主要分析内容:
一、BeanPostProcessor简述与demo示例
二、BeanPostProcessor源码分析:注册时机和触发点
一、BeanPostProcessor简述与demo示例
BeanPostProcessor是spring非常重要的拓展接口,例如aop通过拓展接口生产代理bean等。接口有两个方法:

/** * Factory hook that allows for custom modification of new bean instances, * e.g. checking for marker interfaces or wrapping them with proxies. * * <p>ApplicationContexts can autodetect BeanPostProcessor beans in their * bean definitions and apply them to any beans subsequently created. * Plain bean factories allow for programmatic registration of post-processors, * applying to all beans created through this factory. * * <p>Typically, post-processors that populate beans via marker interfaces * or the like will implement {@link #postProcessBeforeInitialization}, * while post-processors that wrap beans with proxies will normally * implement {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization}. * * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 10.10.2003 * @see InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor * @see DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor * @see ConfigurableBeanFactory#addBeanPostProcessor * @see BeanFactoryPostProcessor */ public interface BeanPostProcessor { /** * Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean * initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet} * or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values. * The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original. * <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is. * @param bean the new bean instance * @param beanName the name of the bean * @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one; * if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked * @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet */ @Nullable default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { return bean; } /** * Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean * initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet} * or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values. * The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original. * <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean * instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The * post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created * objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks. * <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a * {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method, * in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks. * <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is. * @param bean the new bean instance * @param beanName the name of the bean * @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one; * if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked * @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean */ @Nullable default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { return bean; } }
以上为spring原始接口,这里说明一下:
- ApplicationContext类型的容器会自动发现和注册该类型的bean,通过BeanPostProcessor可以对bean进行定制化,接口作用域是所有bean创建。
- postProcessBeforeInitialization触发时机在bean实例化(Instantiation)之后,所有初始化(Initialization)动作(包括 InitializingBean#afterPrpertiesSet() 和 定制化init-method())以前。
- postProcessAfterInitialization触发时机在bean实例化(Instantiation)之后,所有初始化(Initialization)动作(包括 InitializingBean#afterPrpertiesSet() 和 定制化init-method())以后。同时还会在InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation 和 FactoryBean(bean工厂)获得bean时候调用。这个也是重要的点,放在往后的博客中阐述。
由于ApplicationContext可以自动发现并注册BeanPostProcessor,如下使用ApplicationContext类型容器实现一个简单demo。 对应的demo代码可参考: https://gitee.com/zhouxiaoxing91/learning-src/tree/master

1 public class BeanPostProcessorTest { 2 3 private ApplicationContext applicationContext ; 4 5 @Before 6 public void beforeApplicationContext(){ 7 /** 8 * ApplicationContext 自动注册 BeanPostProcessor 9 * 不需要手动注册 10 * */ 11 applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ioc-beanPostProcessor.xml") ; 12 } 13 14 @Test 15 public void test(){ 16 Bean bean = applicationContext.getBean("bean", Bean.class) ; 17 System.out.println(bean); 18 } 19 20 @After 21 public void after(){ 22 ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)applicationContext).close(); 23 } 24 }

1 public class Bean { 2 3 public Bean(){ 4 5 } 6 7 public Bean(String name){ 8 System.out.println("构造函数被调用啦"); 9 this.name = name ; 10 } 11 12 private String name ; 13 14 15 public String getName() { 16 return name; 17 } 18 19 public void setName(String name) { 20 this.name = name; 21 } 22 23 @Override 24 public String toString() { 25 return "Bean{" + 26 "name='" + name + '\'' + 27 '}'; 28 } 29 }

1 public class LogicBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { 2 3 @Nullable 4 @Override 5 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 6 System.out.println("LogicBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization 执行啦 beanName = " + beanName); 7 return bean; 8 } 9 10 @Nullable 11 @Override 12 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 13 System.out.println("LogicBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization 执行啦 beanName = " + beanName); 14 return bean; 15 } 16 }

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> 5 6 <bean id="bean" class="com.nancy.ioc.Bean"> 7 <constructor-arg name="name" value="zhouxiaoxing"/> 8 </bean> 9 10 <bean id="logicBeanPostProcessor" class="com.nancy.ioc.BeanPostProcessor.LogicBeanPostProcessor"/> 11 </beans>
运行结果符合以上的结论:
构造函数被调用啦
LogicBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization 执行啦 beanName = bean
LogicBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization 执行啦 beanName = bean
Bean{name='zhouxiaoxing'}
提出两个疑问:
1、在ApplicationContext容器中何时注册BeanPostProcessor接口 ?
