1; ret->left=ret->right=NULL; return ret; } int getHeight(node *root){ if(root==NULL) return 0; return root->height; } int getBalance(node *root){ return getHeight(root->left)-getHeight(root->right); } void updateHeight(node *root){ int hleft=getHeight(root->left); int hright=getHeight(root->right); root->height=max(hleft,hright)+1; } void L(node* &root){ node *temp=root->right; root->right=temp->left; temp->left=root; updateHeight(root); updateHeight(temp); root=temp; } void R(node* &root){ node *temp=root->left; root->left=temp->right; temp->right=root; updateHeight(root); updateHeight(temp); root=temp; } void insert(node* &root,int x){ if(root==NULL){ root=newNode(x); return;//空return更简洁,不用else } if(x<root->data){ insert(root->left,x); updateHeight(root);//* if(getBalance(root)==2){ if(getBalance(root->left)==1){ R(root); }else if(getBalance(root->left)==-1){ L(root->left);//* R(root);//* } } }else{ insert(root->right,x); updateHeight(root); if(getBalance(root)==-2){ if(getBalance(root->right)==-1){ L(root); }else if(getBalance(root->right)==1){ R(root->right); L(root); } } } } int main(){ int n,v; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ scanf("%d",&v); insert(root,v); } printf("%d",root->data); return 0; }