Algorithm | Coursera - by Robert Sedgewick
Type the code one by one!
不要拜读——只写最有感触的!而不是仅仅做一个笔记摘录员,那样毫无意义!
动手实现。看懂不等于会写——用sublime 写,而非ide(强迫白板写代码)—— 默写代码
直接看ppt优先, 而不是被动看视频
不要拜读——没必要看废话
循循善诱——要是我大一时候看这本书就好了!但是现在开始也不算晚.
很多知识不用查,自己拿编译器print查看
时刻记得资源有限——这样才能写出能够应对大数据时代的高效率代码
要学会写完整能跑起来的程序,及时反馈,有成就感 —— 多巴胺
Inspiration
1.link-list vs resizing array
确保每个操作都能很快完成 —— 链表实现
如果只关心总的实现实现 —— 数组实现
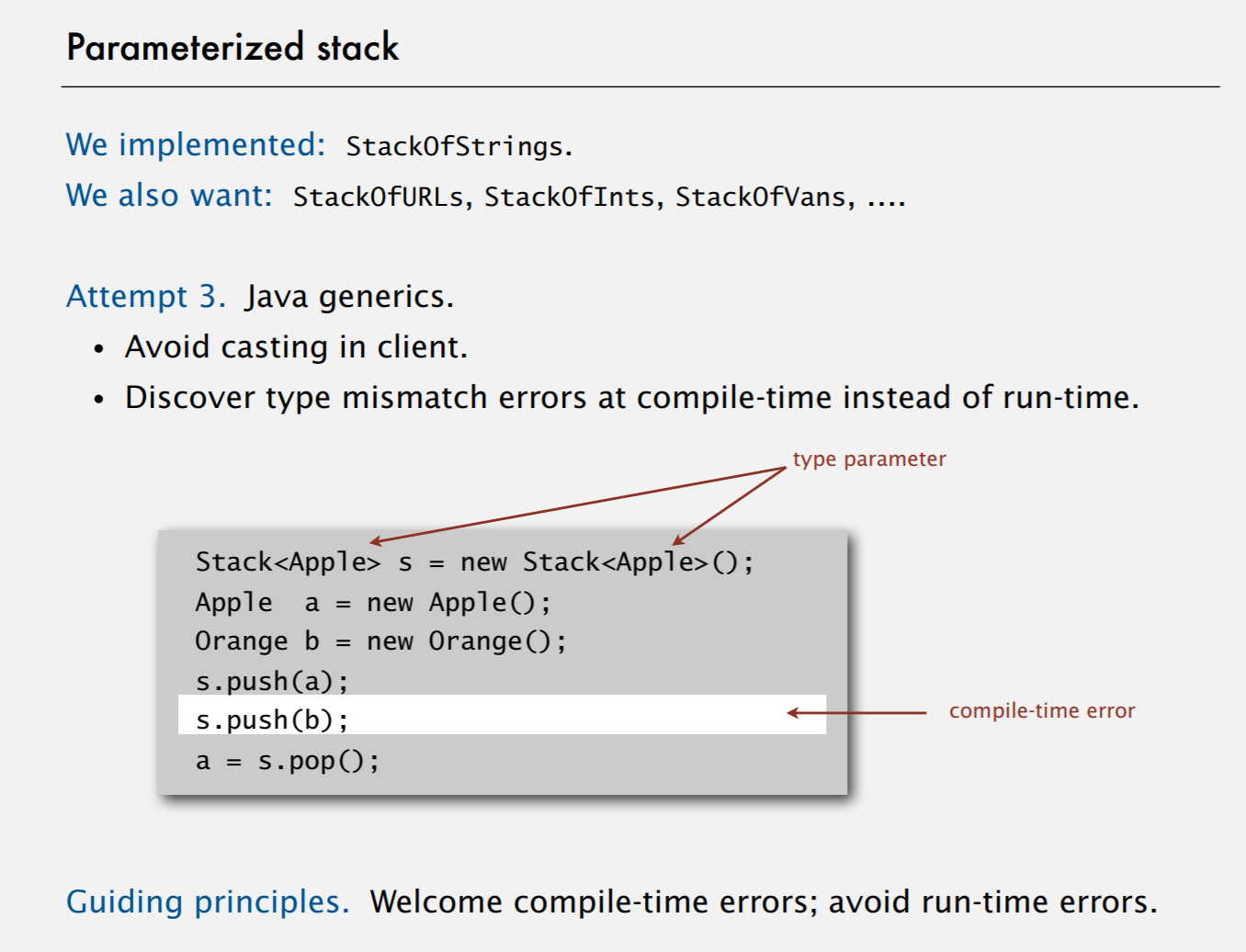
2.errors - Guiding Principles - use generics
- Welcome compile-time errors; //有问题在编译时提前发现
- Avoid run-time errors. // 确保在交给客户时避免runtime error
3.优秀的代码不该使用强制类型转换
若类型不匹配,容易发生runtime error
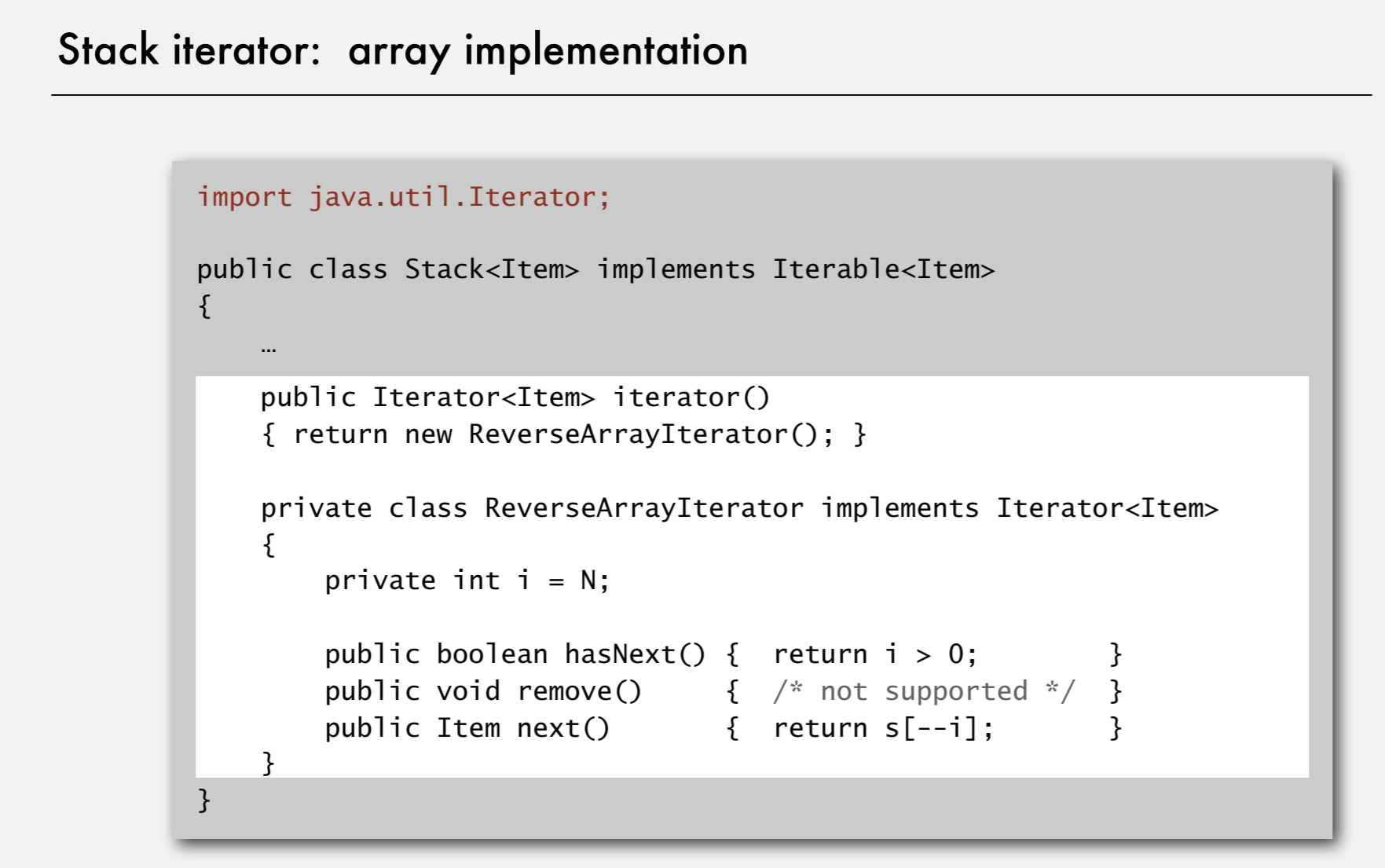
4.Iterator
Java supports elegant client code
What I can use - Code
Stack(Generic +iteration)
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac Stack.java
* Execution: java Stack < input.txt
* Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java
* Data files: https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks/tobe.txt
*
* A generic stack, implemented using a singly linked list.
