本文建立在上一篇文章《SpringCloud踩坑笔记(二)-------Eureka》之上。启动 Eureka Server 之后,我们将注册一个服务到 Eureka Server 中,然后尝试去消费它。
一、创建服务提供者
按照你一贯的做法,去创建一个 Spring Boot 项目,然后写一个可以调用的 Controller 即可。
需要注意的是,pom 文件中仅仅需要引入 spring-cloud-starter-eureka 即可,不需要引入 spring-boot-starter-web ,因为前者已经包含引入了后者。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>然后,将 @EnableDiscoveryClient 注解到启动类上,把这个服务声明为允许被发现。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}在 application.yml 中,设置 Eureka Server 地址及本身的相关信息,本服务以 9090 端口启动。
spring:
application:
name: spring-cloud-service
server:
port: 9090
# eureka 配置
eureka:
client:
# 设置与Eureka Server交互的地址,查询服务和注册服务都需要依赖这个地址。
serviceUrl:
# 默认是http://localhost:8761/eureka;多个地址可使用 , 分隔。
defaultZone: http://localhost:8080/eureka/然后启动 Eureka Server 和这个服务,就能在 Eureka Server 的管理页面看到这个服务了。
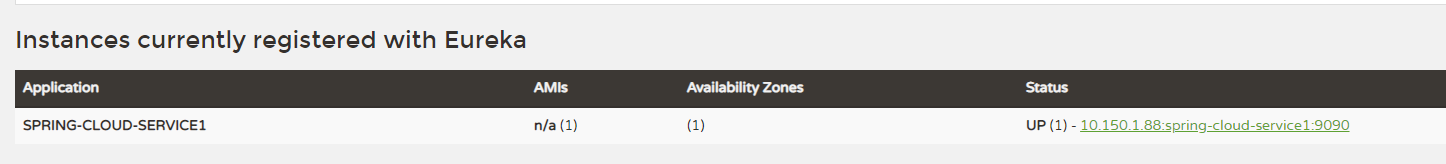
然后写两个简单的 Controller 作为服务,一个用 GET 方式访问,一个用 POST 方式访问。POST的例子为 POST json 数据,放在 request body 中。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("service")
public class ProviderController {
private final static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ProviderController.class);
@RequestMapping(value = "hello", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String hello(@RequestParam String name) throws AnkonException {
String result = "hello " + name + ", you get the service";
return new RestJson(result).toJson();
}
@RequestMapping(value = "hello2", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String hello2(HttpServletRequest request) throws AnkonException, IOException {
String charset = request.getCharacterEncoding();
String param;
try (InputStream input = request.getInputStream();
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream()) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int length;
while ((length = input.read(buffer)) != -1) {
out.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
param = out.toString(charset);
}
LOGGER.debug("Reqeust body:" + param);
String result = "hello, you post the service with param " + param;
return new RestJson(result).toJson();
}
}二、创建服务消费者
在 Spring Cloud 体系中,服务的消费者是不直接访问服务的提供者的URL地址的,而是通过 Eureka Server 根据指定的服务名称,由 Eureka Server 来最终决定消费者将访问哪个服务获取信息。我们可以通过 Ribbon+RestTemplate 或者 Feign 两种方式,来访问服务。这里我们只讲 Feign。
Feign是Netflix开发的声明式、模板化的HTTP客户端,可以帮助我们更快捷、优雅地调用HTTP API。使用上有点像以前的远程 EJB 调用。Spring Cloud 对 Feign 做了很多的注解支持,所以使用起来非常方便。
同样的,按照你惯用的方式创建一个 Spring Boot 项目,然后在 pom 里面引用 spring-cloud-starter-eureka 和 spring-cloud-starter-feign 即可。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>配置 application.yml 将自己注册到 Eureka Server,消费者以 9000 端口启动
spring:
application:
name: spring-cloud-consumer
server:
port: 9000
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8080/eureka/在启动类上,加上 @EnableDiscoveryClient 和 @EnableFeignClients 这两个注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableFeignClients
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}创建一个 Interface,用来注册远程服务调用。
@FeignClient(name= "spring-cloud-service1")
@RequestMapping("service")
public interface IService1Remote {
@RequestMapping(value = "hello")
public String hello(@RequestParam(value = "name") String name);
@RequestMapping(value = "hello2",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String hello2(@RequestBody UserParam user);
}写一个 Controller 来方便我们进行浏览器调试,Controller 中通过 Feign 调用远程服务。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("consumer")
public class ConsumerController {
@Autowired
private IService1Remote serviceRemote;
@RequestMapping(value = "hello/{name}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String hello(@PathVariable String name) throws AnkonException {
String result = this.serviceRemote.hello(name);
return result;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "hello2", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String hello2() throws AnkonException {
UserParam userParam = new UserParam();
userParam.setUserName("张三");
userParam.setGender(1);
userParam.setBirthday(new Date());
String result = this.serviceRemote.hello2(userParam);
return result;
}
}UserParam:
public class UserParam implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String userName;
private Integer gender;
private Date birthday;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public Integer getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(Integer gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
}项目代码写完之后,启动 Eureka Server, Provider 和 Consumer 三个项目。
然后我们浏览器依次访问 consumer 暴露出来的 url 地址, http://localhost:9000/consumer/hello/walli 和 http://localhost:9000/consumer/hello2 即可看到对应的 Provider 返回结果。
![]()
![]()
至此,我们创建了一个服务,将其注册到 Eureka 中,并且成功使用消费者通过 Feign 来访问到创建的服务。