二、BeanPostProcessor源码分析:注册时机和触发点
在AbstractApplicationContext容器启动的refresh()会注册BeanPostProcessor,源码如下:
1 @Override 2 public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { 3 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { 4 // Prepare this context for refreshing. 5 prepareRefresh(); 6 7 // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. 8 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); 9 10 // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. 11 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); 12 13 try { 14 // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. 15 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); 16 17 // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. 18 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); 19 20 // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. 21 // 注册BeanPostProcessor 在bean创建的时候进行拦截 22 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); 23 24 // Initialize message source for this context. 25 initMessageSource(); 26 27 // Initialize event multicaster for this context. 28 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); 29 30 // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. 31 onRefresh(); 32 33 // Check for listener beans and register them. 34 registerListeners(); 35 36 // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. 37 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); 38 39 // Last step: publish corresponding event. 40 finishRefresh(); 41 } 42 43 catch (BeansException ex) { 44 if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { 45 logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + 46 "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); 47 } 48 49 // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. 50 destroyBeans(); 51 52 // Reset 'active' flag. 53 cancelRefresh(ex); 54 55 // Propagate exception to caller. 56 throw ex; 57 } 58 59 finally { 60 // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we 61 // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... 62 resetCommonCaches(); 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 67 ...... 68 69 /** 70 * Instantiate and invoke all registered BeanPostProcessor beans, 71 * respecting explicit order if given. 72 * <p>Must be called before any instantiation of application beans. 73 */ 74 protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { 75 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this); 76 }
跟进PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors
1 public static void registerBeanPostProcessors( 2 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) { 3 4 /** 5 * 此时bean的定义加载已经完成,但是还没有实例化。 获得所有BeanPostProcessor bean对应的beanName 6 */ 7 String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); 8 9 /** 10 * 注册日志BeanPostProcessor, 检测注册的bean是否为spring基础服务类并打印日志 11 */ 12 // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when 13 // a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when 14 // a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors. 15 int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length; 16 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); 17 18 /** 19 * 当有注册多个BeanPostProcessor接口时会按顺序进行,即 实现PriorityOrdered->实现Ordered->普通类型接口->内部系统MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 20 */ 21 // Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, 22 // Ordered, and the rest. 23 List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); 24 List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); 25 List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); 26 List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); 27 for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { 28 if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { 29 30 /** 31 * 通过beanFactory.getBean(), 将会提前初始化BeanPostProcessor类型实例 32 */ 33 BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); 34 priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); 35 if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { 36 internalPostProcessors.add(pp); 37 } 38 } 39 else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { 40 orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); 41 } 42 else { 43 nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); 44 } 45 } 46 47 // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. 