目录
启动时检查
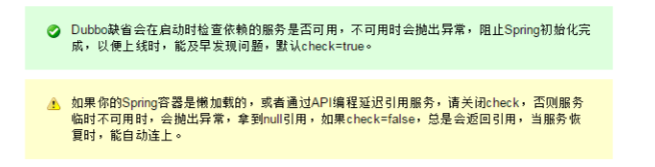
Dubbo缺省会在启动时检查依赖的服务是否可用,不可用时会抛出异常,阻止Spring初始化完成,以便上线时,能及早发现问题,默认check=true。
如果你的Spring容器是懒加载的,或者通过API编程延迟引用服务,请关闭check,否则服务临时不可用时,会抛出异常,拿到null引用,如果check=false,总是会返回引用,当服务恢复时,能自动连上。
可以通过check="false"关闭检查,比如,测试时,有些服务不关心,或者出现了循环依赖,必须有一方先启动。
关闭某个服务的启动时检查:(没有提供者时报错)
<dubbo:referenceinterface="com.foo.BarService"check="false"/>例:
<!-- 调用账户服务 -->
<dubbo:reference interface="edu.pay.facade.account.service.AccountTransactionFacade" id="accountTransactionFacade" check="false" />
<dubbo:reference interface="edu.pay.facade.account.service.AccountQueryFacade" id="accountQueryFacade" check="false" />关闭所有服务的启动时检查:(没有提供者时报错)
<dubbo:consumercheck="false"/>
关闭注册中心启动时检查:(注册订阅失败时报错)
<dubbo:registrycheck="false"/>
也可以用dubbo.properties配置:
dubbo.properties
dubbo.reference.com.foo.BarService.check=false
dubbo.reference.check=false
dubbo.consumer.check=false
dubbo.registry.check=false
也可以用-D参数:
java -Ddubbo.reference.com.foo.BarService.check=false
java -Ddubbo.reference.check=false
java -Ddubbo.consumer.check=false
java -Ddubbo.registry.check=false
注意区别
dubbo.reference.check=false,强制改变所有reference的check值,就算配置中有声明,也会被覆盖。
dubbo.consumer.check=false,是设置check的缺省值,如果配置中有显式的声明,如:<dubbo:reference check="true"/>,不会受影响。
dubbo.registry.check=false,前面两个都是指订阅成功,但提供者列表是否为空是否报错,如果注册订阅失败时,也允许启动,需使用此选项,将在后台定时重试。
引用缺省是延迟初始化的,只有引用被注入到其它Bean,或被getBean()获取,才会初始化。
如果需要饥饿加载,即没有人引用也立即生成动态代理,可以配置:
<dubbo:referenceinterface="com.foo.BarService"init="true"/>负载均衡


Random LoadBalance
- 随机,按权重设置随机概率。
- 在一个截面上碰撞的概率高,但调用量越大分布越均匀,而且按概率使用权重后也比较均匀,有利于动态调整提供者权重。
RandomLoadBalance 算法
public class RandomLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static final String NAME = "random";
private final Random random = new Random();
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
int length = invokers.size(); // 总个数
int totalWeight = 0; // 总权重
boolean sameWeight = true; // 权重是否都一样
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
totalWeight += weight; // 累计总权重
if (sameWeight && i > 0
&& weight != getWeight(invokers.get(i - 1), invocation)) {
sameWeight = false; // 计算所有权重是否一样
}
}
if (totalWeight > 0 && ! sameWeight) {
// 如果权重不相同且权重大于0则按总权重数随机
int offset = random.nextInt(totalWeight);
// 并确定随机值落在哪个片断上
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
offset -= getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
if (offset < 0) {
return invokers.get(i);
}
}
}
// 如果权重相同或权重为0则均等随机
return invokers.get(random.nextInt(length));
}
}
RoundRobin LoadBalance
- 轮循,按公约后的权重设置轮循比率。
- 存在慢的提供者累积请求问题,比如:第二台机器很慢,但没挂,当请求调到第二台时就卡在那,久而久之,所有请求都卡在调到第二台上。
Round-Robin既是轮询算法,是按照公约后的权重设置轮询比率,即权重轮询算法(Weighted Round-Robin) ,它是基于轮询算法改进而来的。这里之所以写RoundRobin是为了跟Dubbo中的内容保持一致。
轮询调度算法的原理是:每一次把来自用户的请求轮流分配给内部中的服务器。如:从1开始,一直到N(其中,N是内部服务器的总个数),然后重新开始循环。
该算法的优点:
其简洁性,它无需记录当前所有连接的状态,所以它是一种无状态调度。
该算法的缺点:
轮询调度算法假设所有服务器的处理性能都相同,不关心每台服务器的当前连接数和响应速度。当请求服务间隔时间变化比较大时,轮询调度算法容易导致服务器间的负载不平衡。
所以此种均衡算法适合于服务器组中的所有服务器都有相同的软硬件配置并且平均服务请求相对均衡的情况。但是,在实际情况中,可能并不是这种情况。由于每台服务器的配置、安装的业务应用等不同,其处理能力会不一样。所以,我们根据服务器的不同处理能力,给每个服务器分配不同的权值,使其能够接受相应权值数的服务请求。
RandomLoadBalance 算法
public class RandomLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static final String NAME = "random";