* Each stack element is of type Item.
*
* This version uses a static nested class Node (to save 8 bytes per
* Node), whereas the version in the textbook uses a non-static nested
* class (for simplicity).
*
* % more tobe.txt
* to be or not to - be - - that - - - is
*
* % java Stack < tobe.txt
* to be not that or be (2 left on stack)
*
******************************************************************************/
//package edu.princeton.cs.algs4;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/**
* The {@code Stack} class represents a last-in-first-out (LIFO) stack of generic items.
* It supports the usual <em>push</em> and <em>pop</em> operations, along with methods
* for peeking at the top item, testing if the stack is empty, and iterating through
* the items in LIFO order.
* <p>
* This implementation uses a singly linked list with a static nested class for
* linked-list nodes. See {@link LinkedStack} for the version from the
* textbook that uses a non-static nested class.
* See {@link ResizingArrayStack} for a version that uses a resizing array.
* The <em>push</em>, <em>pop</em>, <em>peek</em>, <em>size</em>, and <em>is-empty</em>
* operations all take constant time in the worst case.
* <p>
* For additional documentation,
* see <a href="https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks">Section 1.3</a> of
* <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*
* @param <Item> the generic type of an item in this stack
*/
public class Stack<Item> implements Iterable<Item> {
private Node<Item> first; // top of stack
private int n; // size of the stack
// helper linked list class
private static class Node<Item> {
private Item item;
private Node<Item> next;
}
/**
* Initializes an empty stack.
*/
public Stack() {
first = null;
n = 0;
}
/**
* Returns true if this stack is empty.
*
* @return true if this stack is empty; false otherwise
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
/**
* Returns the number of items in this stack.
*
* @return the number of items in this stack
*/
public int size() {
return n;
}
/**
* Adds the item to this stack.
*
* @param item the item to add
*/
public void push(Item item) {
Node<Item> oldfirst = first;
first = new Node<Item>();
first.item = item;
first.next = oldfirst;
n++;
}
/**
* Removes and returns the item most recently added to this stack.
*
* @return the item most recently added
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this stack is empty
*/
public Item pop() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow");
Item item = first.item; // save item to return
first = first.next; // delete first node
n--;
return item; // return the saved item
}
/**
* Returns (but does not remove) the item most recently added to this stack.
*
* @return the item most recently added to this stack
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this stack is empty
*/
public Item peek() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow");
return first.item;
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this stack.
*
* @return the sequence of items in this stack in LIFO order, separated by spaces
*/
public String toString() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
for (Item item : this) {
s.append(item);
s.append(' ');
}
return s.toString();
}
/**
* Returns an iterator to this stack that iterates through the items in LIFO order.
*
* @return an iterator to this stack that iterates through the items in LIFO order
*/
public Iterator<Item> iterator() {
return new ListIterator<Item>(first);
}
// an iterator, doesn't implement remove() since it's optional
private class ListIterator<Item> implements Iterator<Item> {
private Node<Item> current;
public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) {
current = first;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return current != null;
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public Item next() {
if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException();
Item item = current.item;
current = current.next;
return item;
}
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code Stack} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
String item = StdIn.readString();
if (!item.equals("-"))
stack.push(item);
else if (!stack.isEmpty())
StdOut.print(stack.pop() + " ");
}
StdOut.println("(" + stack.size() + " left on stack)");
}
}
/******************************************************************************
* Copyright 2002-2018, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook
*
* Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne,
* Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X.
* http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
*
*
* algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
******************************************************************************/Queue(Generic +iteration)
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac Queue.java
* Execution: java Queue < input.txt
* Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java
* Data files: https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks/tobe.txt
*
* A generic queue, implemented using a linked list.
*
* % java Queue < tobe.txt
* to be or not to be (2 left on queue)
*
******************************************************************************/
//package edu.princeton.cs.algs4;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/**
* The {@code Queue} class represents a first-in-first-out (FIFO)
* queue of generic items.
* It supports the usual <em>enqueue</em> and <em>dequeue</em>
* operations, along with methods for peeking at the first item,
* testing if the queue is empty, and iterating through
* the items in FIFO order.
* <p>
* This implementation uses a singly linked list with a static nested class for
* linked-list nodes. See {@link LinkedQueue} for the version from the
* textbook that uses a non-static nested class.
* See {@link ResizingArrayQueue} for a version that uses a resizing array.
* The <em>enqueue</em>, <em>dequeue</em>, <em>peek</em>, <em>size</em>, and <em>is-empty</em>
* operations all take constant time in the worst case.
* <p>
* For additional documentation, see <a href="https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks">Section 1.3</a> of
* <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*
* @param <Item> the generic type of an item in this queue
*/
public class Queue<Item> implements Iterable<Item> {
private Node<Item> first; // beginning of queue
private Node<Item> last; // end of queue
private int n; // number of elements on queue
// helper linked list class
private static class Node<Item> {
private Item item;
private Node<Item> next;
}
/**
* Initializes an empty queue.
*/
public Queue() {
first = null;
last = null;
n = 0;
}
/**
* Returns true if this queue is empty.
*
* @return {@code true} if this queue is empty; {@code false} otherwise
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
/**
* Returns the number of items in this queue.
*
* @return the number of items in this queue
*/
public int size() {
return n;
}
/**
* Returns the item least recently added to this queue.
*
* @return the item least recently added to this queue
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty
*/
public Item peek() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow");
return first.item;
}
/**
* Adds the item to this queue.
*
* @param item the item to add
*/
public void enqueue(Item item) {
Node<Item> oldlast = last;
last = new Node<Item>();
last.item = item;
last.next = null;
if (isEmpty()) first = last;
else oldlast.next = last;
n++;
}
/**
* Removes and returns the item on this queue that was least recently added.
*
* @return the item on this queue that was least recently added
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty
*/
public Item dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow");
Item item = first.item;
first = first.next;
n--;
if (isEmpty()) last = null; // to avoid loitering
return item;
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this queue.
*
* @return the sequence of items in FIFO order, separated by spaces
*/
public String toString() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
for (Item item : this) {
s.append(item);
s.append(' ');
}
return s.toString();
}
/**
* Returns an iterator that iterates over the items in this queue in FIFO order.
