一、@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootApplication是spring boot的核心注解,源码如下:
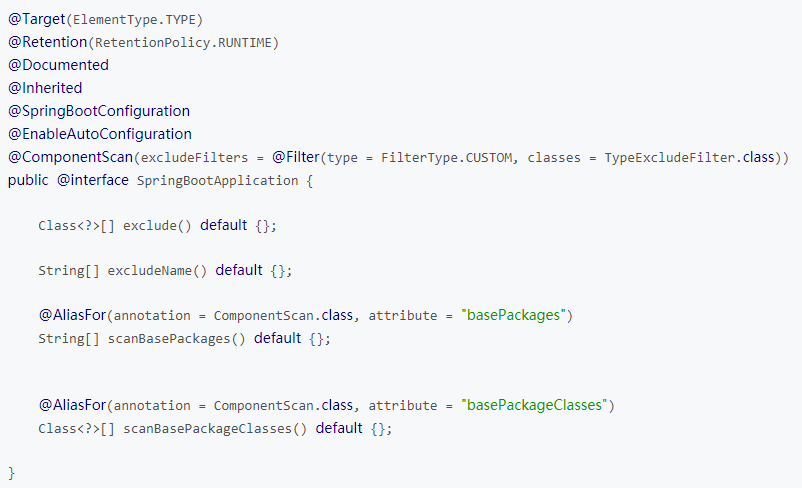
相当于:@Configuration+@EnableAutoConfiguration+@ComponentScan
@Configuration:此类是一个配置
@EnableAutoConfiguration:让springboot根据类路径中的jar包依赖为当前项目进行自动配置
@ComponentScan:springboot自动扫描入口类所在包以及其子包里的bean
另外springboot也可以关闭特定的自动配置:@SpringBootApplication(exlude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
二、SpringBoot配置文件
1、application.properties或application.yml
SpringBoot的全局配置文件为applicaiton.properties或者application.yml,通常放在src/main/resources/下,如下:
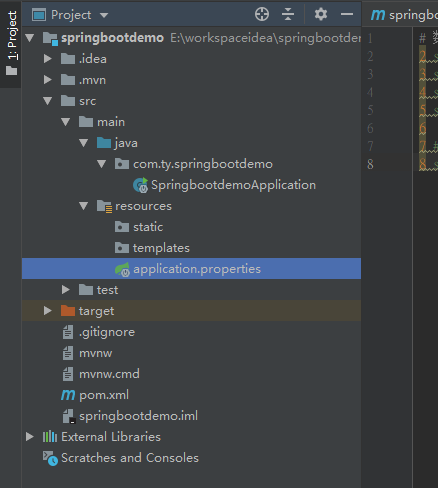
同样也可以使用yml编写,示例如下(将tomcat默认端口修改为8001、将默认访问路径修改为/index):
A、application.properties
server.port=8001
server.context-path=/index
B、application.yml
server:
port:8001
context-path: /index
2、加载xml
springboot提倡零配置,但是项目中难免需要使用xml配置,引入方式如下:
@ImportResource({"classpath:some-context.xml", "classpath:another-context.xml"})
三、外部配置
1、常规属性配置
在spring的项目中,通过@PropertySource指明properties文件的位置,然后可以通过@Value注入值。在SpringBoot里,只需要在appllication.properties文件中定义属性,直接使用@Value即可
示例:
application.properties文件增加属性:
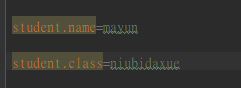

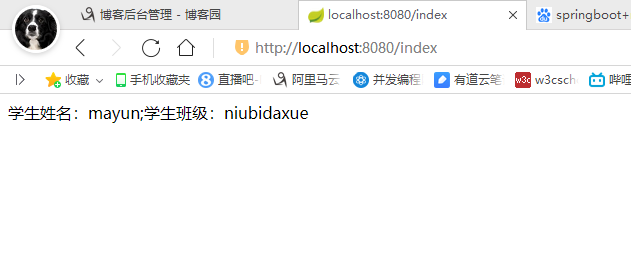
运行结果:

注意点:
A、@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class}) ----------------------->项目启动的时候会报错,提示没有数据源,因此在初始化bean的时候,排除这个bean
B、项目运行地址是不需要项目名的,直接使用http://localhost:8080/index,而不是http://localhost:8080/项目名称/index
2、类型安全的配置
通过@Value的方式配置属性也可以,但是当属性过多时,会写许多个@Value,同时也不美观,因此springboot还提供了@ConfigurationProperties将属性与一个bean关联,示例如下:
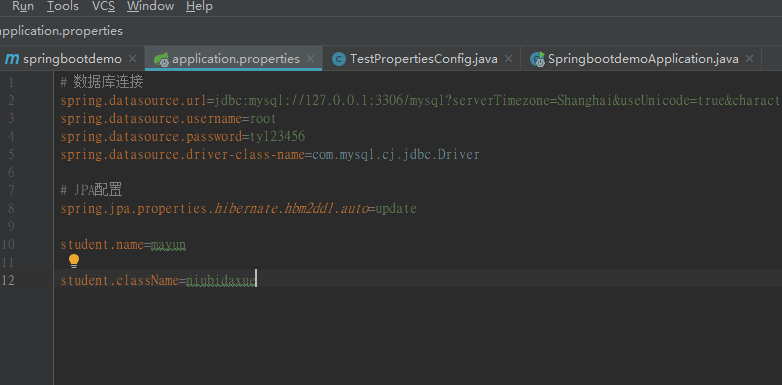


运行结果:
注意点:
A、使用lombok的@Data可以省去写get、set方法
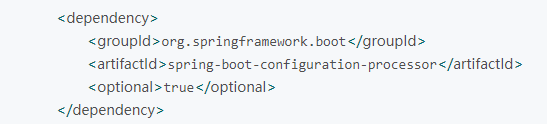
B、有时候会提示一个错误:Spring Boot Annotion processor not found in classpath
这时需要添加一个依赖,如下:
C、在加载application.properties中的属性时,不需要指定location,如果是在其他自定义的properties文件中去加载属性,则需要加上location
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "xxx", locations = {"classpath:/xxx.properties"})
四、日志配置
springboot支持log4j、logback等等作为日志框架,但是默认日志框架使用的是logback,示例如下:
配置日志文件:
logging.file=D:/mylog/log.log
配置日志级别:
logging.level.org.springframework.web=DEBUG