private final Random random = new Random();
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
int length = invokers.size(); // 总个数
int totalWeight = 0; // 总权重
boolean sameWeight = true; // 权重是否都一样
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
totalWeight += weight; // 累计总权重
if (sameWeight && i > 0
&& weight != getWeight(invokers.get(i - 1), invocation)) {
sameWeight = false; // 计算所有权重是否一样
}
}
if (totalWeight > 0 && ! sameWeight) {
// 如果权重不相同且权重大于0则按总权重数随机
int offset = random.nextInt(totalWeight);
// 并确定随机值落在哪个片断上
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
offset -= getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
if (offset < 0) {
return invokers.get(i);
}
}
}
// 如果权重相同或权重为0则均等随机
return invokers.get(random.nextInt(length));
}
}
LeastActive LoadBalance
- 最少活跃调用数,相同活跃数的随机,活跃数指调用前后计数差。
- 使慢的提供者收到更少请求,因为越慢的提供者的调用前后计数差会越大。
LeastActiveLoadBalance 算法
public class LeastActiveLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static final String NAME = "leastactive";
private final Random random = new Random();
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
int length = invokers.size(); // 总个数
int leastActive = -1; // 最小的活跃数
int leastCount = 0; // 相同最小活跃数的个数
int[] leastIndexs = new int[length]; // 相同最小活跃数的下标
int totalWeight = 0; // 总权重
int firstWeight = 0; // 第一个权重,用于于计算是否相同
boolean sameWeight = true; // 是否所有权重相同
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Invoker<T> invoker = invokers.get(i);
int active = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive(); // 活跃数
int weight = invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.WEIGHT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_WEIGHT); // 权重
if (leastActive == -1 || active < leastActive) { // 发现更小的活跃数,重新开始
leastActive = active; // 记录最小活跃数
leastCount = 1; // 重新统计相同最小活跃数的个数
leastIndexs[0] = i; // 重新记录最小活跃数下标
totalWeight = weight; // 重新累计总权重
firstWeight = weight; // 记录第一个权重
sameWeight = true; // 还原权重相同标识
} else if (active == leastActive) { // 累计相同最小的活跃数
leastIndexs[leastCount ++] = i; // 累计相同最小活跃数下标
totalWeight += weight; // 累计总权重
// 判断所有权重是否一样
if (sameWeight && i > 0
&& weight != firstWeight) {
sameWeight = false;
}
}
}
// assert(leastCount > 0)
if (leastCount == 1) {
// 如果只有一个最小则直接返回
return invokers.get(leastIndexs[0]);
}
if (! sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) {
// 如果权重不相同且权重大于0则按总权重数随机
int offsetWeight = random.nextInt(totalWeight);
// 并确定随机值落在哪个片断上
for (int i = 0; i < leastCount; i++) {
int leastIndex = leastIndexs[i];
offsetWeight -= getWeight(invokers.get(leastIndex), invocation);
if (offsetWeight <= 0)
return invokers.get(leastIndex);
}
}
// 如果权重相同或权重为0则均等随机
return invokers.get(leastIndexs[random.nextInt(leastCount)]);
}
}
ConsistentHash LoadBalance
- 一致性Hash,相同参数的请求总是发到同一提供者。
- 当某一台提供者挂时,原本发往该提供者的请求,基于虚拟节点,平摊到其它提供者,不会引起剧烈变动。
算法参见:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Consistent_hashing。
缺省只对第一个参数Hash,如果要修改,请配置<dubbo:parameter key="hash.arguments" value="0,1" />
缺省用160份虚拟节点,如果要修改,请配置<dubbo:parameter key="hash.nodes" value="320" />
ConsistentHashLoadBalance 算法
public class ConsistentHashLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
