分享一下我老师大神的人工智能教程!零基础,通俗易懂!http://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow
也欢迎大家转载本篇文章。分享知识,造福人民,实现我们中华民族伟大复兴!
Problem Set-2





Programming Question-2
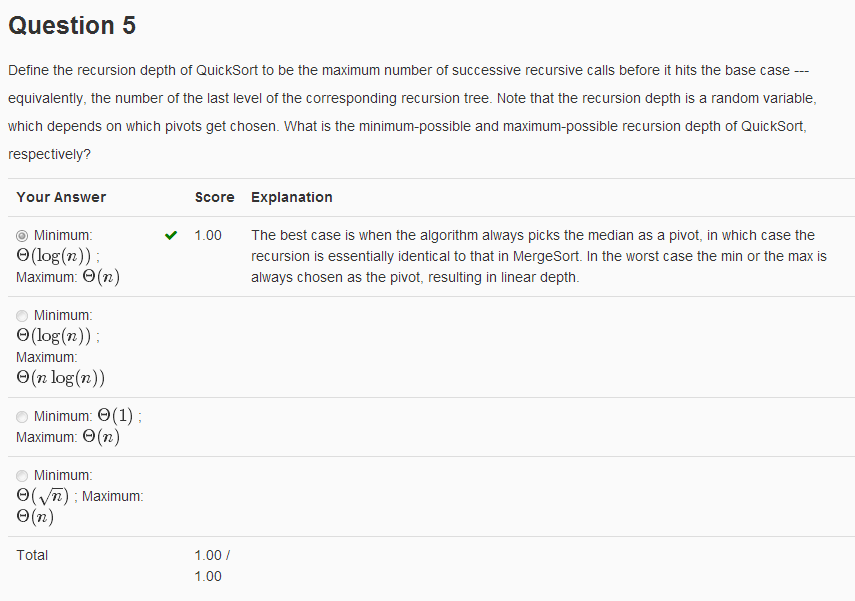
Question 1
Download the text file here.
The file contains all of the integers between 1 and 10,000 (inclusive, with no repeats) in unsorted order. The integer in the row of the file gives you the entry of an input array.
Your task is to compute the total number of comparisons used to sort the given input file by QuickSort. As you know, the number of comparisons depends on which elements are chosen as pivots, so we'll ask you to explore three different pivoting rules.
You should not count comparisons one-by-one. Rather, when there is a recursive call on a subarray of length , you should simply add to your running total of comparisons. (This is because the pivot element is compared to each of the other elements in the subarray in this recursive call.)
WARNING: The Partition subroutine can be implemented in several different ways, and different implementations can give you differing numbers of comparisons. For this problem, you should implement the Partition subroutine exactly as it is described in the video lectures (otherwise you might get the wrong answer).
DIRECTIONS FOR THIS PROBLEM:
For the first part of the programming assignment, you should always use the first element of the array as the pivot element.
HOW TO GIVE US YOUR ANSWER:
Type the numeric answer in the space provided.
So if your answer is 1198233847, then just type 1198233847 in the space provided without any space / commas / other punctuation marks. You have 5 attempts to get the correct answer.
(We do not require you to submit your code, so feel free to use the programming language of your choice, just type the numeric answer in the following space.)
Question 2
See the first question.
DIRECTIONS FOR THIS PROBLEM:
Compute the number of comparisons (as in Problem 1), always using the final element of the given array as the pivot element. Again, be sure to implement the Partition subroutine exactly as it is described in the video lectures. Recall from the lectures that, just before the main Partition subroutine, you should exchange the pivot element (i.e., the last element) with the first element.
Question 3
See the first question.
DIRECTIONS FOR THIS PROBLEM:
Compute the number of comparisons (as in Problem 1), using the "median-of-three" pivot rule. [The primary motivation behind this rule is to do a little bit of extra work to get much better performance on input arrays that are nearly sorted or reverse sorted.] In more detail, you should choose the pivot as follows. Consider the first, middle, and final elements of the given array. (If the array has odd length it should be clear what the "middle" element is; for an array with even length , use the element as the "middle" element. So for the array 4 5 6 7, the "middle" element is the second one ---- 5 and not 6!) Identify which of these three elements is the median (i.e., the one whose value is in between the other two), and use this as your pivot. As discussed in the first and second parts of this programming assignment, be sure to implement Partition exactly as described in the video lectures (including exchanging the pivot element with the first element just before the main Partition subroutine).