*
* @return an iterator that iterates over the items in this queue in FIFO order
*/
public Iterator<Item> iterator() {
return new ListIterator<Item>(first);
}
// an iterator, doesn't implement remove() since it's optional
private class ListIterator<Item> implements Iterator<Item> {
private Node<Item> current;
public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) {
current = first;
}
public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; }
public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }
public Item next() {
if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException();
Item item = current.item;
current = current.next;
return item;
}
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code Queue} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> queue = new Queue<String>();
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
String item = StdIn.readString();
if (!item.equals("-"))
queue.enqueue(item);
else if (!queue.isEmpty())
StdOut.print(queue.dequeue() + " ");
}
StdOut.println("(" + queue.size() + " left on queue)");
}
}
/******************************************************************************
* Copyright 2002-2018, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook
*
* Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne,
* Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X.
* http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
*
*
* algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
******************************************************************************/
Queues,and Stacks
- stacks
- resizing arrays
- queues
- generics
- iterators
- applications
1 Stack
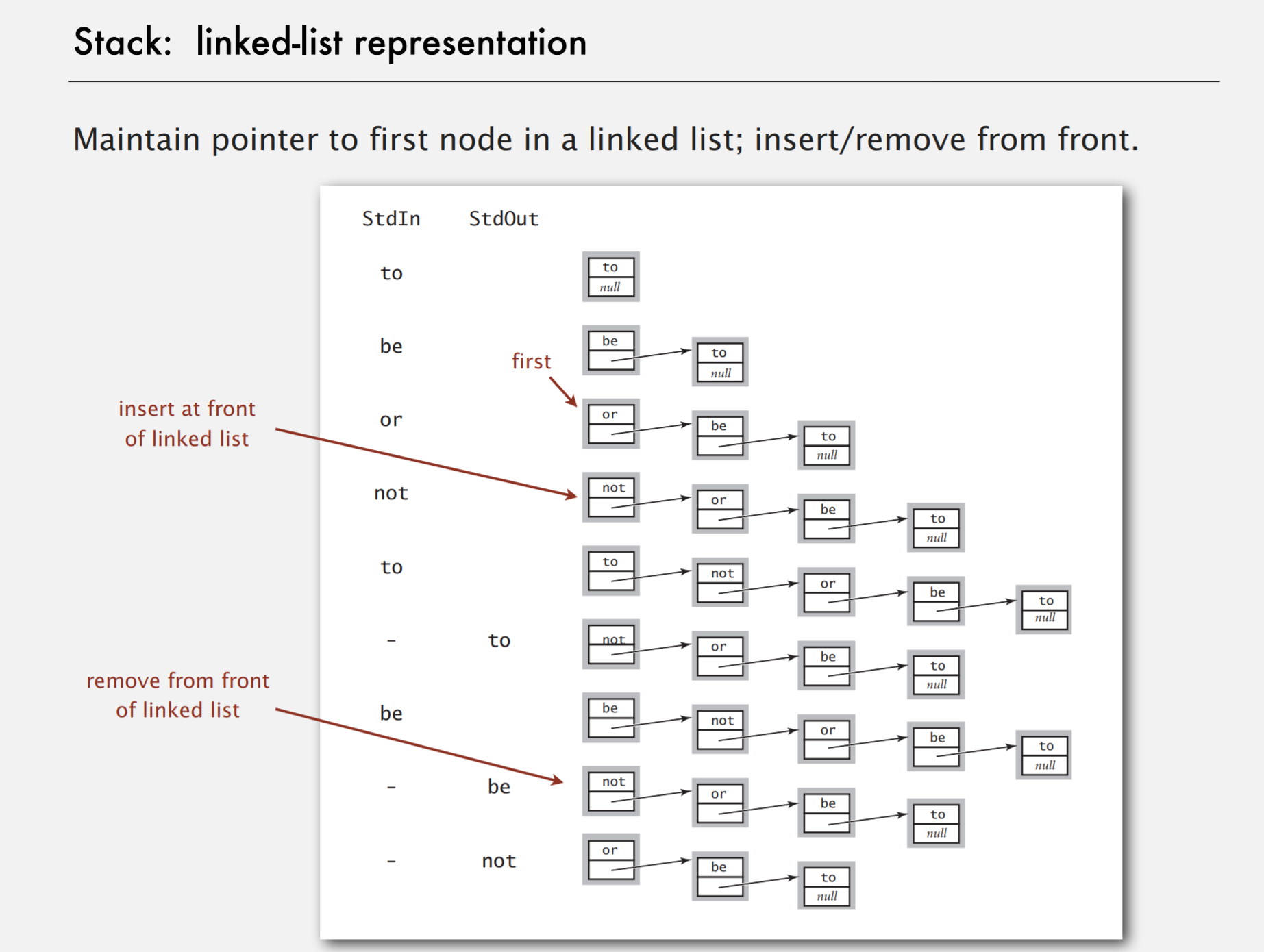
Stack1:linked-list implementation
链表在进行循环遍历时效率不高,但是插入和删除时优势明显。
用链表实现栈
Pop Operation
Push Operation

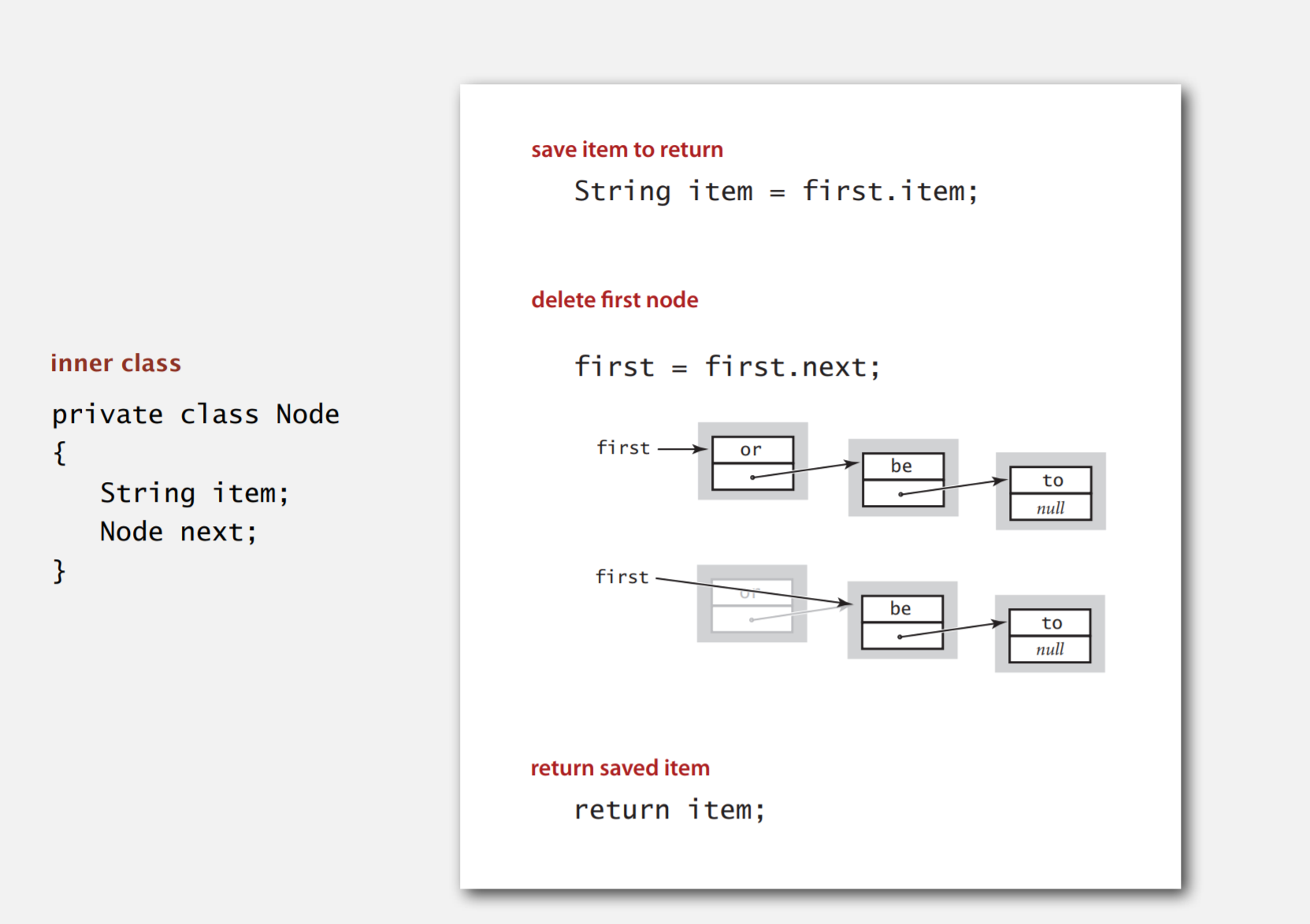
public class LinkedStackOfStrings
{
private Node first = null;
//inner class
private class Node
{
String item;
Node next;
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return first == null;
}
private String pop()
{
String item = first.item;//pop the first item
first = first.next;
return first;
}
public void push(String item){
Node oldfirst = first;
first = new Node();
first.item = item;//push the new item
first.next = oldfirst;
}
}Stack2:array implementation
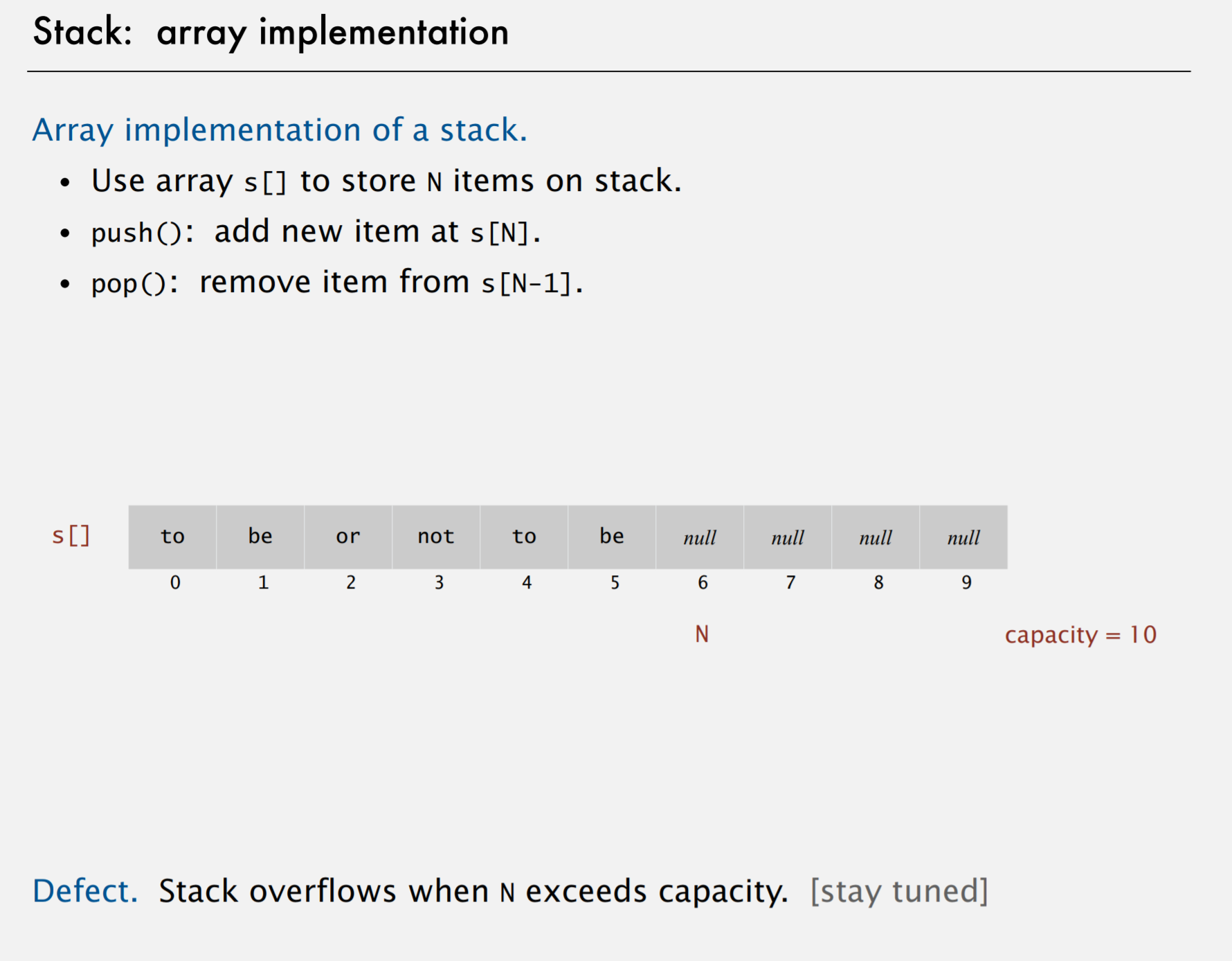
Solve Defect —— use resizing array
lower running time
Considerations
the art of coding
Loitering 对象游离
在栈的数组实现中有对象的引用,而我们没有真正使用它。
最好将去除的元素对应的项设为空。
否则只是没有引用指向它,但是那个位置的内存仍然被占用着
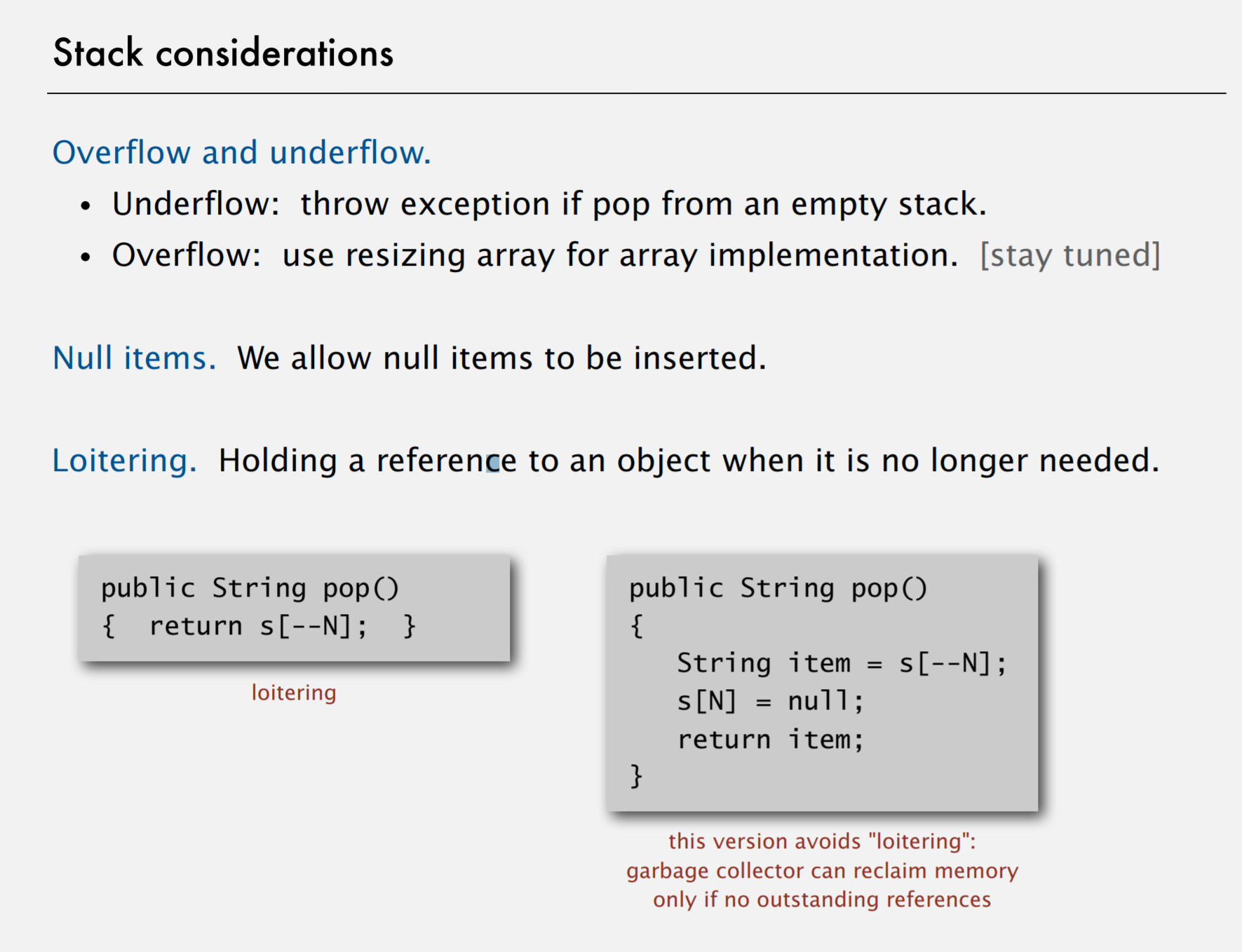
public class ResizingArrayStackOfStrings()
{
private String[] s;
private int N = 0;
// public FixedCapacityStackOfStrings(int capacity)
// {
// s = new String[capacity];//constructor;fixedcappacity
// }
public ResizingArrayStackOfStrings()//constructor
{
s = new String[1];
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return N == 0;
}
//Array is between 25% and 100% full.
private void resize(int capacity)
{
String[] copy = new String[capacity];
for (int i = 0;i < N; i++)
copy[i] = s[i];
s = copy; // assign copy to s
}
//Q. How to grow array?
//A. If array is full, create a new array of twice the size, and copy items
//Consequence:Inserting first N items takes time proportional to N (not N^2 ).
public void push(String item)
{