48 sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); 49 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); 50 51 // Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered. 52 List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); 53 for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { 54 BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); 55 orderedPostProcessors.add(pp); 56 if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { 57 internalPostProcessors.add(pp); 58 } 59 } 60 sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); 61 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); 62 63 // Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors. 64 List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); 65 for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { 66 BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); 67 nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); 68 if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { 69 internalPostProcessors.add(pp); 70 } 71 } 72 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); 73 74 // Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors. 75 sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory); 76 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); 77 78 /** 79 * ApplicationListener探测器,当bean实现ApplicationListener接口时自动注册监听 80 */ 81 // Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners, 82 // moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc). 83 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext)); 84 } 85 86 /** 87 * 按照给定Ordered的顺序排序 88 */ 89 private static void sortPostProcessors(List<?> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { 90 Comparator<Object> comparatorToUse = null; 91 if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) { 92 comparatorToUse = ((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory).getDependencyComparator(); 93 } 94 if (comparatorToUse == null) { 95 comparatorToUse = OrderComparator.INSTANCE; 96 } 97 postProcessors.sort(comparatorToUse); 98 } 99 100 /** 101 * Register the given BeanPostProcessor beans. 102 */ 103 private static void registerBeanPostProcessors( 104 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanPostProcessor> postProcessors) { 105 106 for (BeanPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) { 107 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor); 108 } 109 }
修改上述demo中LogicBeanPostProcessor.java文件,并debug模式查看:
1 public class LogicBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { 2 3 public LogicBeanPostProcessor(){ 4 System.out.println("LogicBeanPostProcessor 被 beanFactory.getBean() 提前初始化"); 5 } 6 7 @Nullable 8 @Override 9 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 10 System.out.println("LogicBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization 执行啦 beanName = " + beanName); 11 return bean; 12 } 13 14 @Nullable 15 @Override 16 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 17 System.out.println("LogicBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization 执行啦 beanName = " + beanName); 18 return bean; 19 } 20 }
查看PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#registerBeanPostProcessors,注册一个普通BeanPostProcessor -> logicBeanPostProcessor
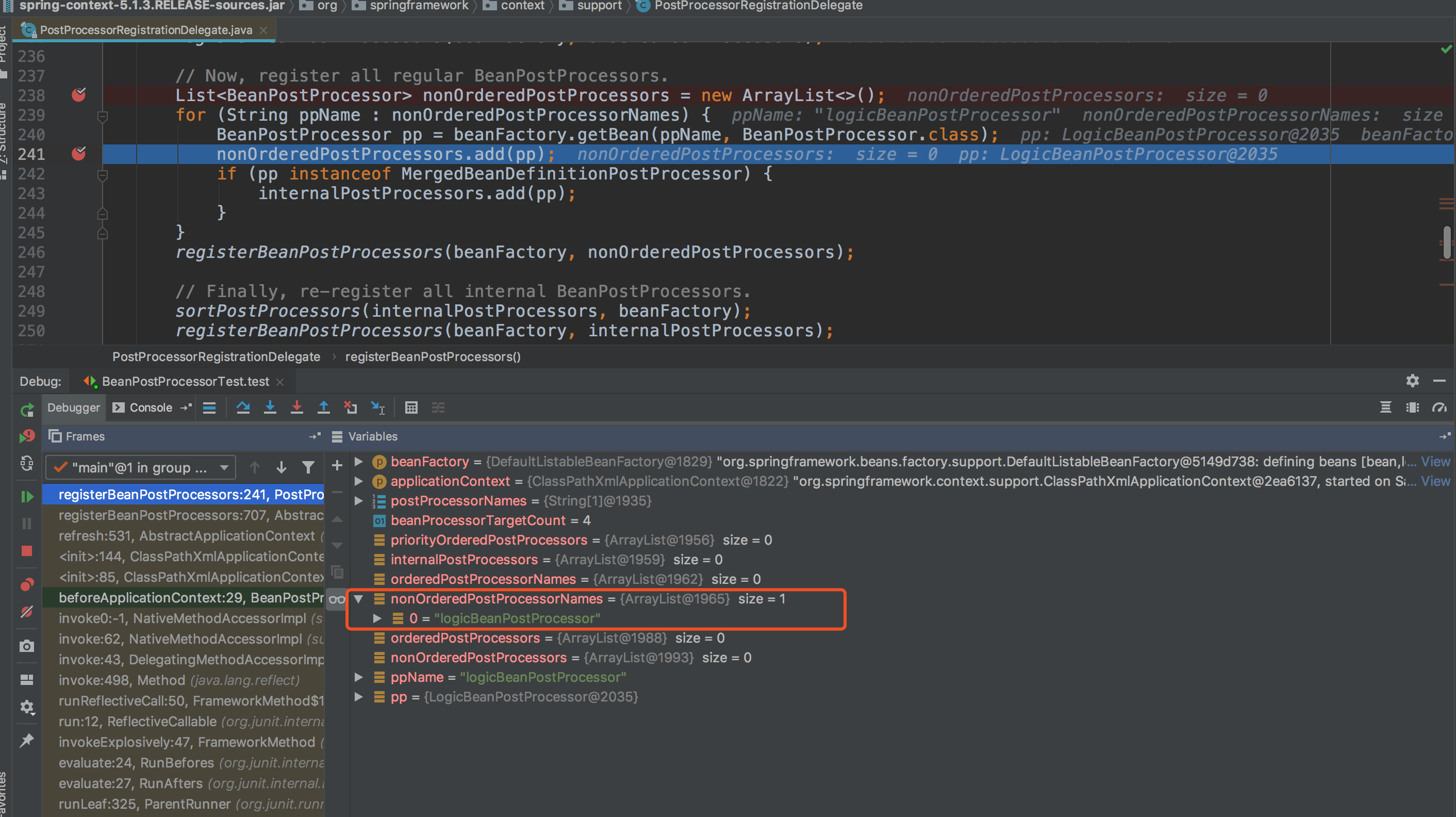
最后运行结果:
LogicBeanPostProcessor 被 beanFactory.getBean() 提前初始化 构造函数被调用啦 LogicBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization 执行啦 beanName = bean LogicBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization 执行啦 beanName = bean Bean{name='zhouxiaoxing'}
总结如下:
(1)、BeanPostProcessor注册的入口在AbstractApplicationContext容器启动的refresh()的AbstractApplicationContext#registerBeanPostProcessors。
(2)、AbstractApplicationContext进而委派PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#registerBeanPostProcessors实现注册。
(3)、当有注册多个BeanPostProcessor接口时会按顺序进行,即 实现PriorityOrdered->实现Ordered->普通类型接口->内部系统MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor。而同种类型也会进行排序,按顺序注册。
(4)、BeanPostProcessor类型实例会通过BeanFactory#getBean()提前初始化。
触发BeanPostProcessor有很多入口,首先分析几个入口后续的再补上。