private final ConcurrentMap<String, ConsistentHashSelector<?>> selectors = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ConsistentHashSelector<?>>();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
int identityHashCode = System.identityHashCode(invokers);
ConsistentHashSelector<T> selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
if (selector == null || selector.getIdentityHashCode() != identityHashCode) {
selectors.put(key, new ConsistentHashSelector<T>(invokers, invocation.getMethodName(), identityHashCode));
selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
}
return selector.select(invocation);
}
private static final class ConsistentHashSelector<T> {
private final TreeMap<Long, Invoker<T>> virtualInvokers;
private final int replicaNumber;
private final int identityHashCode;
private final int[] argumentIndex;
public ConsistentHashSelector(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, String methodName, int identityHashCode) {
this.virtualInvokers = new TreeMap<Long, Invoker<T>>();
this.identityHashCode = System.identityHashCode(invokers);
URL url = invokers.get(0).getUrl();
this.replicaNumber = url.getMethodParameter(methodName, "hash.nodes", 160);
String[] index = Constants.COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url.getMethodParameter(methodName, "hash.arguments", "0"));
argumentIndex = new int[index.length];
for (int i = 0; i < index.length; i ++) {
argumentIndex[i] = Integer.parseInt(index[i]);
}
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
for (int i = 0; i < replicaNumber / 4; i++) {
byte[] digest = md5(invoker.getUrl().toFullString() + i);
for (int h = 0; h < 4; h++) {
long m = hash(digest, h);
virtualInvokers.put(m, invoker);
}
}
}
}
public int getIdentityHashCode() {
return identityHashCode;
}
public Invoker<T> select(Invocation invocation) {
String key = toKey(invocation.getArguments());
byte[] digest = md5(key);
Invoker<T> invoker = sekectForKey(hash(digest, 0));
return invoker;
}
private String toKey(Object[] args) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder();
for (int i : argumentIndex) {
if (i >= 0 && i < args.length) {
buf.append(args[i]);
}
}
return buf.toString();
}
private Invoker<T> sekectForKey(long hash) {
Invoker<T> invoker;
Long key = hash;
if (!virtualInvokers.containsKey(key)) {
SortedMap<Long, Invoker<T>> tailMap = virtualInvokers.tailMap(key);
if (tailMap.isEmpty()) {
key = virtualInvokers.firstKey();
} else {
key = tailMap.firstKey();
}
}
invoker = virtualInvokers.get(key);
return invoker;
}
private long hash(byte[] digest, int number) {
return (((long) (digest[3 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 24)
| ((long) (digest[2 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 16)
| ((long) (digest[1 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 8)
| (digest[0 + number * 4] & 0xFF))
& 0xFFFFFFFFL;
}
private byte[] md5(String value) {
MessageDigest md5;
try {
md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
md5.reset();
byte[] bytes = null;
try {
bytes = value.getBytes("UTF-8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
md5.update(bytes);
return md5.digest();
}
}
}线程模式线程优化
