关于 HTTP 协议
HTTP(即超文本传输协议)是现代网络中最常见和常用的协议之一,设计它的目的是保证客户机和服务器之间的通信。
HTTP 的工作方式是客户机与服务器之间的 “请求-应答” 协议。
客户端可以是 Web 浏览器,服务器端可以是计算机上的某些网络应用程序。
通常情况下,由浏览器向服务器发起 HTTP 请求,服务器向浏览器返回响应。响应包含了请求的状态信息以及可能被请求的内容。
Go 语言中要请求网页时,使用net/http包实现。官方已经提供了详细的说明,但是比较粗略,我自己做了一些增加。
一般情况下有以下几种方法可以请求网页:
Get, Head, Post, 和 PostForm 发起 HTTP (或 HTTPS) 请求:
?
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
resp, err := http.Get("http://example.com/")
...
//参数 详解
//1. 请求的目标 URL
//2. 将要 POST 数据的资源类型(MIMEType)
//3. 数据的比特流([]byte形式)
resp, err := http.Post("http://example.com/upload", "image/jpeg", &buf)
...
//参数 详解
//1. 请求的目标 URL
//2. 提交的参数值 可以使用 url.Values 或者 使用 strings.NewReader("key=value&id=123")
// 注意,也可以 url.Value 和 strings.NewReader 并用 strings.NewReader(url.Values{}.Encode())
resp, err := http.PostForm("http://example.com/form",
url.Values{"key": {"Value"}, "id": {"123"}})
|
下面是分析:
Get 请求
?
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
resp, err := http.Get("http://example.com/")
if err != nil {
// handle error
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
// handle error
}
fmt.Println(string(body))
|
Post 请求(资源提交,比如 图片上传)
?
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
resp, err := http.Post("http://example.com/upload", "image/jpeg", &buf)
if err != nil {
// handle error
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
// handle error
}
fmt.Println(string(body))
|
Post 表单提交
?
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
postValue := url.Values{
"email": {"[email protected]"},
"password": {"123456"},
}
resp, err := http.PostForm("http://example.com/login", postValue)
if err != nil {
// handle error
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
// handle error
}
fmt.Println(string(body))
|
扩展 Post 表单提交(包括 Header 设置)
?
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
postValue := url.Values{
"email": {"[email protected]"},
"password": {"123456"},
}
postString := postValue.Encode()
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST","http://example.com/login_ajax", strings.NewReader(postString))
if err != nil {
// handle error
}
// 表单方式(必须)
req.Header.Add("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
//AJAX 方式请求
req.Header.Add("x-requested-with", "XMLHttpRequest")
client := &http.Client{}
resp, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
// handle error
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
// handle error
}
fmt.Println(string(body))
|
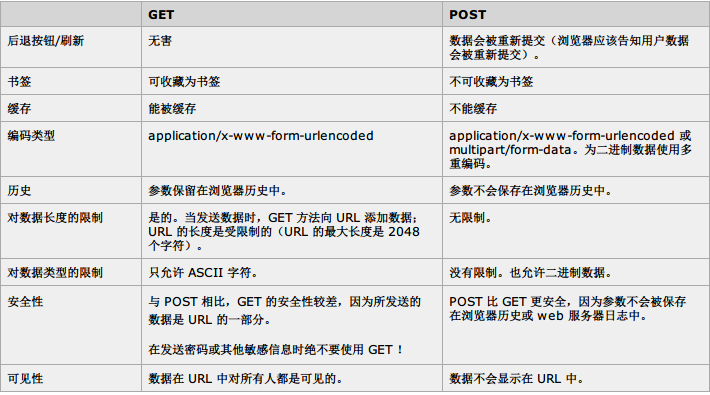
比较 GET 和 POST
下面的表格比较了两种 HTTP 方法:GET 和 POST
转自https://www.jb51.net/article/128683.htm