触发(1)AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean 中:
1 /** 2 * Central method of this class: creates a bean instance, 3 * populates the bean instance, applies post-processors, etc. 4 * @see #doCreateBean 5 */ 6 @Override 7 protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) 8 throws BeanCreationException { 9 10 // 省略...... 11 12 try { 13 // bean 创建 14 Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args); 15 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 16 logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'"); 17 } 18 return beanInstance; 19 } 20 catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) { 21 // A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already, 22 // or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry. 23 throw ex; 24 } 25 catch (Throwable ex) { 26 throw new BeanCreationException( 27 mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex); 28 } 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened 33 * at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks. 34 * <p>Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a 35 * factory method, and autowiring a constructor. 36 * @param beanName the name of the bean 37 * @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean 38 * @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation 39 * @return a new instance of the bean 40 * @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created 41 * @see #instantiateBean 42 * @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod 43 * @see #autowireConstructor 44 */ 45 protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args) 46 throws BeanCreationException { 47 48 // Instantiate the bean. 49 BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; 50 if (mbd.isSingleton()) { 51 instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); 52 } 53 if (instanceWrapper == null) { 54 instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); 55 } 56 57 // 省略...... 58 59 // Initialize the bean instance. 60 Object exposedObject = bean; 61 try { 62 // 根据加载到的bean definition给 bean赋值 63 populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); 64 // 调用bean初始化方法 65 exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); 66 } 67 catch (Throwable ex) { 68 if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) { 69 throw (BeanCreationException) ex; 70 } 71 else { 72 throw new BeanCreationException( 73 mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex); 74 } 75 } 76 77 // 省略...... 78 79 return exposedObject; 80 }
跟进AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean方法:
1 /** 2 * Initialize the given bean instance, applying factory callbacks 3 * as well as init methods and bean post processors. 4 * <p>Called from {@link #createBean} for traditionally defined beans, 5 * and from {@link #initializeBean} for existing bean instances. 6 * @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes) 7 * @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize 8 * @param mbd the bean definition that the bean was created with 9 * (can also be {@code null}, if given an existing bean instance) 10 * @return the initialized bean instance (potentially wrapped) 11 * @see BeanNameAware 12 * @see BeanClassLoaderAware 13 * @see BeanFactoryAware 14 * @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization 15 * @see #invokeInitMethods 16 * @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization 17 */ 18 protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { 19 // 1、工厂factory类 接口回调 20 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { 21 AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { 22 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); 23 return null; 24 }, getAccessControlContext()); 25 } 26 else { 27 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); 28 } 29 30 Object wrappedBean = bean; 31 if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { 32 // 2、BeanPostProcessor前置执行 33 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); 34 } 35 36 try { 37 // 3、InitializingBean接口方法 or 自定义 init method 执行 38 invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); 39 } 40 catch (Throwable ex) { 41 throw new BeanCreationException( 42 (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), 43 beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); 44 } 45 if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { 46 // 4、BeanPostProcessor后置执行 47 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); 48 } 49 50 return wrappedBean; 51 }