if (N == s.length) resize(2 * s.length);//If array is full, create a new array of twice the size, and copy items.
S[N++] = item; //use the index into array,then increment N // brilliant!
}
// Q. How to shrink array?
//halve size of array s[] when array is one-quarter full.
//当数组1/4满的时候再将容量减半——防止thrashing 在临界值抖动 不断扩数组和缩数组造成浪费
public String pop()
{
String item = s[--N];//decrement N ;then use to index into array
s[N] = null;//to solve the Loitering problem. assign null to wasted space
if (N > 0 && N == s.length/4){
resize(s.length/2);
}
return item;
}
}Tradeoffs:resizing array vs. linked list

- 确保每个操作都能很快完成 —— 链表实现
- 如果只关心总的实现实现 —— 数组实现
2 Queue
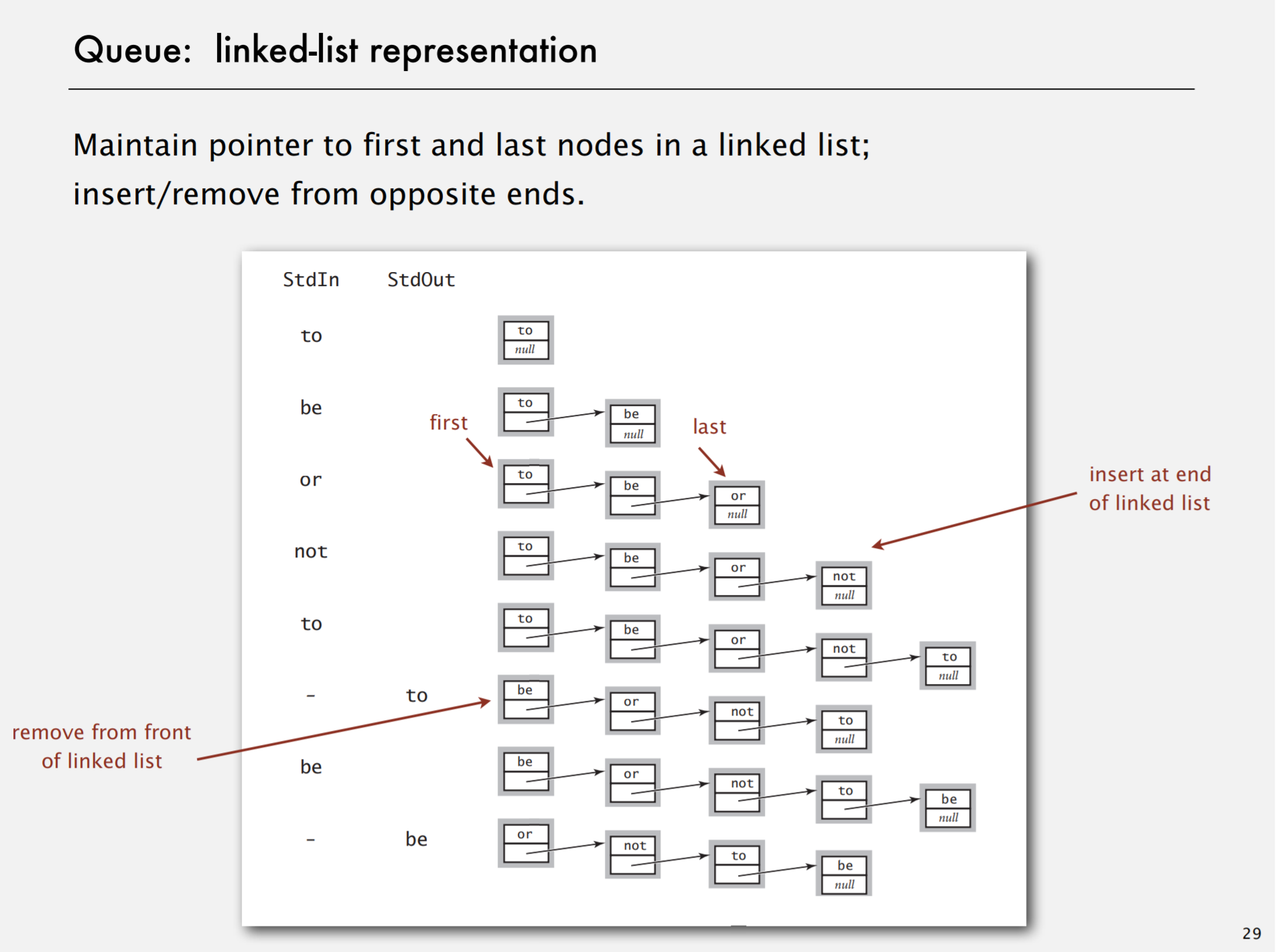
Queue1:linked-list implementation
dequeue

enqueue

public class LinkedQueueOfStrings
{
private Node first,last;
private class Node
{
String item;
Node next;
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return first == null;
}
public String enqueue(String item)
{
Node oldlast = last;
last = new Node();
last.item = item;
last.next = null;
if(isEmpty()) first = last;//special cases for empty queue
else oldlast.next = last;
}
public String dequeue()
{
String item = first.item;
firt = first.next;
if(isEmpty()) last = null;//special cases for empty queue
return item;
}
}Queue2:resizing array implementation

public class ResizingArrayQueue<Item> implements Iterable<Item> //generic type name
{
private Item[] q; // queue elements
public ResizingArrayQueue(){
q = (Item[]) new Object[2];
n = 0;//the real number of items in this queue.
first = 0;
last = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return n == 0;
}
public int size(){
return n;//Returns the number of items in this queue.
