37.1 线程清理和控制函数
1 #include <pthread.h> 2 3 void pthread_cleanup_push(void (* rtn)(void *), void *arg); 4 void pthread_cleanup_pop(int execute);
- 函数参数
- rtn:清理函数指针
- arg:调用清理函数传递的参数
- execute:值 1 时,执行线程清理函数;值 0 时,不执行线程清理函数
- 返回值
- 成功,返回 0;否则,返回错误编号
- 触发线程调用清理函数的工作
- 调用 pthread_exit
- 响应取消请求
- 用非零 execute 参数调用 thread_cleanup_pop 时
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <pthread.h> 4 5 /** 定义线程清理函数 */ 6 void clean_fun(void *arg) 7 { 8 char *s = (char *)arg; 9 printf("clean_fun: %s\n", s); 10 } 11 12 void *th_fun(void *arg) 13 { 14 int execute = (int )arg; 15 16 pthread_cleanup_push(clean_fun, "first clean func"); 17 pthread_cleanup_push(clean_fun, "second clean func"); 18 printf("thread running %lx\n", pthread_self()); 19 20 pthread_cleanup_pop(execute); 21 pthread_cleanup_pop(execute); 22 return (void *)0; 23 } 24 25 int main(void) 26 { 27 int err; 28 pthread_t th1, th2; 29 30 if((err = pthread_create(&th1, NULL, th_fun, (void *)1)) != 0) { 31 perror("pthread create error"); 32 } 33 34 pthread_join(th1, NULL); 35 printf("th1(%lx) finished\n", th1); 36 37 38 if((err = pthread_create(&th2, NULL, th_fun, (void *)1)) != 0) { 39 perror("pthread create error"); 40 } 41 42 pthread_join(th2, NULL); 43 printf("th2(%lx) finished\n", th2); 44 45 return 0; 46 }
运行如下:

线程结束,会触发调用最终的 clean 函数,调用的时候会根据 pop 里面的入栈顺序,先入后出进行调用。
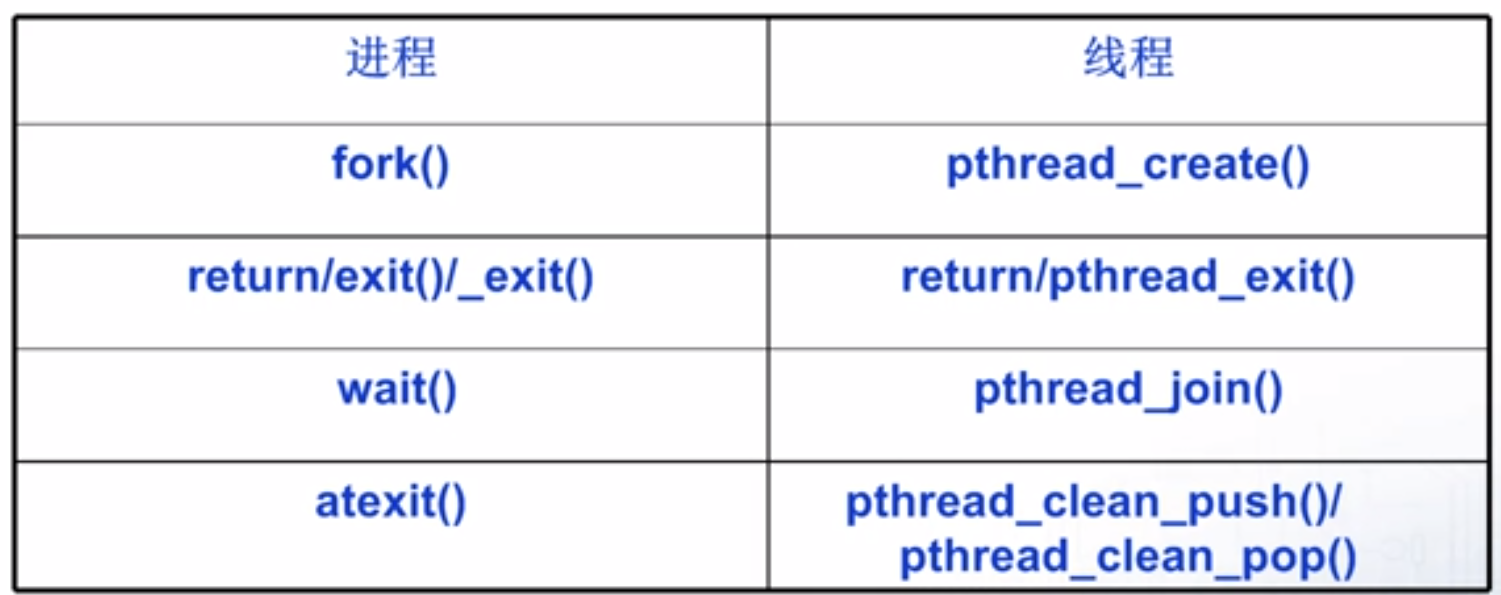
37.2 进程和线程启动方式比较
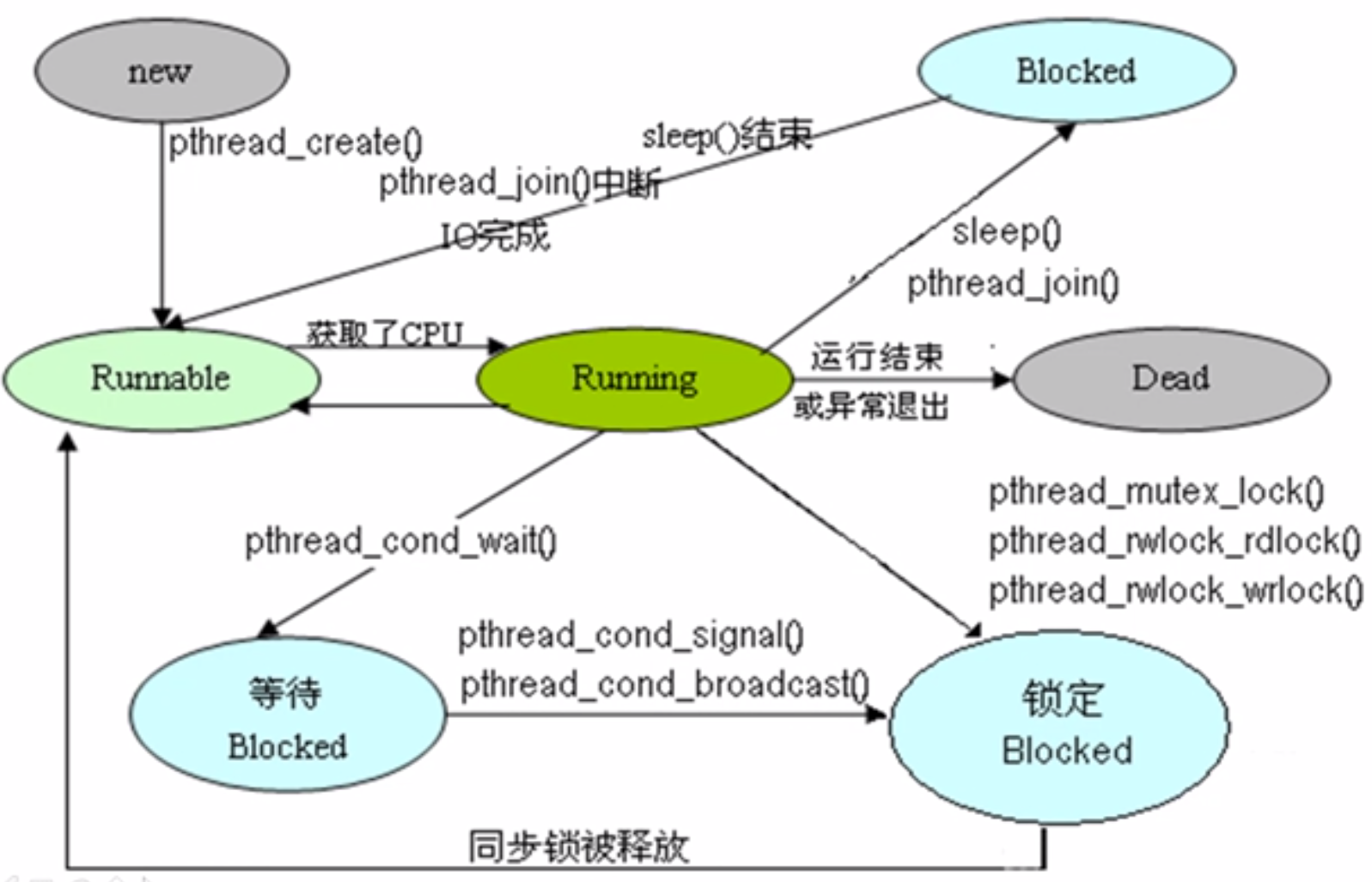
37.3 线程的状态转换