学习使用stat(1),并用C语言实现
1. 提交学习 stat(1) 的截图
2. man -k ,grep -r的使用
3. 编写mystate.c的伪代码
4. 产品代码 mystate.c,提交码云链接
5. 测试代码,mystat 与 stat(1) 对比,提交截图
一、学习 stat
二、实现 mystat
1. 提交学习 stat(1) 的截图
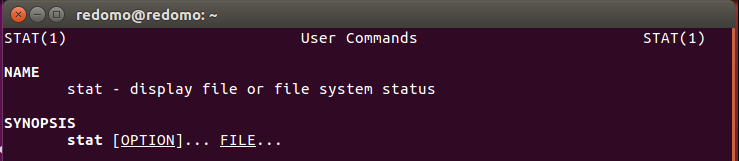
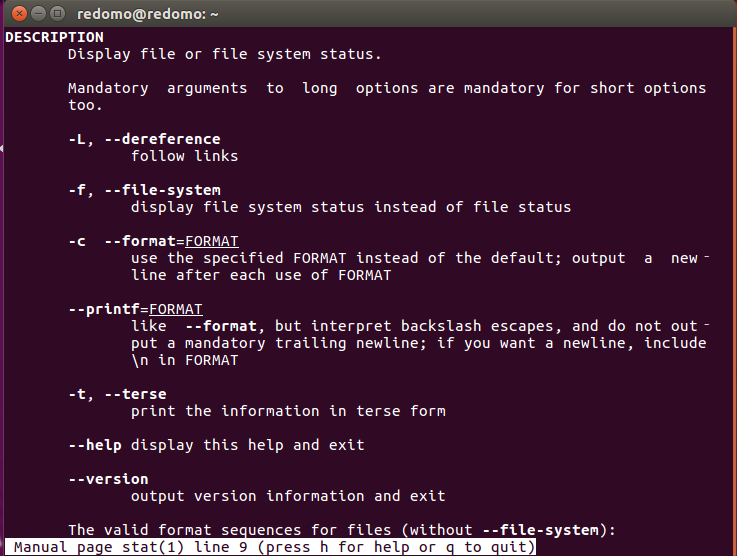
- 使用命令 man 1 stat 查看
2. man -k ,grep -r的使用
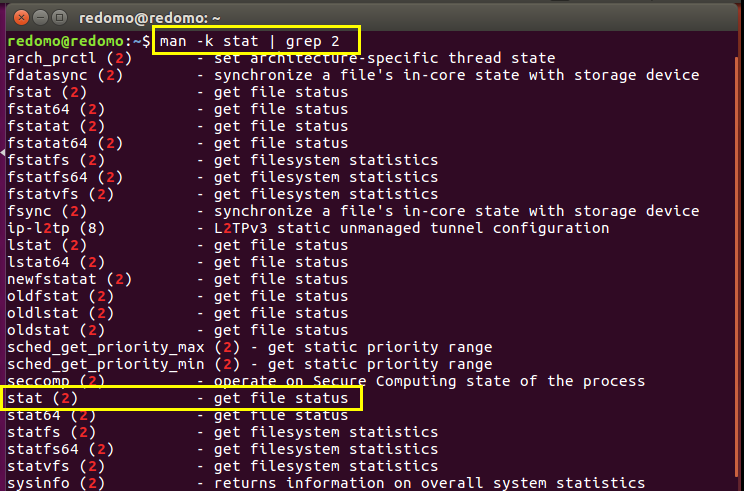
- 使用 man -k stat | grep 2 查找stat相关函数
- 使用 man 2 stat 学习函数
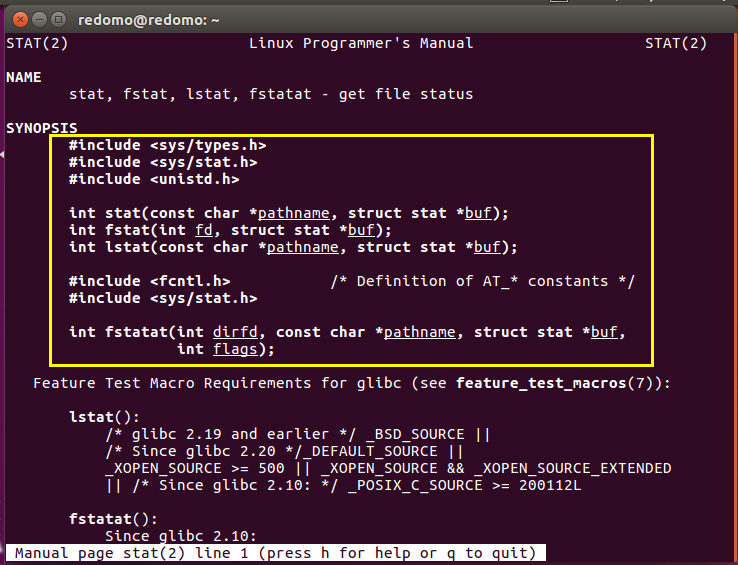
3. 编写mystate.c的伪代码
4. 产品代码 mystate.c,提交码云链接
- 产品代码(有参考) mystat.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct stat sb;
if (argc != 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <pathname>\n", argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (stat(argv[1], &sb) == -1) {
perror("stat");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("File type: ");
switch (sb.st_mode & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFBLK: printf("block device\n");
break;
case S_IFCHR: printf("character device\n");
break;
case S_IFDIR: printf("directory\n");
break;
case S_IFIFO: printf("FIFO/pipe\n");
break;
case S_IFLNK: printf("symlink\n");
break;
case S_IFREG: printf("regular file\n");
break;
case S_IFSOCK: printf("socket\n");
break;
default: printf("unknown?\n");
break;
}
