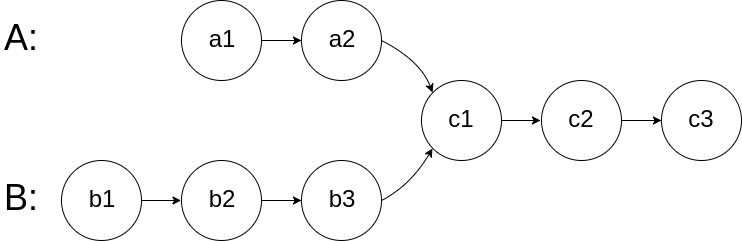
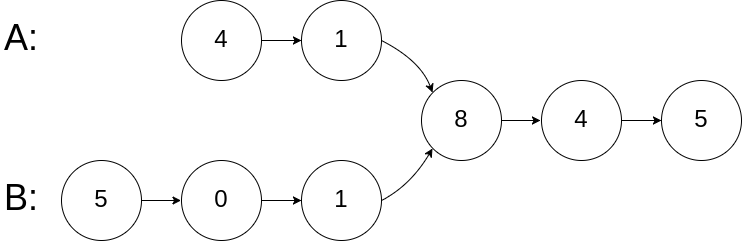
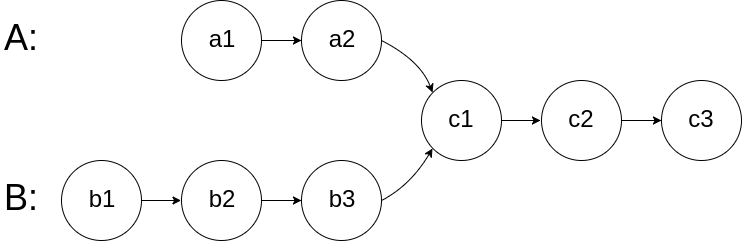
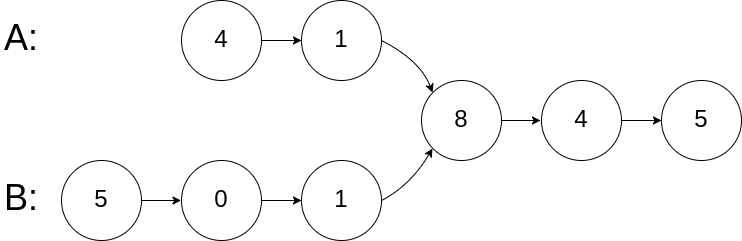
思路:
第一种:先得到两个链表的各自长度,然后看哪个链表长,哪个链表先走和另一个链表长度的差值,然后相当于现在两个链表一样长了,因为链表交点后面的 元素肯定是相同的,所以两个 链表从当前一起往后,看是否是一个节点,若都 空则没交点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int lenOfList(ListNode * li)
{
int len=0;
while(li)
{
len++;
li=li->next;
}return len;
}
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if(!headA || !headB) return NULL;
int len1=lenOfList(headA),len2=lenOfList(headB);
if(len1<len2)
for(int i=0;i<len2-len1;++i) headB=headB->next;
else
for(int i=0;i<len1-len2;++i) headA=headA->next;
while(headA && headB && headA!=headB)
{
headA=headA->next;
headB=headB->next;
}
return (headA && headB)? headA : NULL;
}
};第二种:很神奇的思路,链表A和B同时遍历,分别遍历到尾的时候从下一个节点开始,如果 两个链表相等,则就是交叉节点,若都为NULL,说明两个遍历指针将两个链表走完了。举个栗子:
A遍历到5的时候,下一个从B的头开始 遍历,B遍历到尾5的时候从A的头开始,等两个 遍历节点相交也就是同时在8的地方,结束。这是为什么第一个链表长度为5, 第二个为6,第一个遍历完又遍历了第二 个的前3个, 相当于走了5+3=8个,第二个 遍历完又遍历了第1个的前2个,就是6+2=8,也就是说他俩相遇就是交点,要么都为空(两个指针分别将两个链表遍历完了)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if(!headA ||!headB) return NULL;
ListNode *a=headA,*b=headB;
while(a!=b)
{
a=a ? a->next :headB;
b=b ? b->next :headA;
}
return a;
}
};