版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_18948359/article/details/85213622
我们都知道二叉树的结构,就是在空间逻辑上面呈现出一颗树状的结构。并且有一个特点,左边的节点比右边的节点值要小。
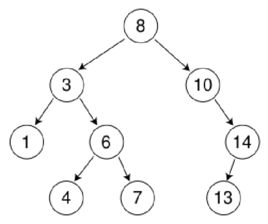
实现
这里使用 Comparable 接口做简单的实现。
定义一个类
这个类重写 Comparable 接口,并且覆写比较的方法。
// 实现 Comparable 接口
class Book implements Comparable<Book> {
private String title;
private double price;
public Book(String title, double price) {
this.title = title;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "书名:《" + this.title + "》,价格:" + this.price + "元。";
}
// 重写 compareTo 方法,返回出比较的大小,这里按照价格排序
@Override
public int compareTo(Book o) {
if (this.price > o.price) {
return 1;
} else if (this.price < o.price) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
树形构建的核心逻辑:
class BinaryTree {
class Node {
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private Comparable data;// 排序的依据是Comparable
private Node left;// 左节点
private Node right;// 右节点
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public Node(Comparable data) {
this.data = data;
}
// 1.添加节点
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void addNode(Node newNode) {
if (this.data.compareTo(newNode.data) > 0) {
if (this.left == null) {
this.left = newNode;
} else {
this.left.addNode(newNode); // 使用递归增加节点
}
} else {
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = newNode;
} else {
this.right.addNode(newNode); // 使用递归增加节点
}
}
}
// 2.对象数组
public void toArrayNode() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.toArrayNode();
}
BinaryTree.this.retArray[BinaryTree.this.foot++] = this.data;
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.toArrayNode();
}
}
}
// =================以上是内部类==================
private Node root;// 根节点
private int count;// 保存元素个数
private int foot;// 脚标
private Object[] retArray;// 对象数组
// 1.添加对象
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public void add(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return;
}
Comparable com = (Comparable) obj;
Node newNode = new Node(com);
if (this.root == null) {
this.root = newNode;
} else {
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
this.count++;
}
// 2.对象数组
public Object[] toArray() {
if (this.root == null) {
return null;
}
this.foot = 0;
this.retArray = new Object[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();
return this.retArray;
}
}
完整的代码
import java.util.Arrays;
class Book implements Comparable<Book> {
private String title;
private double price;
public Book(String title, double price) {
this.title = title;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "书名:《" + this.title + "》,价格:" + this.price + "元。";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Book o) {
if (this.price > o.price) {
return 1;
} else if (this.price < o.price) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
class BinaryTree {
class Node {
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private Comparable data;// 排序的依据是Comparable
private Node left;// 左节点
private Node right;// 右节点
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public Node(Comparable data) {
this.data = data;
}
// 1.添加节点
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void addNode(Node newNode) {
if (this.data.compareTo(newNode.data) > 0) {
if (this.left == null) {
this.left = newNode;
} else {
this.left.addNode(newNode);
}
} else {
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = newNode;
} else {
this.right.addNode(newNode);
}
}
}
// 2.对象数组
public void toArrayNode() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.toArrayNode();
}
BinaryTree.this.retArray[BinaryTree.this.foot++] = this.data;
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.toArrayNode();
}
}
}
// =================以上是内部类==================
private Node root;// 根节点
private int count;// 保存元素个数
private int foot;// 脚标
private Object[] retArray;// 对象数组
// 1.添加对象
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public void add(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return;
}
Comparable com = (Comparable) obj;
Node newNode = new Node(com);
if (this.root == null) {
this.root = newNode;
} else {
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
this.count++;
}
// 2.对象数组
public Object[] toArray() {
if (this.root == null) {
return null;
}
this.foot = 0;
this.retArray = new Object[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();
return this.retArray;
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree();
bt.add(new Book("Java从入门到精通", 88.6));
bt.add(new Book("Oracle从入门到精通", 99.6));
bt.add(new Book("Android开发", 88.5));
Object[] data = bt.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}