EXAMPLE: For the input array 8 2 4 5 7 1 you would consider the first (8), middle (4), and last (1) elements; since 4 is the median of the set {1,4,8}, you would use 4 as your pivot element.
SUBTLE POINT: A careful analysis would keep track of the comparisons made in identifying the median of the three candidate elements. You should NOT do this. That is, as in the previous two problems, you should simply add to your running total of comparisons every time you recurse on a subarray with length .
import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.DataInputStream;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStreamReader;import java.util.Arrays;public class QuickSort { private static int a[] = new int[10000]; private static long comparisonsCount = 0; /** * Returns first element as pivot * * @param start * @param end * @return */ public static int chooseFirstElementAsPivot(int start, int end) { return start; } /** * Returns the last element as pivot * * @param start * @param end * @return */ public static int chooseLastElementAsPivot(int start, int end) { // Move pivot to start index. int temp = a[start]; a[start] = a[end]; a[end] = temp; return start; } /** * Returns the median of start, end and mid as pivot * * @param start * @param end * @return */ public static int chooseMedianOfThreeAsPivot(int start, int end) { int pivotIndex = -1; int mid = ((end - start) / 2) + start; int b[] = new int[3]; b[0] = a[start]; b[1] = a[mid]; b[2] = a[end]; Arrays.sort(b); if (b[1] == a[start]) { pivotIndex = start; }else if(b[1] == a[mid]) { pivotIndex = mid; }else { pivotIndex = end; } // Move pivot to start index. int temp = a[start]; a[start] = a[pivotIndex]; a[pivotIndex] = temp; return start; } /** * Partitions the array about the pivot * * @param start * @param end * @param pivot */ public static int partition(int start, int end, int pivotIndex) { // Update comparisonsCount comparisonsCount += (long)end - start; // Partition int i = start; int pivot = a[pivotIndex]; for (int j = start; j <= end; j++) { if (a[j] < pivot) { i++; int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; } } // Put pivot into correct position int temp = a[i]; a[i] = pivot; a[pivotIndex] = temp; return i; } /** * Quick sort * * @param start * @param end */ public static void sort(int start, int end) { if (end - start == 1) { // Base case, no recursive calls. 2 Element, just sort them. if (a[start] > a[end]) { int temp = a[start]; a[start] = a[end]; a[end] = temp; } // Increment comparisons count by 1 as there is 1 comparison happening here. comparisonsCount ++; }else if(end <= start) { // Base case, only one element. Nothing to do. } else { //change pivot options here int pivotIndex = chooseMedianOfThreeAsPivot(start, end); int partitionIndex = partition(start, end, pivotIndex); sort(start, partitionIndex - 1); sort(partitionIndex + 1, end); } } /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { File inputFile = new File("E:\\QuickSort.txt"); String inputFilePath = inputFile.getAbsolutePath(); // read and parse input file try { String strLine = ""; int count = 0; FileInputStream fstream = new FileInputStream(inputFilePath); DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(fstream); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in)); while ((strLine = br.readLine()) != null) { a[count ++] = Integer.parseInt(strLine); } br.close(); in.close(); fstream.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } sort(0, a.length - 1); for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.println(a[i]); } System.out.println(comparisonsCount); }}给我老师的人工智能教程打call!http://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow

新的改变
我们对Markdown编辑器进行了一些功能拓展与语法支持,除了标准的Markdown编辑器功能,我们增加了如下几点新功能,帮助你用它写博客:
- 全新的界面设计 ,将会带来全新的写作体验;
- 在创作中心设置你喜爱的代码高亮样式,Markdown 将代码片显示选择的高亮样式 进行展示;
- 增加了 图片拖拽 功能,你可以将本地的图片直接拖拽到编辑区域直接展示;
- 全新的 KaTeX数学公式 语法;
- 增加了支持甘特图的mermaid语法1 功能;
- 增加了 多屏幕编辑 Markdown文章功能;
- 增加了 焦点写作模式、预览模式、简洁写作模式、左右区域同步滚轮设置 等功能,功能按钮位于编辑区域与预览区域中间;
- 增加了 检查列表 功能。
功能快捷键
撤销:Ctrl/Command + Z
重做:Ctrl/Command + Y
加粗:Ctrl/Command + B
斜体:Ctrl/Command + I
标题:Ctrl/Command + Shift + H
无序列表:Ctrl/Command + Shift + U
有序列表:Ctrl/Command + Shift + O
检查列表:Ctrl/Command + Shift + C
插入代码:Ctrl/Command + Shift + K
插入链接:Ctrl/Command + Shift + L
插入图片:Ctrl/Command + Shift + G
合理的创建标题,有助于目录的生成
直接输入1次#,并按下space后,将生成1级标题。
输入2次#,并按下space后,将生成2级标题。
以此类推,我们支持6级标题。有助于使用TOC语法后生成一个完美的目录。
如何改变文本的样式
强调文本 强调文本
加粗文本 加粗文本
标记文本
删除文本
引用文本
H2O is是液体。
210 运算结果是 1024.
