数据类型
基础数据类型
包括7中基础数据类型

每种类型都有一个is 函数的判别类型,还有一个as的转换类型
| > x <- c(1,2,3,4) > is.na(x) [1] FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE > as.character(x) [1] "1" "2" "3" "4" > is.character(x) [1] FALSE > x1 <- as.character(x) > is.character(x1) [1] TRUE
|
时间数据类型
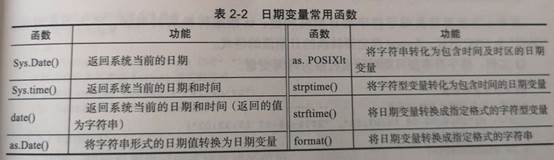
> x2 <- c("2018-12-18 18:08:00") > x2 [1] "2018-12-18 18:08:00" > is.character(x2) [1] TRUE > typeof(x2) [1] "character" > x3 <- strptime(x2, format = "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") > typeof(x3) [1] "list" > class(x3) [1] "POSIXlt" "POSIXt"
|
查看类
在查看类中,有3种方法,分别是class(), mode(), typeof()
使用格式
class(x), mode(x) typeof(x)
|
3个函数的区别
在数据细节的展示上,mode<class<typeof。
mode只查看数据的大类
class查看数据的类
typeof产看更加细化,查看数据的细类
等差序列的创建
在R中使用seq函数生产等间隔的数列
| seq(from = 1, to = 1, by = ((to - from)/(length.out - 1)), length.out = NULL, along.with = NULL, ...)
seq.int(from, to, by, length.out, along.with, ...)
seq_along(along.with) seq_len(length.out) |
by 等差数值
length.out 产生序列的长度
| > seq(from= 1, to= 10, length.out=10) [1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 > seq(from= 1, to= 8, length.out=10) [1] 1.000000 1.777778 2.555556 3.333333 4.111111 4.888889 5.666667 [8] 6.444444 7.222222 8.000000
|
这里的步长 by 就是 by = ((to - from)/(length.out - 1))
使用rep创建重复序列
| rep(x, ...)
rep.int(x, times)
rep_len(x, length.out)
|
x为预重复的序列
times 重复的次数
length.out 产生序列的长度
each 预重复序列中,每个元素重复的次数,初始值为1
| > rep(c(1,2,3), times=3, each=2) [1] 1 1 2 2 3 3 1 1 2 2 3 3 1 1 2 2 3 3 > rep(c(1,2,3), times=3, each=2, length=5) [1] 1 1 2 2 3 > rep(c(c(1,2), c(7,9,0), c(2)) ,times=2) [1] 1 2 7 9 0 2 1 2 7 9 0 2 > rep(c(c(1,2), c(7,9,0), c(2)) ,times=5, length= 14) [1] 1 2 7 9 0 2 1 2 7 9 0 2 1 2
|