一、Volume
为了持久化保存容器的数据,可以使用 Kubernetes Volume。
Volume的生命周期独立于容器,Pod中的容器可能被销毁和重建,但Volume会被保存。
本质上,Kubernetes Volume 是一个目录,这一点与 Docker Volume 类似。当 Volume 被 mount 到 Pod,Pod 中的所有容器都可以访问这个 Volume。
Kubernetes 也支持多种 backend 类型, 包括 emptyDir、hostPath、GCEPersistent Disk、AWS Elastic Block Store、NFS、Ceph等。Volume提供了对各种 backend 的抽象,容器在使用 Volume 读写数据的时候不需要关心数据到底是存放在本地节点的文件系统中还是云硬盘中。对它来说,所有类型的 Volume 都只是一个目录。
二、emptyDir
emptyDIr 是最基础的 Volume 类型。正如其名字所示,一个 emptyDir Volume 是 Host 上的一个空目录。
empty Volume 对于容器来说是持久的,对于 Pod 则不是。当 Pod 从节点删除时,Volume 的内容也会被删除。但如果只是容器被销毁而 Pod 还在,则 Volume 不受影响。
也就是说: emptyDir Volume 的生命周期与 Pod 一致。
Pod 中所有的容器可以共享 Volume,他们可以制定各自的 mount 路径。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: producer-consumer
spec:
containers:
- image: busybox
name: producer-consumer
spec:
containers:
- image: busybox
name: producer
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /producer_dir
name: shared-volume
args:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- echo "hello world" > /producer_dir/hello ; sleep 30000
- image: busybox
name: consumer
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /consumer_dir
name: shared-volume
args:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- cat /consumer_dir/hello ; sleep 30000
volumes:
- name: shared-volume
emptyDir: {}
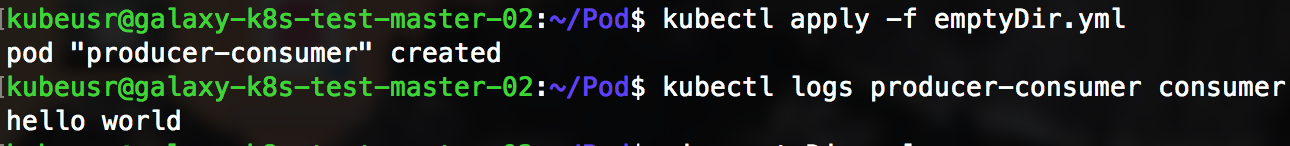
模拟一个producer-consumer场景。Pod 有两个容器 producer 和 consumer,他们共享一个 Volume。producer 负责往 Volume中写数据, consumer 负责从 Volume 中读取数据。
1) 文件最底部 volumes 定义一个 emptyDir 类型的 Volume shared-volume
2) producer 容器将 shared-volume mount 到 /producer_dir 目录
3) producer 通过 echo 将数据写到文件 hello 里
4) consumer 容器将 shared-volume mount 到 /consumer_dir 目录
5) consumer 通过 cat 从文件 hello 读取数据
执行创建 Pod: