版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,欢迎转载,转载请注明出处。 https://blog.csdn.net/shanglianlm/article/details/86376627
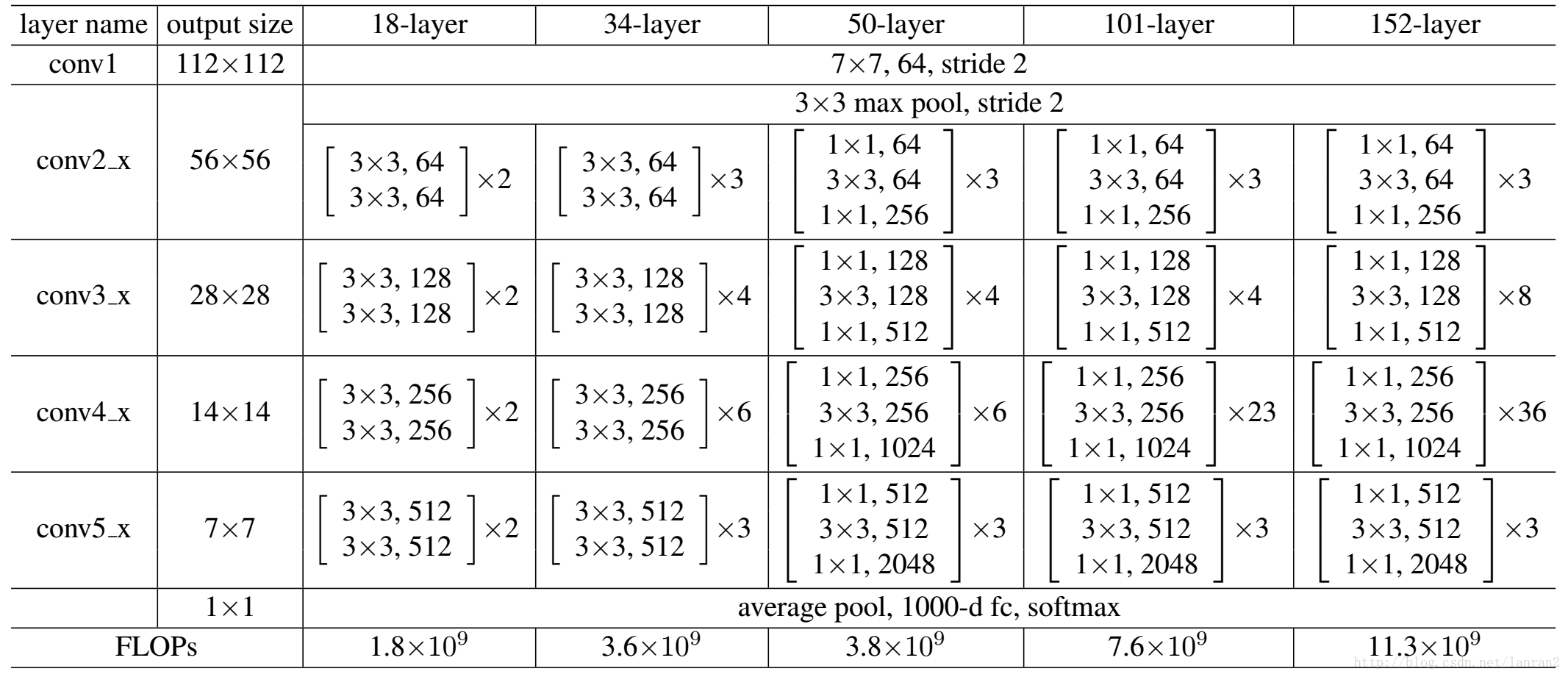
PyTorch实现的ResNet50、ResNet101和ResNet152
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision
import numpy as np
print("PyTorch Version: ",torch.__version__)
print("Torchvision Version: ",torchvision.__version__)
__all__ = ['ResNet50', 'ResNet101','ResNet152']
def Conv1(in_planes, places, stride=2):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_planes,out_channels=places,kernel_size=7,stride=stride,padding=3, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(places),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
)
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_places,places, stride=1,downsampling=False, expansion = 4):
super(Bottleneck,self).__init__()
self.expansion = expansion
self.downsampling = downsampling
self.bottleneck = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_places,out_channels=places,kernel_size=1,stride=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(places),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=places, out_channels=places, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(places),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=places, out_channels=places*self.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(places*self.expansion),
)
if self.downsampling:
self.downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_places, out_channels=places*self.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(places*self.expansion)
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.bottleneck(x)
if self.downsampling:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,blocks, num_classes=1000, expansion = 4):
super(ResNet,self).__init__()
self.expansion = expansion
self.conv1 = Conv1(in_planes = 3, places= 64)
self.layer1 = self.make_layer(in_places = 64, places= 64, block=blocks[0], stride=1)
self.layer2 = self.make_layer(in_places = 256,places=128, block=blocks[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self.make_layer(in_places=512,places=256, block=blocks[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self.make_layer(in_places=1024,places=512, block=blocks[3], stride=2)
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(7, stride=1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(2048,num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def make_layer(self, in_places, places, block, stride):
layers = []
layers.append(Bottleneck(in_places, places,stride, downsampling =True))
for i in range(1, block):
layers.append(Bottleneck(places*self.expansion, places))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def ResNet50():
return ResNet([3, 4, 6, 3])
def ResNet101():
return ResNet([3, 4, 23, 3])
def ResNet152():
return ResNet([3, 8, 36, 3])
if __name__=='__main__':
#model = torchvision.models.resnet50()
model = ResNet50()
print(model)
input = torch.randn(8, 3, 224, 224)
out = model(input)
print(out.shape)