版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/nk_wang/article/details/51514016
为了实现多个进程之间的通信,我们可以用系统页面文件来作为共享内存文件。
1.首先我们创建第一个进程,用系统函数CreateFileMapping创建共享内存文件,用函数MapViewOfFile映射共享内存文件到进程,具体操作见代码:
#include <Windows.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <tchar.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const size_t BUF_SIZE = 256;
TCHAR szName[]=TEXT("Local\\MyFileMappingObject");
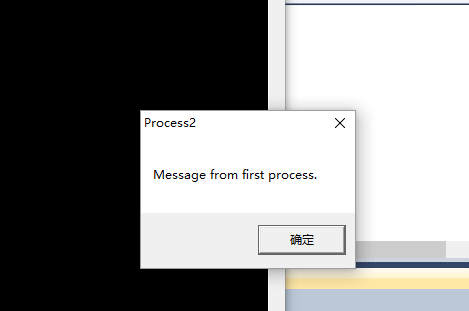
TCHAR szMsg[]=TEXT("Message from first process.");
int main(void)
{
HANDLE hAndle = CreateFileMapping(INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE,
NULL,
PAGE_READWRITE,
0,
BUF_SIZE,
szName);
if (NULL == hAndle)
{
cout<<"Could not create file mapping object:"<<GetLastError()<<endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
LPCTSTR pBuf = (LPCTSTR)MapViewOfFile(hAndle,
FILE_MAP_ALL_ACCESS,
0,
0,
BUF_SIZE);
if (NULL == pBuf)
{
cout<<"Could not map view of file :"<<GetLastError()<<endl;
CloseHandle(hAndle);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
CopyMemory((PVOID)pBuf,szMsg,(_tcslen(szMsg)*sizeof(TCHAR)));
_getch();
UnmapViewOfFile(pBuf);
CloseHandle(hAndle);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}2.这下我们可以创建第二个进程对共享内存文件访问,用系统函数OpenFileMapping打开内存映射文件对象,具体操作见如下代码:
#include <Windows.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const size_t BUF_SIZE = 256;
TCHAR szName[]=TEXT("Local\\MyFileMappingObject");
int main(void)
{
HANDLE hAndle = OpenFileMapping(FILE_MAP_ALL_ACCESS,false,szName);
if (NULL == hAndle)
{
cout<<"Could not open file mapping object :"<<::GetLastError()<<endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
LPCTSTR pBuf = (LPCTSTR)MapViewOfFile(hAndle,
FILE_MAP_ALL_ACCESS,
0,
0,
BUF_SIZE);
if (NULL == pBuf)
{
cout<<"Could not map view of file :"<<GetLastError()<<endl;
CloseHandle(hAndle);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
MessageBox(NULL,pBuf,TEXT("Process2"),MB_OK);
UnmapViewOfFile(hAndle);
CloseHandle(hAndle);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}3.运行时运行第一个进程后运行第二个进程,第二个进程能够获取到第一个进程的信息,这样我们进程间通讯已经完整完成。