版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/zhongqianli/article/details/85700681
本文实现了《A Morphological Approach to Curvature-Based Evolution of Curves and Surfaces》提出的MorphGAC。
作者巧妙地将将求解偏微分方程问题近似转换为形态学运算,高效,稳定。
用途:医学图像分割、手掌图像分割等,只要是图像分割问题,都可以试试,而且速度比GAC快很多。
项目地址
c++版本:https://github.com/zhongqianli/morph_snakes
matlab版本:https://github.com/zhongqianli/MorphGAC
原理
核心思想是将求解偏微分方程近似转换为形态学运算,提高了算法的速度。
要求解的偏微分方程
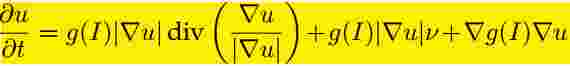
转换成形态学运算

算法实现
g(I)实现

/**
* @brief gborders: g(I)
* @param image: SNAKE_DATA_TYPE, 1 channel
* @param gI: SNAKE_DATA_TYPE, 1 channel, g(I)
* @param alpha: g(I) parameter
* @param sigma: gaussian filter standard variance
*/
void gborders(const cv::Mat &image, cv::Mat &gI, double alpha, double sigma)
{
cv::Mat gaus_blur_image(image.size(), SNAKE_DATA_TYPE, cv::Scalar(0));
cv::GaussianBlur(image, gaus_blur_image, cv::Size(0,0), sigma, sigma);
// gradient
int scale = 1;
int delta = 0;
int ddepth = SNAKE_DATA_TYPE;
cv::Mat grad(image.size(), SNAKE_DATA_TYPE, cv::Scalar(0));
cv::Mat grad_x(image.size(), SNAKE_DATA_TYPE, cv::Scalar(0));
cv::Mat grad_y(image.size(), SNAKE_DATA_TYPE, cv::Scalar(0));
// Sobel function works well in segmentation
// Scharr function works wrong in segmentation
// Scharr function , 3x3, as fast but more accurate than the standar Sobel function
cv::Sobel(gaus_blur_image, grad_x, ddepth, 1, 0, 3, scale, delta, cv::BORDER_DEFAULT);
cv::Sobel(gaus_blur_image, grad_y, ddepth, 0, 1, 3, scale, delta, cv::BORDER_DEFAULT);
// gradient; 2 method
// cv::pow(grad_x, 2, grad_x);
// cv::pow(grad_y, 2, grad_y);
// cv::add(grad_x, grad_y, grad);
// cv::sqrt(grad, grad);
cv::Mat angle;
cv::cartToPolar(grad_x, grad_y, grad, angle);
// g(I)
gI = alpha*grad + 1e-20;
cv::sqrt(gI, gI);
cv::pow(gI, -1, gI);
}
IS实现
/**
* @brief IS
* @param u: mask
*/
void IS(cv::Mat &u)
{
std::vector<cv::Mat> P(4);
int p0[3][3] = {
{1, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 1}
};
P[0] = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_8UC1, p0);
int p1[3][3] = {
{0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0}
};
P[1] = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_8UC1, p1);
int p2[3][3] = {
{0, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 0}
};
P[2] = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_8UC1, p2);
int p3[3][3] = {
{0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0}
};
P[3] = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_8UC1, p3);
std::vector<cv::Mat> aux(4);
cv::Mat res = cv::Mat::ones(u.size(), u.type());
for(int i=0; i<4; ++i)
{
cv::dilate(u, aux[i], P[i]);
res = res.mul(aux[i]);
}
u = res.clone();
}
SI实现
/**
* @brief SI
* @param u: mask
*/
void SI(cv::Mat &u)
{
std::vector<cv::Mat> P(4);
int p0[3][3] = {
{1, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 1}
};
P[0] = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_8UC1, p0);
int p1[3][3] = {
{0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0}
};
P[1] = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_8UC1, p1);
int p2[3][3] = {
{0, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 0}
};
P[2] = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_8UC1, p2);
int p3[3][3] = {
{0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0}
};
P[3] = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_8UC1, p3);
std::vector<cv::Mat> aux(4);
cv::Mat res = cv::Mat::zeros(u.size(), u.type());
for(int i=0; i<4; ++i)
{
cv::erode(u, aux[i], P[i]);
res = res + aux[i];
}
u = res.clone();
}
SIoIS实现
/**
* @brief SIoIS: smoothing force; step.3
* @param u: mask
*/
void SIoIS(cv::Mat &u)
{
IS(u);
SI(u);
}
ISoSI实现
/**
* @brief ISoSI: smoothing force; step.3
* @param u: mask
*/
void ISoSI(cv::Mat &u)
{
SI(u);
IS(u);
}
morph_gac实现
/**
* @brief morph_gac
* @param gI_threshold_mask: CV_8UC1
* @param derivative_gI_X
* @param derivative_gI_Y
* @param u: mask. input type: CV_8UC1; output type: CV_8UC1