http://dubbo.io/User+Guide-zh.htm 用户指南>>线程模型 类似于数据库的连接池
(+) (#)
- 事件处理线程说明
如果事件处理的逻辑能迅速完成,并且不会发起新的IO请求,比如只是在内存中记个标识,则直接在IO线程上处理更快,因为减少了线程池调度。
但如果事件处理逻辑较慢,或者需要发起新的IO请求,比如需要查询数据库,则必须派发到线程池,否则IO线程阻塞,将导致不能接收其它请求。
如果用IO线程处理事件,又在事件处理过程中发起新的IO请求,比如在连接事件中发起登录请求,会报“可能引发死锁”异常,但不会真死锁。
Dispatcher
- all 所有消息都派发到线程池,包括请求,响应,连接事件,断开事件,心跳等。
- 对应相关的类:com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.dispatcher.all.AllChannelHandler
- direct 所有消息都不派发到线程池,全部在 IO 线程上直接执行。
- 对应的类:com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.dispatcher.direct.DirectDispatcher
- message 只有请求响应消息派发到线程池,其它连接断开事件,心跳等消息,直接在 IO 线程上执行。
- 对应的类:com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.dispatcher.message.MessageOnlyDispatcher
- execution 只请求消息派发到线程池,不含响应,响应和其它连接断开事件,心跳等消息,直接在 IO 线程上执行。
- 对应的类:com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.dispatcher.execution.ExecutionDispatcher
- connection 在 IO 线程上,将连接断开事件放入队列,有序逐个执行,其它消息派发到线程池。
- 对应的类:com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.dispatcher.connection.ConnectionOrderedDispatcher
ThreadPool
- fixed 固定大小线程池,启动时建立线程,不关闭,一直持有。(缺省)
- cached 缓存线程池,空闲一分钟自动删除,需要时重建。
- limited 可伸缩线程池,但池中的线程数只会增长不会收缩。只增长不收缩的目的是为了避免收缩时突然来了大流量引起的性能问题。
- eager 优先创建Worker线程池。在任务数量大于corePoolSize但是小于maximumPoolSize时,优先创建Worker来处理任务。当任务数量大于maximumPoolSize时,将任务放入阻塞队列中。阻塞队列充满时抛出RejectedExecutionException。(相比于cached:cached在任务数量超过maximumPoolSize时直接抛出异常而不是将任务放入阻塞队列)
配置如:
<dubbo:protocolname="dubbo"dispatcher="all"threadpool="fixed"threads="100"/>配置标签
#供应者配置
<dubbo:provider/>
#dubbo协议配置
<dubbo:protocol/>例:
<!-- 当ProtocolConfig和ServiceConfig某属性没有配置时,采用此缺省值 -->
<dubbo:provider timeout="10000" threadpool="fixed" threads="100" accepts="1000" /><dubbo:protocol/>
(+) (#)
服务提供者协议配置:
配置类:com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ProtocolConfig
说明:如果需要支持多协议,可以声明多个<dubbo:protocol>标签,并在<dubbo:service>中通过protocol属性指定使用的协议。
标签 属性 对应URL参数 类型 是否必填 缺省值 作用 描述 兼容性
<dubbo:protocol> id string 可选 dubbo 配置关联 协议BeanId,可以在<dubbo:service protocol="">中引用此ID,如果ID不填,缺省和name属性值一样,重复则在name后加序号。 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> name <protocol> string 必填 dubbo 性能调优 协议名称 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> port <port> int 可选 dubbo协议缺省端口为20880,rmi协议缺省端口为1099,http和hessian协议缺省端口为80
如果配置为-1 或者 没有配置port,则会分配一个没有被占用的端口。Dubbo 2.4.0+,分配的端口在协议缺省端口的基础上增长,确保端口段可控。 服务发现 服务端口 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> host <host> string 可选 自动查找本机IP 服务发现 -服务主机名,多网卡选择或指定VIP及域名时使用,为空则自动查找本机IP,-建议不要配置,让Dubbo自动获取本机IP 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> threadpool threadpool string 可选 fixed 性能调优 线程池类型,可选:fixed/cached 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> threads threads int 可选 100 性能调优 服务线程池大小(固定大小) 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> iothreads threads int 可选 cpu个数+1 性能调优 io线程池大小(固定大小) 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> accepts accepts int 可选 0 性能调优 服务提供方最大可接受连接数 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> payload payload int 可选 88388608(=8M) 性能调优 请求及响应数据包大小限制,单位:字节 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> codec codec string 可选 dubbo 性能调优 协议编码方式 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> serialization