1 package pet; 2 //宠物类---父类 3 public abstract class Pet { 4 private int heath; 5 private String name; 6 7 public Pet(int heath, String name) { 8 super(); 9 this.heath = heath; 10 this.name = name; 11 } 12 public int getHeath() { 13 return heath; 14 } 15 public void setHeath(int heath) { 16 if(heath<0) { 17 System.out.println("健康值不能为负,默认为60"); 18 heath = 60; 19 } 20 this.heath = heath; 21 } 22 public String getName() { 23 return name; 24 } 25 public void setName(String name) { 26 this.name = name; 27 } 28 //自白方法 29 public void show() { 30 System.out.println("宠物的姓名为:"+this.getName()+",健康值为:"+this.getHeath()); 31 } 32 //抽象玩的方法 33 public abstract void play(); 34 //抽象吃的方法 35 public abstract void eat(); 36 }
1 package pet; 2 //狗类---子类 3 public class Dog extends Pet{ 4 public Dog(int heath, String name) { 5 super(heath,name); 6 } 7 //重写父类玩的方法 8 public void play() { 9 if(this.getHeath()>0) { 10 System.out.println("狗狗叼飞碟"); 11 this.setHeath(this.getHeath()-10); 12 System.out.println("叼玩飞碟后,"+this.getName()+"的健康值为:"+this.getHeath()); 13 }else if(this.getHeath()<0) { 14 System.out.println("体力耗光了,不能再玩了"); 15 } 16 } 17 //重写父类吃的方法 18 public void eat() { 19 if(this.getHeath()<100) { 20 System.out.println("给狗狗吃根骨头"); 21 this.setHeath(this.getHeath()+3); 22 System.out.println(this.getName()+"的健康值为:"+this.getHeath()); 23 }else { 24 System.out.println("狗狗吃饱了"); 25 } 26 } 27 }
1 package pet; 2 //企鹅类---子类 3 public class Penguin extends Pet { 4 public Penguin(int heath, String name) { 5 super(heath, name); 6 } 7 //重写父类玩的方法 8 public void play() { 9 if(this.getHeath()>0) { 10 System.out.println("让企鹅游泳"); 11 this.setHeath(this.getHeath()-15); 12 System.out.println(this.getName()+"的健康值为"+this.getHeath()); 13 }else if(this.getHeath()<0) { 14 System.out.println("体力耗光了,不能再玩了"); 15 } 16 } 17 //重写父类吃的方法 18 public void eat() { 19 if(this.getHeath()<100) { 20 System.out.println("给企鹅吃条鱼"); 21 this.setHeath(this.getHeath()+5); 22 System.out.println(this.getName()+"的健康值为:"+this.getHeath()); 23 }else { 24 System.out.println("企鹅吃饱了"); 25 } 26 } 27 }