}
private void resize(int capacity){
assert capacity >=n;
Item[] temp = (Item[]) new Object[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
temp[i] = q[(first+i)%q.length];//q.length (empty array included)
}
q = temp;
first = 0;
last = n;
}
public String enqueue(Item item)
{
if (n == q.length) resize(2 * q.length);
q[last++] = item;//add first ,then increment
if (last == q.length) last = 0;// wrap-around
n++;
}
public Item dequeue()
{
if(isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow");//underflow堆栈下溢
Item item = q[first];
q[first] = null;// to avoid loitering 指针游离;without reference ,but wasted left
n--;
first++;
if (first == q.length) first = 0;// wrap-around
// shrink size of array if necessary
if (n > 0 && n == q.length / 4 ) resize(q.length /2); // 25%-100%
return item;
}
/**
* Returns the item least recently added to this queue.
*
* @return the item least recently added to this queue
* @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty
*/
public Item peek() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow");
return q[first];
}
public static void main(String[] args){
ResizingArrayQueue<String> queue = new ResizingArrayQueue<String>();
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()){
String item = StdIn.readString();
if(!item.equals("-")) queue.enqueue(item);
else if (!queue.isEmpty()) StdOut.print(queue.dequeue() + " ");
StdOut.println(queue.size() + "left on the queue");
}
}
3 Generics | 泛型
Java 泛型(generics)是 JDK 5 中引入的一个新特性, 泛型提供了编译时类型安全检测机制,该机制允许程序员在编译时检测到非法的类型。泛型的本质是参数化类型,也就是说所操作的数据类型被指定为一个参数。
假定我们有这样一个需求:写一个排序方法,能够对整型数组、字符串数组甚至其他任何类型的数组进行排序,该如何实现?答案是可以使用 Java 泛型。
We implemented: StackOfStrings.
We also want: StackOfURLs, StackOfInts, StackOfVans, ….
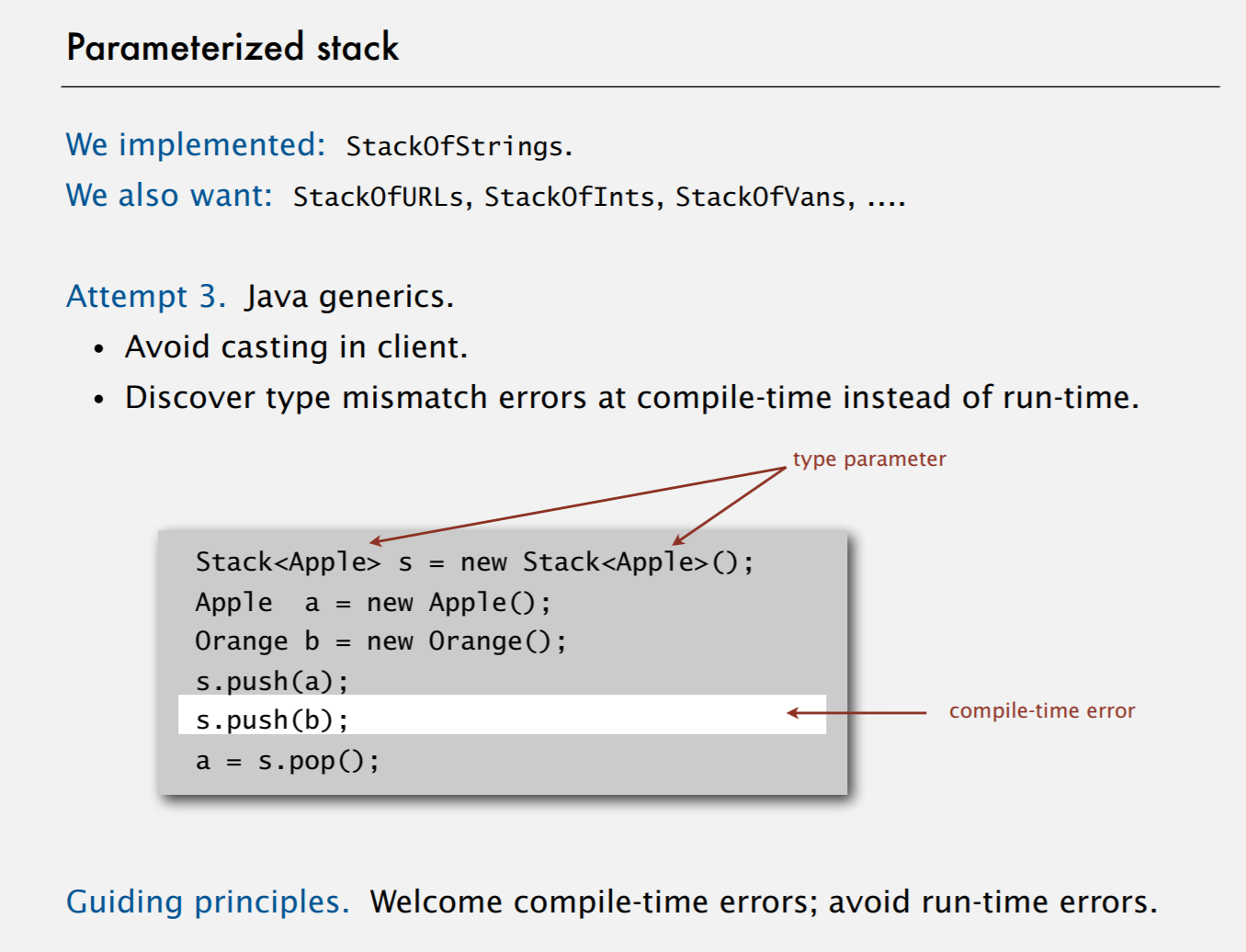
Principles
- Welcome compile-time errors;
- Avoid run-time errors.