serialization string 可选 dubbo协议缺省为hessian2,rmi协议缺省为java,http协议缺省为json 性能调优 协议序列化方式,当协议支持多种序列化方式时使用,比如:dubbo协议的dubbo,hessian2,java,compactedjava,以及http协议的json等 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> accesslog accesslog string/boolean 可选 服务治理 设为true,将向logger中输出访问日志,也可填写访问日志文件路径,直接把访问日志输出到指定文件 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> path <path> string 可选 服务发现 提供者上下文路径,为服务path的前缀 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> transporter transporter string 可选 dubbo协议缺省为netty 性能调优 协议的服务端和客户端实现类型,比如:dubbo协议的mina,netty等,可以分拆为server和client配置 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> server server string 可选 dubbo协议缺省为netty,http协议缺省为servlet 性能调优 协议的服务器端实现类型,比如:dubbo协议的mina,netty等,http协议的jetty,servlet等 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> client client string 可选 dubbo协议缺省为netty 性能调优 协议的客户端实现类型,比如:dubbo协议的mina,netty等 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> dispatcher dispatcher string 可选 dubbo协议缺省为all 性能调优 协议的消息派发方式,用于指定线程模型,比如:dubbo协议的all, direct, message, execution, connection等 2.1.0以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> queues queues int 可选 0 性能调优 线程池队列大小,当线程池满时,排队等待执行的队列大小,建议不要设置,当线程程池时应立即失败,重试其它服务提供机器,而不是排队,除非有特殊需求。 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> charset charset string 可选 UTF-8 性能调优 序列化编码 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> buffer buffer int 可选 8192 性能调优 网络读写缓冲区大小 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> heartbeat heartbeat int 可选 0 性能调优 心跳间隔,对于长连接,当物理层断开时,比如拔网线,TCP的FIN消息来不及发送,对方收不到断开事件,此时需要心跳来帮助检查连接是否已断开 2.0.10以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> telnet telnet string 可选 服务治理 所支持的telnet命令,多个命令用逗号分隔 2.0.5以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> register register boolean 可选 true 服务治理 该协议的服务是否注册到注册中心 2.0.8以上版本
<dubbo:protocol> contextpath contextpath String 可选 缺省为空串 服务治理 2.0.6以上版本
Linux 用户线程数限制导致的 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: unable to create new native thread异常
系统默认最大的线程数为1024个
[root@edu-provider-01 ~]# cat /etc/security/limits.d/90-nproc.conf
# Default limit for number of user's processes to prevent
# accidental fork bombs.
# See rhbz #432903 for reasoning.
* soft nproc 1024
root soft nproc unlimited
[root@edu-provider-01 ~]# vi /etc/security/limits.d/90-nproc.conf
调整时要注意:
1、 尽量不要使用 root 用户来部署应用程序,避免资源耗尽后无法登录操作系统。
因为root用户默认没有限制线程数,如果线程过多,会使资源占用很多,导致不能关机,只能硬关机
2、 普通用户的线程数限制值要看可用物理内存容量来配置
[root@edu-provider-01 ~]# cat /proc/meminfo |grep MemTotal
MemTotal: 2941144 kB
[root@edu-provider-01 ~]# echo "2941144/128"|bc
22977
[root@edu-provider-01 ~]# ulimit -u
1024
[1]+ Stopped vi /etc/security/limits.d/90-nproc.conf
[root@edu-provider-01 ~]# vi /etc/security/limits.d/90-nproc.conf
[root@edu-provider-01 ~]# cat /etc/security/limits.d/90-nproc.conf
# Default limit for number of user's processes to prevent
# accidental fork bombs.
# See rhbz #432903 for reasoning.
* soft nproc 12000
root soft nproc unlimited
[root@edu-provider-01 ~]#
计算方式:
default_nproc = total_memory/128K;
$ cat /proc/meminfo |grep MemTotal
$ echo "2941144/128"|bc
$ ulimit -u
ulimit -a # 显示目前资源限制的设定
ulimit -u # 用户最多可开启的程序数目
重启,使之生效:# reboot