插入链接与图片
链接: link.
图片: ![]()
带尺寸的图片: ![]()
当然,我们为了让用户更加便捷,我们增加了图片拖拽功能。
如何插入一段漂亮的代码片
去博客设置页面,选择一款你喜欢的代码片高亮样式,下面展示同样高亮的 代码片.
// An highlighted block var foo = 'bar'; 生成一个适合你的列表
- 项目
- 项目
- 项目
- 项目
- 项目1
- 项目2
- 项目3
- 计划任务
- 完成任务
创建一个表格
一个简单的表格是这么创建的:
| 项目 | Value |
|---|---|
| 电脑 | $1600 |
| 手机 | $12 |
| 导管 | $1 |
设定内容居中、居左、居右
使用:---------:居中
使用:----------居左
使用----------:居右
| 第一列 | 第二列 | 第三列 |
|---|---|---|
| 第一列文本居中 | 第二列文本居右 | 第三列文本居左 |
SmartyPants
SmartyPants将ASCII标点字符转换为“智能”印刷标点HTML实体。例如:
| TYPE | ASCII | HTML |
|---|---|---|
| Single backticks | 'Isn't this fun?' |
‘Isn’t this fun?’ |
| Quotes | "Isn't this fun?" |
“Isn’t this fun?” |
| Dashes | -- is en-dash, --- is em-dash |
– is en-dash, — is em-dash |
创建一个自定义列表
- Markdown
- Text-to- HTML conversion tool
- Authors
- John
- Luke
如何创建一个注脚
一个具有注脚的文本。2
注释也是必不可少的
Markdown将文本转换为 HTML。
KaTeX数学公式
您可以使用渲染LaTeX数学表达式 KaTeX:
Gamma公式展示 是通过欧拉积分
你可以找到更多关于的信息 LaTeX 数学表达式here.
新的甘特图功能,丰富你的文章
gantt
dateFormat YYYY-MM-DD
title Adding GANTT diagram functionality to mermaid
section 现有任务
已完成 :done, des1, 2014-01-06,2014-01-08
进行中 :active, des2, 2014-01-09, 3d
计划一 : des3, after des2, 5d
计划二 : des4, after des3, 5d
- 关于 甘特图 语法,参考 这儿,
UML 图表
可以使用UML图表进行渲染。 Mermaid. 例如下面产生的一个序列图::
这将产生一个流程图。:
- 关于 Mermaid 语法,参考 这儿,
FLowchart流程图
我们依旧会支持flowchart的流程图:
- 关于 Flowchart流程图 语法,参考 这儿.
导出与导入
导出
如果你想尝试使用此编辑器, 你可以在此篇文章任意编辑。当你完成了一篇文章的写作, 在上方工具栏找到 文章导出 ,生成一个.md文件或者.html文件进行本地保存。
导入
如果你想加载一篇你写过的.md文件或者.html文件,在上方工具栏可以选择导入功能进行对应扩展名的文件导入,
继续你的创作。
注脚的解释 ↩︎