对应回调方法:

1 private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) { 2 if (bean instanceof Aware) { 3 if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) { 4 ((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName); 5 } 6 if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) { 7 ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader(); 8 if (bcl != null) { 9 ((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl); 10 } 11 } 12 if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) { 13 ((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this); 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 18 /** 19 * Give a bean a chance to react now all its properties are set, 20 * and a chance to know about its owning bean factory (this object). 21 * This means checking whether the bean implements InitializingBean or defines 22 * a custom init method, and invoking the necessary callback(s) if it does. 23 * @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes) 24 * @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize 25 * @param mbd the merged bean definition that the bean was created with 26 * (can also be {@code null}, if given an existing bean instance) 27 * @throws Throwable if thrown by init methods or by the invocation process 28 * @see #invokeCustomInitMethod 29 */ 30 protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) 31 throws Throwable { 32 33 boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean); 34 if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) { 35 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 36 logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'"); 37 } 38 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { 39 try { 40 AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> { 41 ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); 42 return null; 43 }, getAccessControlContext()); 44 } 45 catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) { 46 throw pae.getException(); 47 } 48 } 49 else { 50 ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); 51 } 52 } 53 54 if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) { 55 String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName(); 56 if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) && 57 !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) && 58 !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) { 59 invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd); 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 64 @Override 65 public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) 66 throws BeansException { 67 68 Object result = existingBean; 69 for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { 70 Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName); 71 if (current == null) { 72 return result; 73 } 74 result = current; 75 } 76 return result; 77 } 78 79 @Override 80 public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) 81 throws BeansException { 82 83 Object result = existingBean; 84 for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { 85 Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName); 86 if (current == null) { 87 return result; 88 } 89 result = current; 90 } 91 return result; 92 }
总结如下:
(1.1)、由此可见BeanPostProcessor的一个触发入口在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean,最终至AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean。
(1.2)、AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean不但会触发BeanPostProcessor回掉方法,并且还会按顺序执行bean生命周期:
- factory类型接口(BeanNameAware#setBeanName)
- factory类型接口(BeanClassLoaderAware#setBeanClassLoader)
- factory类型接口(BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory)
- BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization
- InitializingBean和自定义的init-method
- BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization
触发(2)FactoryBeanRegistrySupport(后续补上)