printf("I-node number: %ld\n", (long) sb.st_ino);
printf("Mode: %lo (octal)\n",(unsigned long) sb.st_mode);
printf("Link count: %ld\n", (long) sb.st_nlink);
printf("Ownership: UID=%ld GID=%ld\n",(long) sb.st_uid, (long) sb.st_gid);
printf("Preferred I/O block size: %ld bytes\n",(long) sb.st_blksize);
printf("File size: %lld bytes\n",(long long) sb.st_size);
printf("Blocks allocated: %lld\n",(long long) sb.st_blocks);
printf("Last status change: %s", ctime(&sb.st_ctime));
printf("Last file access: %s", ctime(&sb.st_atime));
printf("Last file modification: %s", ctime(&sb.st_mtime));
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}- 编译运行 mystat
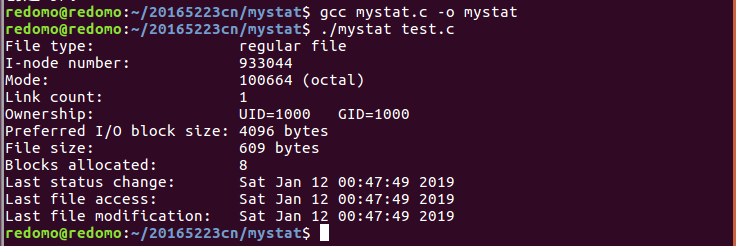
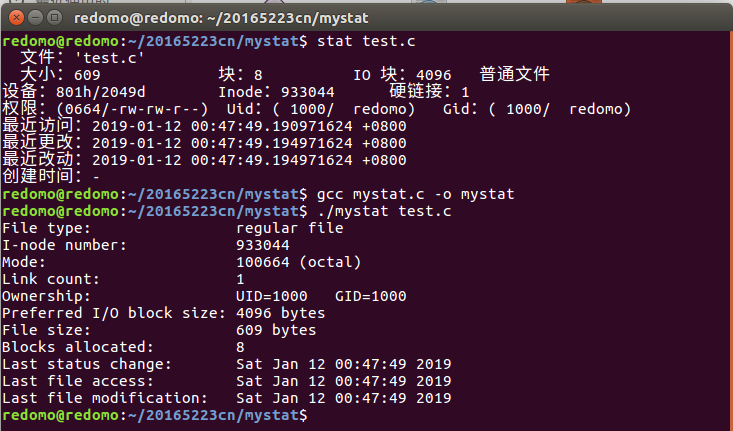
5. 测试代码,mystat 与 stat(1) 对比,提交截图
程序运行
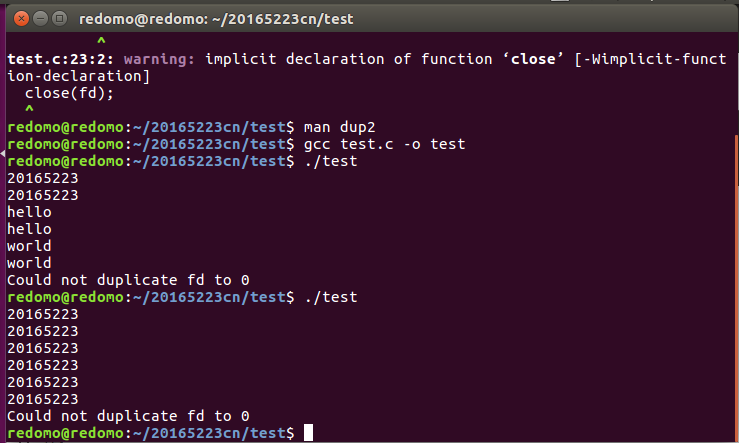
1. 理解test.c, 说出程序功能
2. 编译运行程序,提交运行截图
1. 理解test.c, 说出程序功能
- 代码 test.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int fd ;
int newfd;
char line[100];
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fd = open("data", O_RDONLY);
newfd = dup2(fd,0);
if ( newfd != 0 ){
fprintf(stderr,"Could not duplicate fd to 0\n");
exit(1);
}
close(fd);
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
}- 理解 test.c
.
2. 编译运行程序,提交运行截图
- 编译运行