Generic stack:linked-list implementation

Generic stack:array implementation
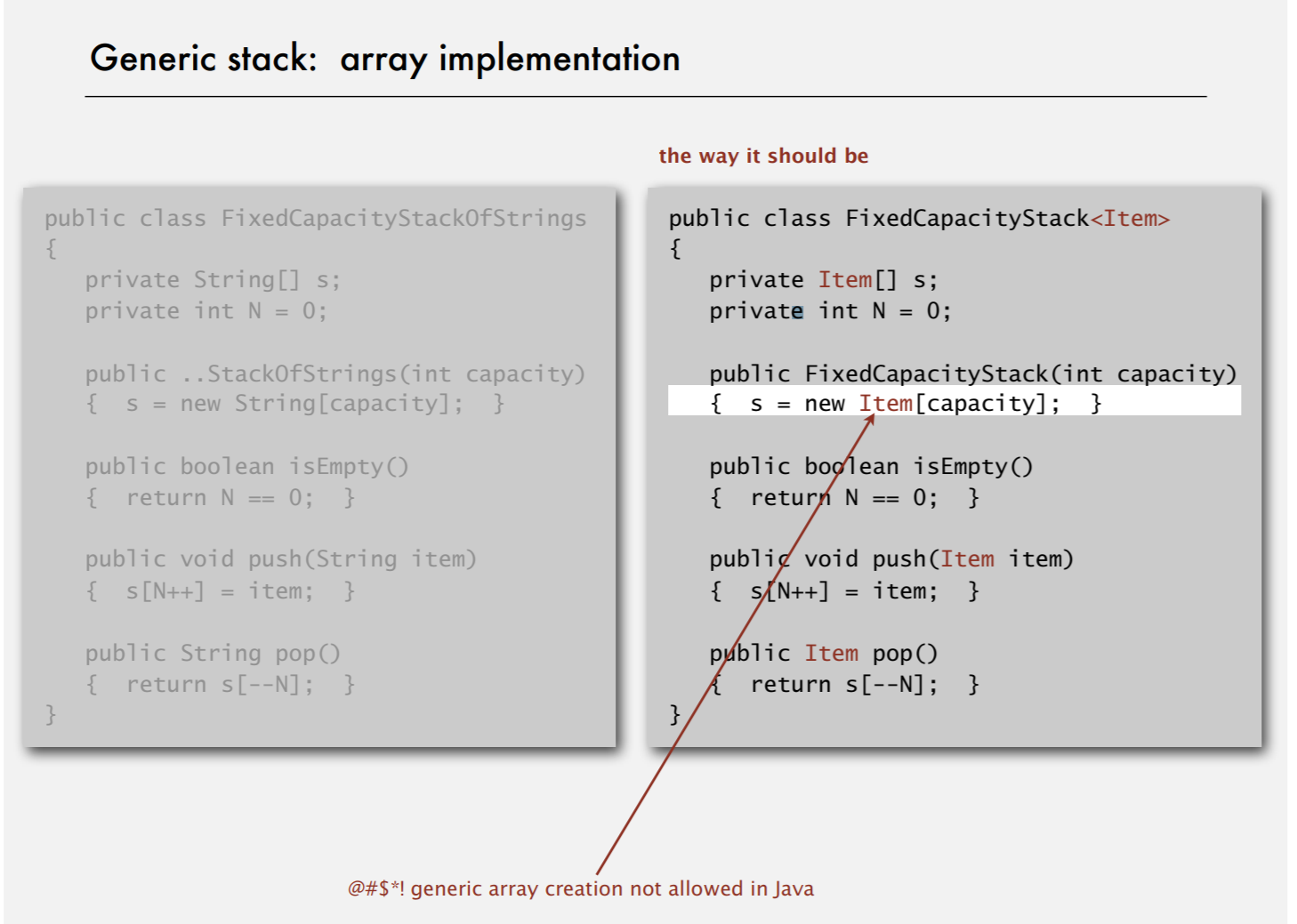
the ugly cast //Cast - 强制类型转换,如果不匹配,容易发生runtime error
generic array creation not allowed in Java

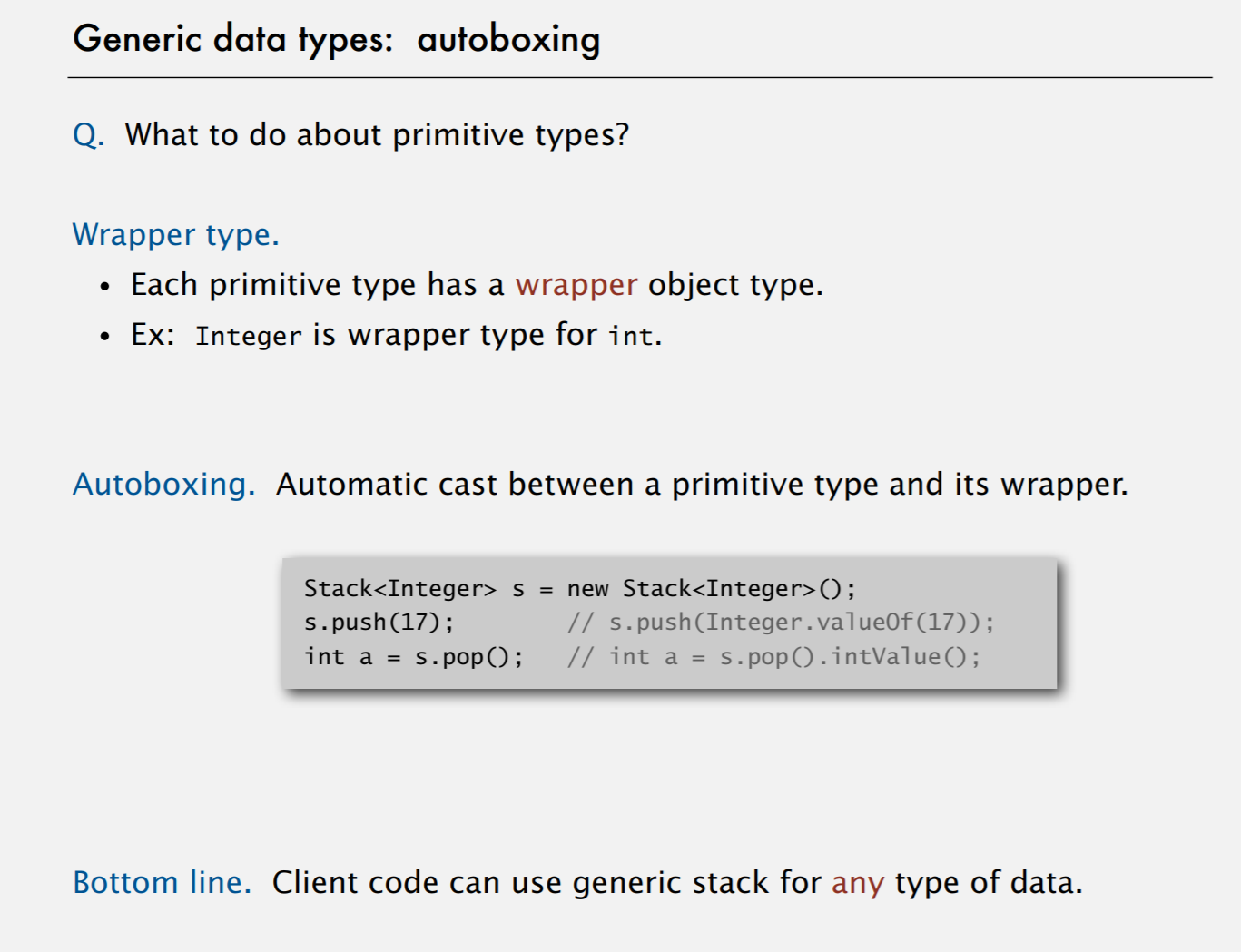
What to do about primitive types?