1 package pet; 2 //主人类 3 public class Master { 4 public void play(Pet pet) { 5 //判断给的宠物是否为狗类 6 if(pet instanceof Dog) { 7 //向下转型,将pet由原来的宠物类强转为狗类 8 Dog d = (Dog)pet; 9 d.eat(); 10 d.play(); 11 }else{ 12 Penguin p = (Penguin)pet; 13 p.eat(); 14 p.play(); 15 } 16 } 17 }
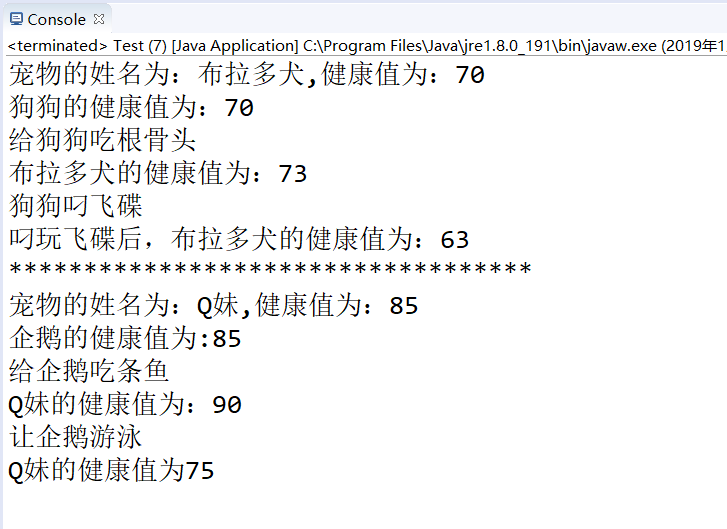
1 package pet; 2 //测试类 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 //父类类型引用子类对象 6 Pet d = new Dog(70, "布拉多犬"); 7 d.show(); 8 Master ms1 = new Master(); 9 System.out.println("狗狗的健康值为:"+d.getHeath()); 10 ms1.play(d); 11 System.out.println("***********************************"); 12 Pet p = new Penguin(85,"Q妹"); 13 p.show(); 14 Master ms2 = new Master(); 15 System.out.println("企鹅的健康值为:"+p.getHeath()); 16 ms2.play(p); 17 } 18 }
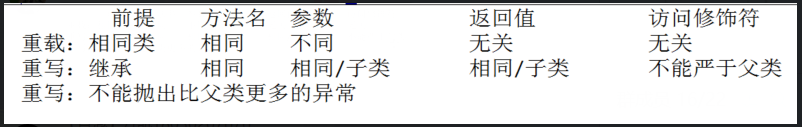
1.重写和重载的区别?
2.八大基本数据类型
整型;byte short int long
浮点型: float double
字符char
布尔型 boolean
3.==和equals的区别?
== 通常做数值的相等关系比较
equals通常做引用型数据类型的相等比较、
.== 比较的是变量的地址
equals比较的是变量指向的值是否是相同的
整型;byte short int long
浮点型: float double
字符char
布尔型 boolean
3.==和equals的区别?
== 通常做数值的相等关系比较
equals通常做引用型数据类型的相等比较、
.== 比较的是变量的地址
equals比较的是变量指向的值是否是相同的
4、什么是多态
同一个引用类型,使用不同的实例,得到不同的结果
5、实现多态的三个要素是什么
继承、方法重写、父类引用指向子类对象
1、使用多态时:是使用父类的类型,但是对象还是子类对象
2、如果子类不重写父类方法,那么当使用多态时,是不能调用子类独有的方法
(谁的类型,调谁的方法)
3、但是当子类重写父类方法,使用多态调用的方法,看似是父类中的方法,
但实际是子类中重写过父类的哪个方法
当:父类引用指向子类对象/父类类型创建子类对象时
这个对象不能够使用子类独有的方法
当使用多态时:创建对象必须是————父类类型 对象名 = new 子类构造方法
抽象类:表示这个类的对象是不存在的,因此抽象类不能够被实例化对象
但是可以用它的类型来创建对象,通常是创建子类对象,也就是多态
因此不需要具体实现的方法,可以把这个方法定义为抽象方法
(抽象方法没有方法体)
抽象类中可以有非抽象方法和抽象方法,但是抽象方法只能存在于抽象类中
实现多态的两种方式:使用父类作为方法参数、使用父类作为方法返回值
同一个引用类型,使用不同的实例,得到不同的结果
5、实现多态的三个要素是什么
继承、方法重写、父类引用指向子类对象
1、使用多态时:是使用父类的类型,但是对象还是子类对象
2、如果子类不重写父类方法,那么当使用多态时,是不能调用子类独有的方法
(谁的类型,调谁的方法)
3、但是当子类重写父类方法,使用多态调用的方法,看似是父类中的方法,
但实际是子类中重写过父类的哪个方法
当:父类引用指向子类对象/父类类型创建子类对象时
这个对象不能够使用子类独有的方法
当使用多态时:创建对象必须是————父类类型 对象名 = new 子类构造方法
抽象类:表示这个类的对象是不存在的,因此抽象类不能够被实例化对象
但是可以用它的类型来创建对象,通常是创建子类对象,也就是多态
因此不需要具体实现的方法,可以把这个方法定义为抽象方法
(抽象方法没有方法体)
抽象类中可以有非抽象方法和抽象方法,但是抽象方法只能存在于抽象类中
实现多态的两种方式:使用父类作为方法参数、使用父类作为方法返回值