* @param gI_balloon_v: >0 ? dilate : erode
*/
void morph_gac(const cv::Mat &gI_threshold_mask, const cv::Mat &derivative_gI_X, const cv::Mat &derivative_gI_Y, cv::Mat &u, double gI_balloon_v)
{
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
double begin_time;
double end_time;
double t;
#endif
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
begin_time = cv::getTickCount();
#endif
// step.1
cv::Mat se = cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_RECT, cv::Size(3,3));
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
end_time = cv::getTickCount();
t = (end_time - begin_time)*1000 / cv::getTickFrequency();
printf("[morph_gac]time of getStructuringElement: %d ms.\n", (int)t);
#endif
// optimize : remove if ... else ..., just expand contour
// if(gI_balloon_v > 0)
// {
// cv::dilate(u, aux, se);
// aux.copyTo(u, gI_threshold_mask);
// }
// else if(gI_balloon_v < 0)
// {
// cv::erode(u, aux, se);
// aux.copyTo(u, gI_threshold_mask);
// }
cv::Mat aux(u.size(), CV_8UC1);
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
begin_time = cv::getTickCount();
#endif
// optimize : remove if ... else ..., just expand contour
// t: 0ms
cv::dilate(u, aux, se);
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
end_time = cv::getTickCount();
t = (end_time - begin_time)*1000 / cv::getTickFrequency();
printf("[morph_gac]time of dilate: %d ms.\n", (int)t);
#endif
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
begin_time = cv::getTickCount();
#endif
// t: 0ms
aux.copyTo(u, gI_threshold_mask);
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
end_time = cv::getTickCount();
t = (end_time - begin_time)*1000 / cv::getTickFrequency();
printf("[morph_gac]time of copy data: %d ms.\n", (int)t);
#endif
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
begin_time = cv::getTickCount();
#endif
// step.2
cv::Mat derivative_u_X, derivative_u_Y;
// calc_derivative(u, derivative_u_X, derivative_u_Y);
// // t: 4ms
cv::Sobel(u, derivative_u_X, SNAKE_DATA_TYPE, 1, 0, 3, 1, 0, cv::BORDER_DEFAULT);
cv::Sobel(u, derivative_u_Y, SNAKE_DATA_TYPE, 0, 1, 3, 1, 0, cv::BORDER_DEFAULT);
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
end_time = cv::getTickCount();
t = (end_time - begin_time)*1000 / cv::getTickFrequency();
printf("[morph_gac]time of calc_derivative: %d ms.\n", (int)t);
#endif
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
begin_time = cv::getTickCount();
#endif
// time: 10ms
// cv::Mat res = derivative_gI_X.mul(derivative_u_X) + derivative_gI_Y.mul(derivative_u_Y);
// res.convertTo(res, CV_8UC1);
// t: 2ms
cv::Mat res(derivative_gI_X.size(), SNAKE_DATA_TYPE);
for(int i=0; i<derivative_gI_X.rows; ++i)
{
for(int j=0; j<derivative_gI_X.cols; ++j)
{
res.at<double>(i,j) = derivative_gI_X.at<double>(i,j)*derivative_u_X.at<double>(i,j) + derivative_gI_Y.at<double>(i,j)*derivative_u_Y.at<double>(i,j);
}
}
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
end_time = cv::getTickCount();
t = (end_time - begin_time)*1000 / cv::getTickFrequency();
printf("[morph_gac]time of derivative multiply: %d ms.\n", (int)t);
#endif
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
begin_time = cv::getTickCount();
#endif
// t: 0ms
res.convertTo(res, CV_8UC1);
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
end_time = cv::getTickCount();
t = (end_time - begin_time)*1000 / cv::getTickFrequency();
printf("[morph_gac]time of convertTo: %d ms.\n", (int)t);
#endif
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
begin_time = cv::getTickCount();
#endif
// t: 0ms
for(int i=0; i<res.rows; ++i)
{
for(int j=0; j<res.cols; ++j)
{
if(res.at<uchar>(i,j) > 0)
{
u.at<uchar>(i,j) = 255;
}
else if(res.at<uchar>(i,j) < 0)
{
u.at<uchar>(i,j) = 0;
}
}
}
#ifdef MORPH_GAC_DEBUG
end_time = cv::getTickCount();
t = (end_time - begin_time)*1000 / cv::getTickFrequency();
printf("[morph_gac]time of res 2 u iterations: %d ms.\n", (int)t);
#endif
}