- wrapped type
Stack<Integer>stack=newStack<Integer>(); - autoboxing
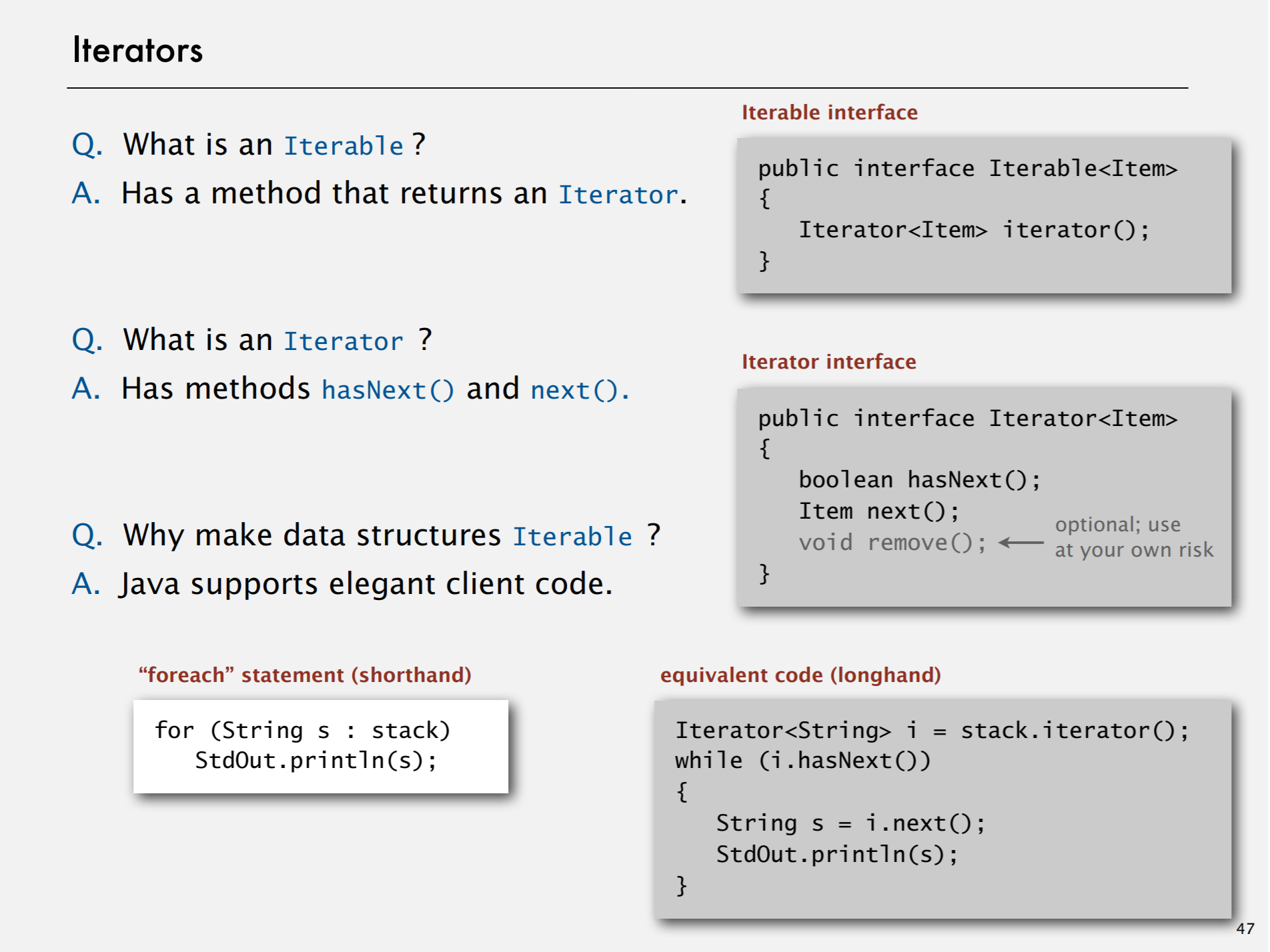
4 Iterators | 迭代器
Purpose: elegant client code.
这种模式用于顺序访问集合对象的元素,不需要知道集合对象的底层表示。
allow the client to iterate through the items
without revealing the internal representation of the stack.(whether link-list or resizing array stack)
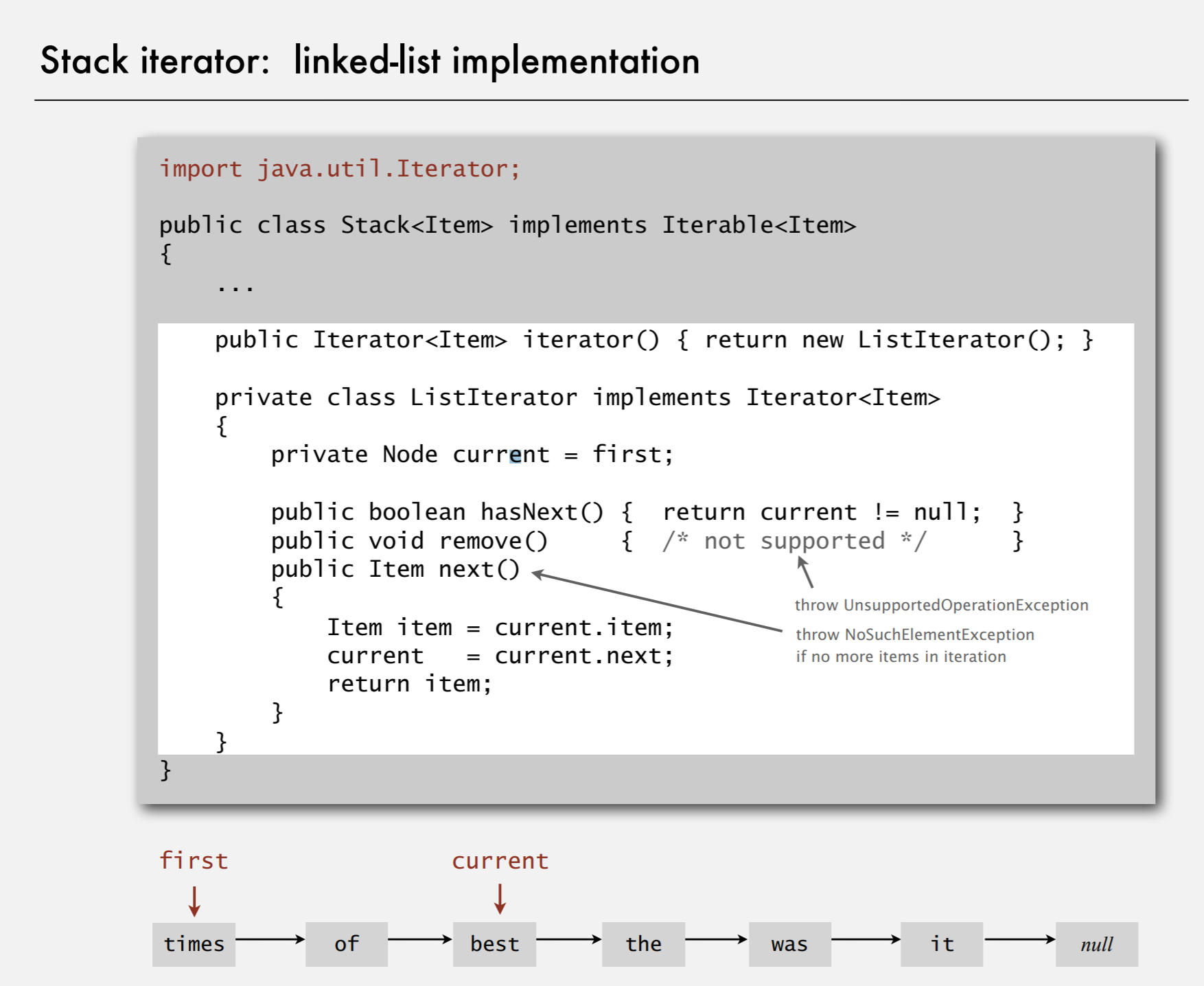
Stack iterator: linked-list implementation
Stack iterator: array implementation